Abstract
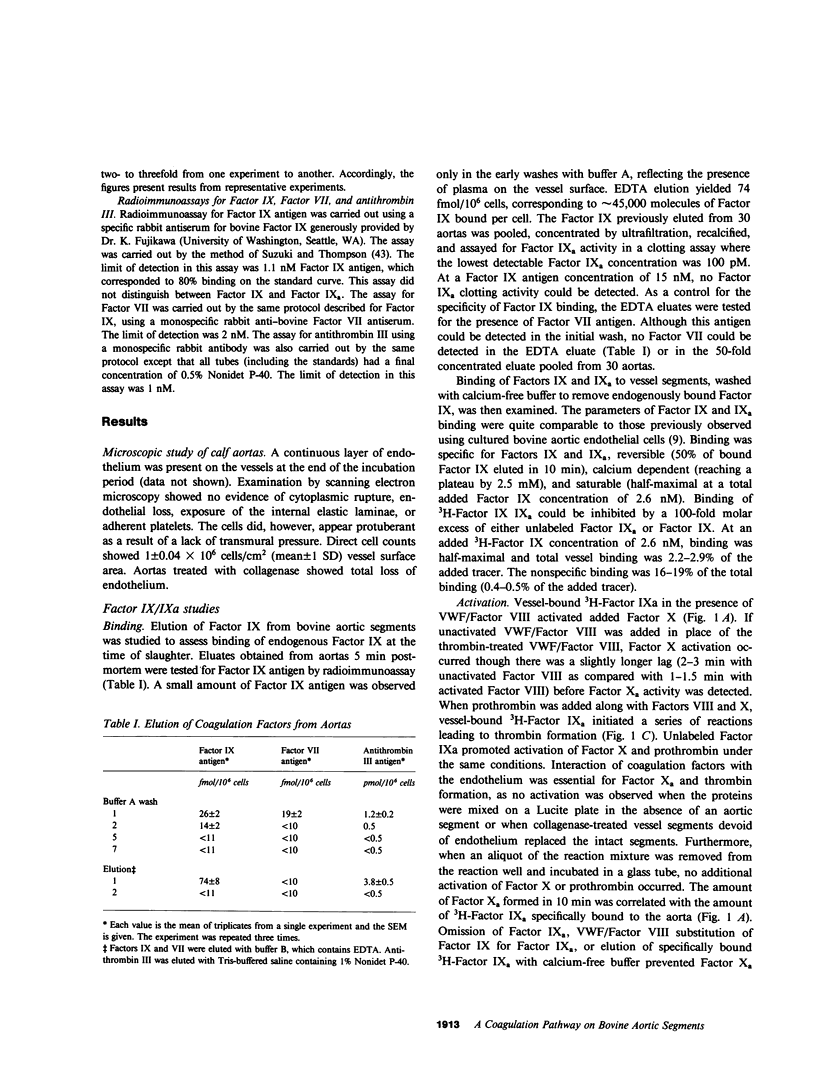
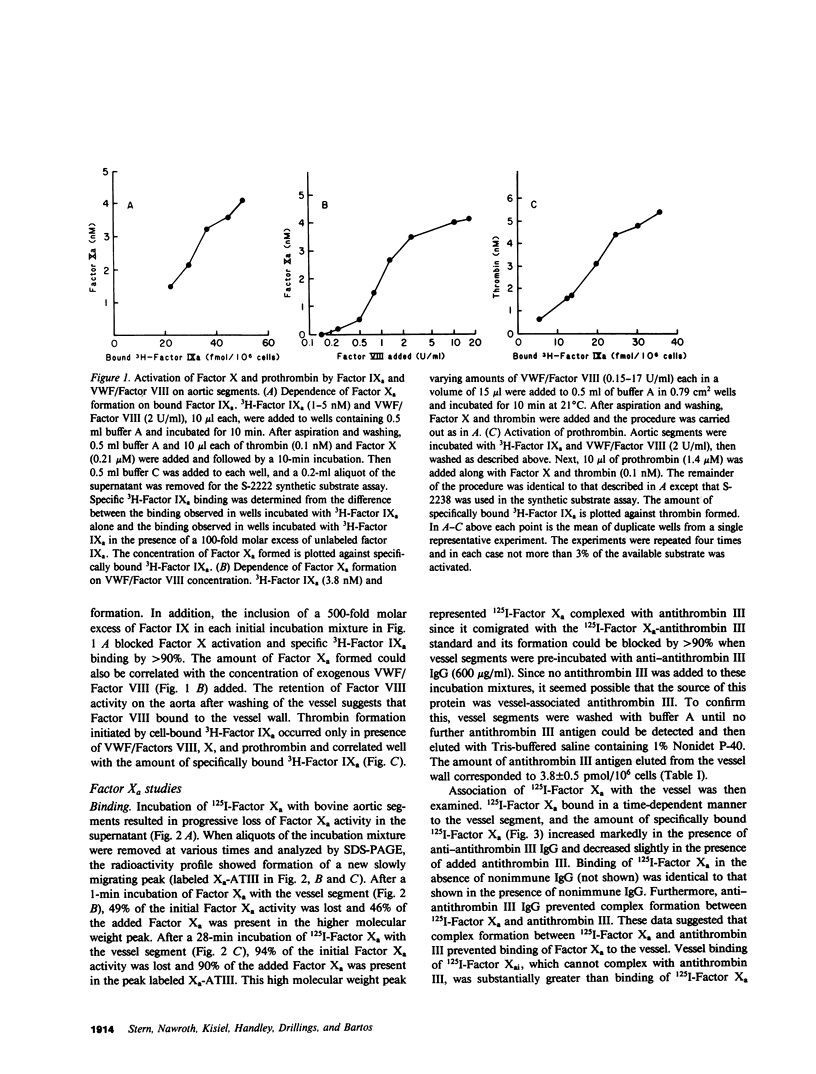
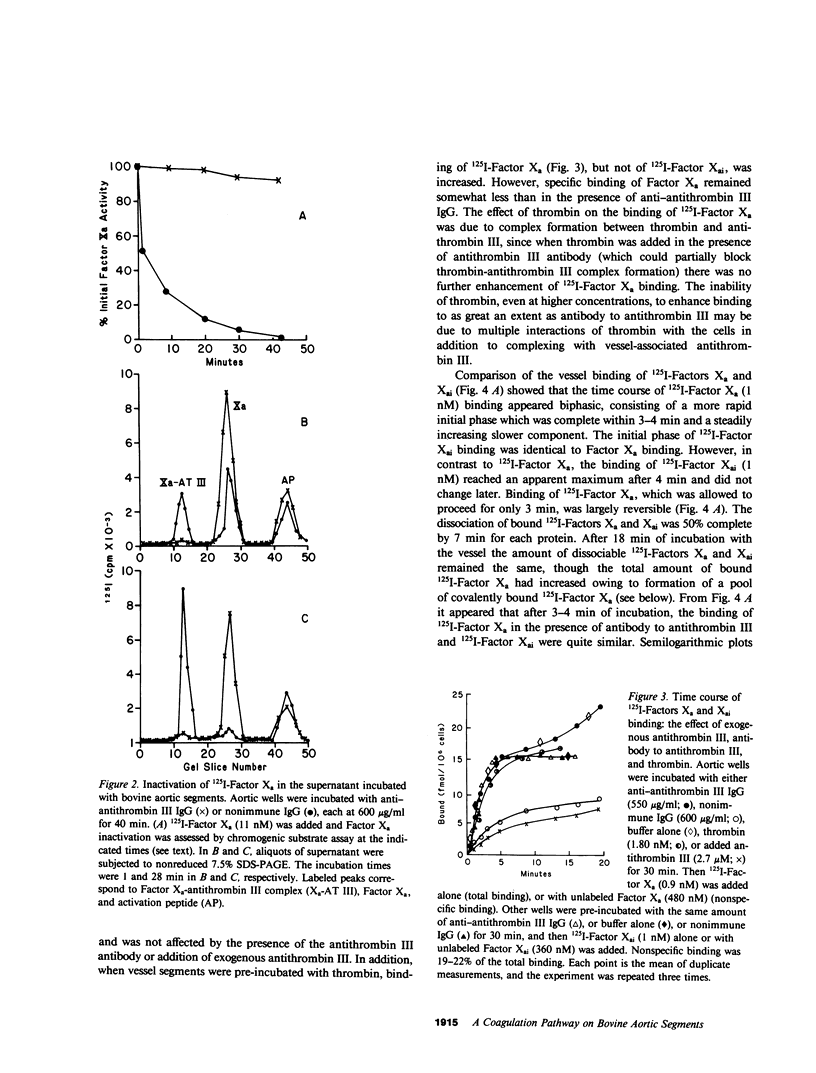
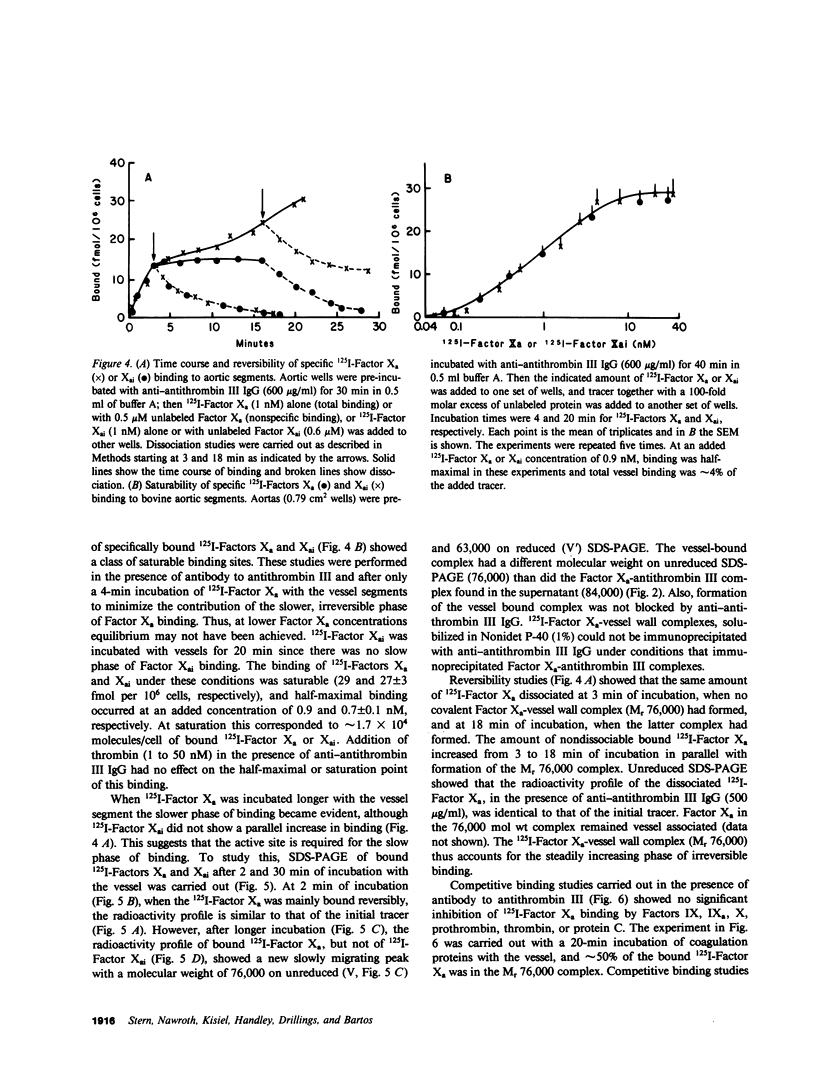
Previous studies have demonstrated the binding of Factors IX and IXa to cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. The present study examines the interaction of Factors IX, IXa, and Xa with the luminal surface of calf aortas, shown by microscopic examination to have a continuous layer of endothelium. Radioimmunoassay of Factor IX showed that 74 fmol/10(6) cells of Factor IX could be eluted from freshly prepared aortic segments. Binding of 3H-Factors IX and IXa to aortic segments was saturable, and comparable to binding in previous studies using cultured endothelial cells. Preincubation of aortic segments with 3H-Factor IXa and von Willebrand factor (VWF)/Factor VIII, followed by washing and addition of Factor X, resulted in formation of Factor Xa. The addition of prothrombin to these activation mixtures resulted in formation of thrombin. Exogenous phospholipid and Factor V were not required for Factor X and prothrombin activation on the intact native endothelium. Incubation of 125I-Factor Xa with the vessel segments resulted in most of the tracer being complexed with antithrombin III originally present on the aortic segment (3.8 pmol antithrombin III/10(6) cells). The Factor Xa-antithrombin III complex was observed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis exclusively in the supernatants. 125I-Factor Xa not complexed with antithrombin III bound specifically to the vessel segment. The time course of binding was biphasic, consisting of an initial more rapid reversible phase followed by a slower irreversible phase. The latter phase correlated with the formation of a covalent complex (Mr, 76,000) between 125I-Factor Xa and a vessel-localized protein presumably distinct from antithrombin III. The activation of prothrombin by vessel-bound Factor Xa was inhibited by anti-bovine Factor V IgG, suggesting that there is interaction of Factor Xa with a Factor V-like molecule provided by the endothelial cell surface. Addition of antibody to antithrombin III prevented formation of Factor Xa-antithrombin III and thrombin-antithrombin III complexes in the supernatant and increased apparent thrombin activity 30-50-fold. These studies demonstrate that freshly obtained vessels with a continuous layer of native endothelium can support activation of Factor X and prothrombin: vessel-bound Factor IXa can activate Factor X in the presence of VWF/Factor VIII. Factor Xa can also bind to the vessel and participate in the activation of prothrombin. The apparent efficiency of prothrombin activation, however, is dampened by the presence of functional antithrombin III on the vessel wall.
Full text
PDF


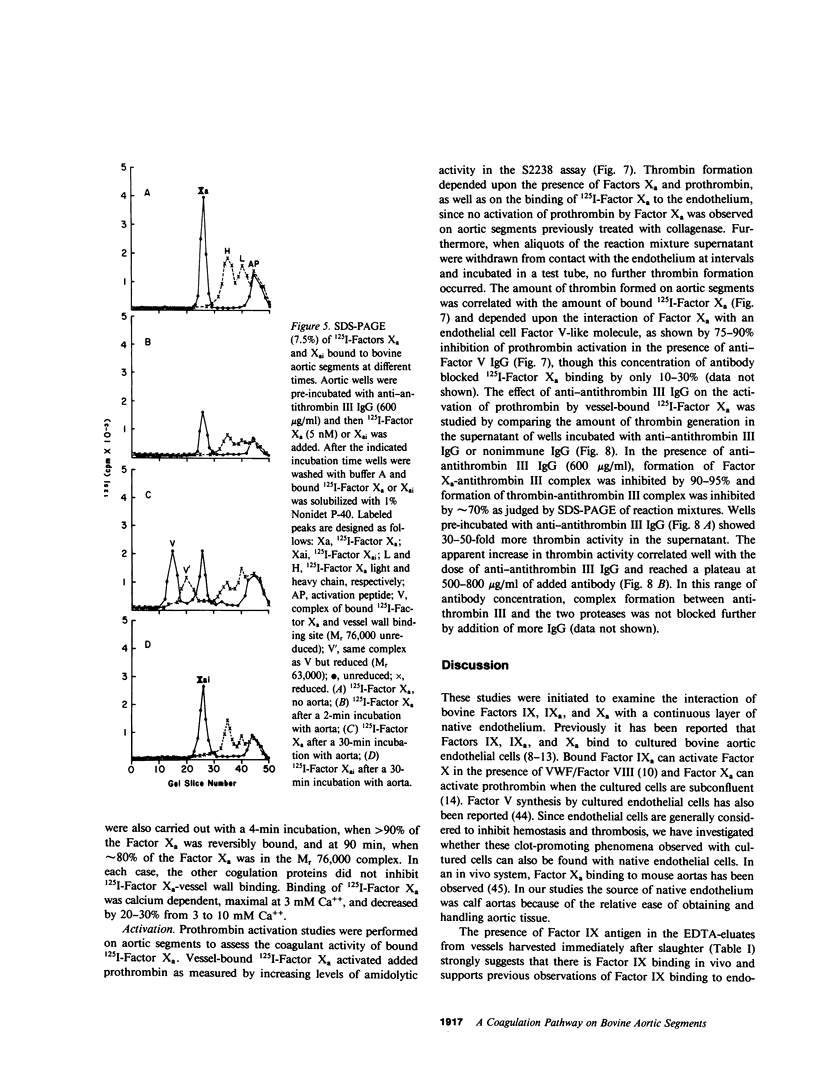
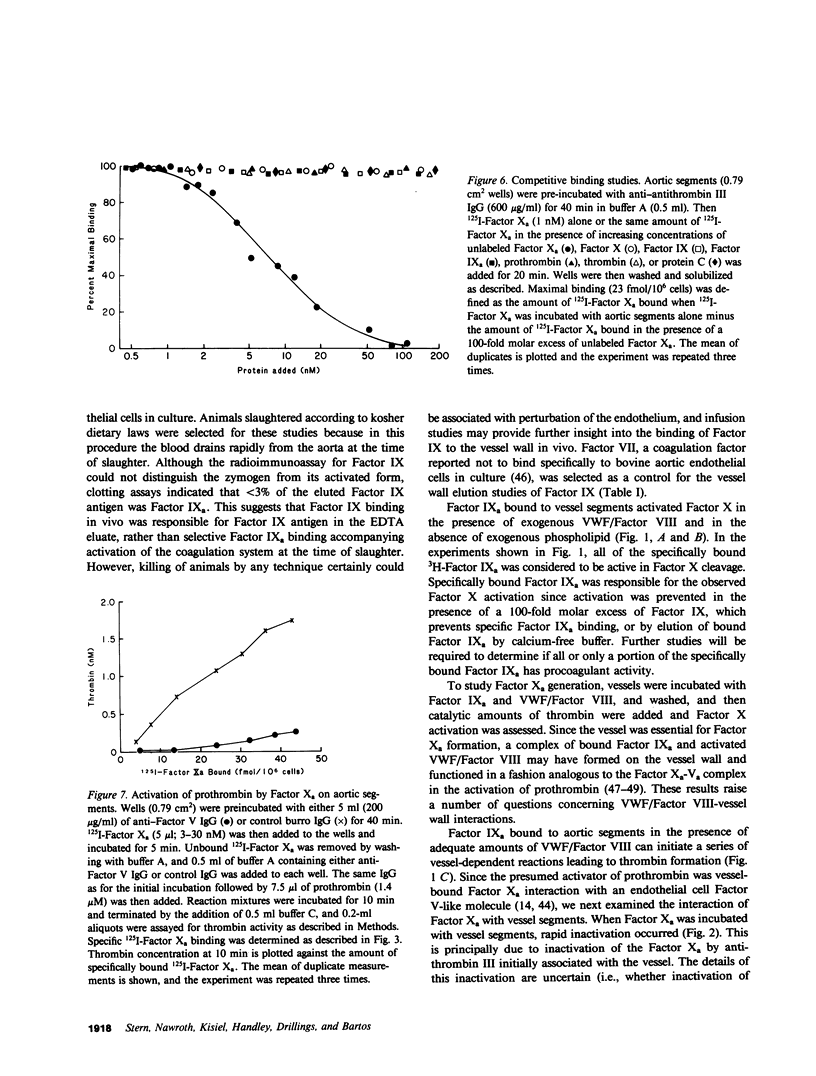
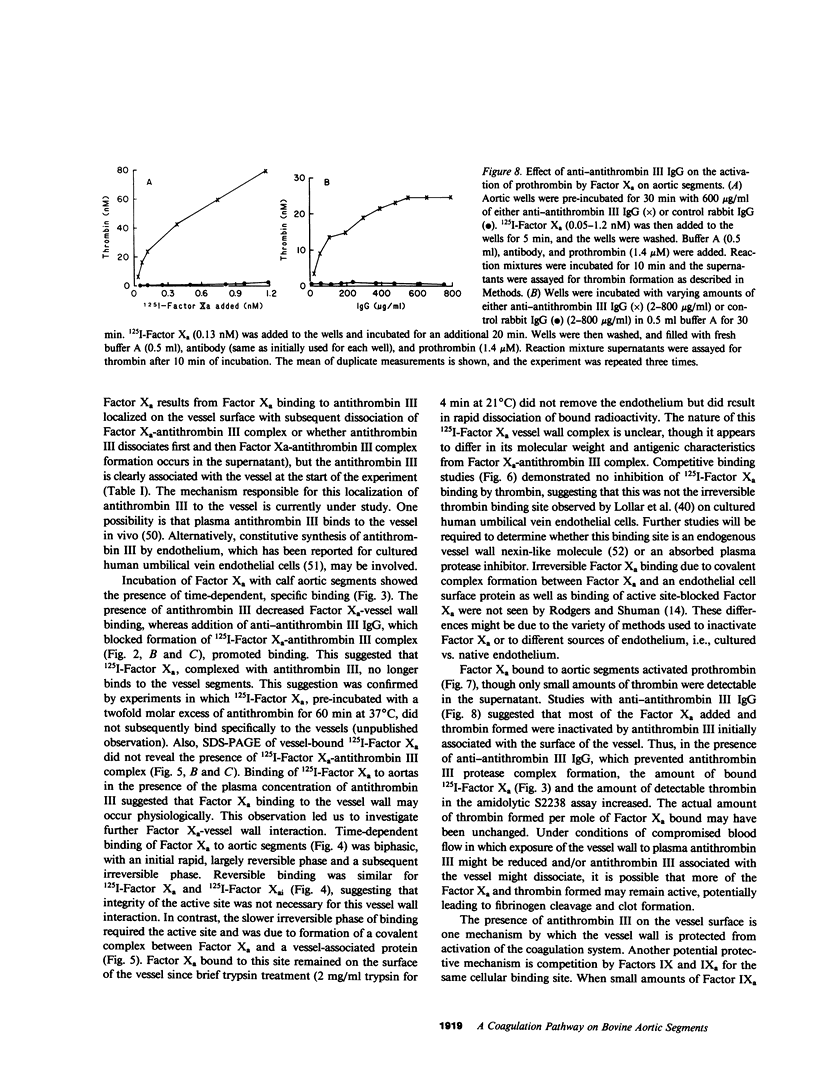


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bajaj S. P., Mann K. G. Simultaneous purification of bovine prothrombin and factor X. Activation of prothrombin by trypsin-activated factor X. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 25;248(22):7729–7741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker J. B., Low D. A., Simmer R. L., Cunningham D. D. Protease-nexin: a cellular component that links thrombin and plasminogen activator and mediates their binding to cells. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):37–45. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broze G. J., Jr Binding of human factor VII and VIIa to monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1982 Sep;70(3):526–535. doi: 10.1172/JCI110644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch C., Owen W. G. Identification in vitro of an endothelial cell surface cofactor for antithrombin III. Parallel studies with isolated perfused rat hearts and microcarrier cultures of bovine endothelium. J Clin Invest. 1982 Mar;69(3):726–729. doi: 10.1172/JCI110502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan V., Chan T. K. Antithrombin III in fresh and cultured human endothelial cells: a natural anticoagulant from the vascular endothelium. Thromb Res. 1979;15(1-2):209–213. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90066-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase T., Jr, Shaw E. Comparison of the esterase activities of trypsin, plasmin, and thrombin on guanidinobenzoate esters. Titration of the enzymes. Biochemistry. 1969 May;8(5):2212–2224. doi: 10.1021/bi00833a063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Stenflo J. Binding of bovine coagulation factor Xa to platelets. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 14;17(23):4938–4945. doi: 10.1021/bi00616a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David G. S., Reisfeld R. A. Protein iodination with solid state lactoperoxidase. Biochemistry. 1974 Feb 26;13(5):1014–1021. doi: 10.1021/bi00702a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detwiler T. C., Feinman R. D. Kinetics of the thrombin-induced release of calcium (II) by platelets. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 16;12(2):282–289. doi: 10.1021/bi00726a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon N. L., Owen W. G., Esmon C. T. Isolation of a membrane-bound cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):859–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs H. E., Pizzo S. V. Regulation of factor Xa in vitro in human and mouse plasma and in vivo in mouse. Role of the endothelium and plasma proteinase inhibitors. J Clin Invest. 1983 Dec;72(6):2041–2049. doi: 10.1172/JCI111169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Coan M. H., Legaz M. E., Davie E. W. The mechanism of activation of bovine factor X (Stuart factor) by intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 17;13(26):5290–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00723a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Legaz M. E., Davie E. W. Bovine factors X 1 and X 2 (Stuart factor). Isolation and characterization. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4882–4891. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Thompson A. R., Legaz M. E., Meyer R. G., Davie E. W. Isolation and characterization of bovine factor IX (Christmas factor). Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 20;12(24):4938–4945. doi: 10.1021/bi00748a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furie B. C., Furie B., Gottlieb A. J., Williams W. J. Activation of bovine factor X by the venom coagulant protein of Vipera russelli: complex formation of the activation fragments. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Sep 13;365(1):121–132. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90256-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harboe N., Ingild A. Immunization, isolation of immunoglobulins, estimation of antibody titre. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:161–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimark R. L., Schwartz S. M. Binding of coagulation factors IX and X to the endothelial cell surface. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 16;111(2):723–731. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90365-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingerman-Wojenski C., Silver M. J., Smith J. B., Macarak E. Bovine endothelial cells in culture produce thromboxane as well as prostacyclin. J Clin Invest. 1981 May;67(5):1292–1296. doi: 10.1172/JCI110157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Hoyer L. W., Nachman R. L. Synthesis of antihemophilic factor antigen by cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2757–2764. doi: 10.1172/JCI107471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisiel W., Davie E. W. Isolation and characterization of bovine factor VII. Biochemistry. 1975 Nov 4;14(22):4928–4934. doi: 10.1021/bi00693a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisiel W., Hermodson M. A., Davie E. W. Factor X activating enzyme from Russell's viper venom: isolation and characterization. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 2;15(22):4901–4906. doi: 10.1021/bi00667a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi K., Fujikawa K., Schmer G., Davie E. W. Inhibition of bovine factor IXa and factor Xabeta by antithrombin III. Biochemistry. 1976 Jan 27;15(2):373–377. doi: 10.1021/bi00647a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laura R., Robison D. J., Bing D. H. (p-Amidinophenyl)methanesulfonyl fluoride, an irreversible inhibitor of serine proteases. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 14;19(21):4859–4864. doi: 10.1021/bi00562a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lollar P., Hoak J. C., Owen W. G. Binding of thrombin to cultured human endothelial cells. Nonequilibrium aspects. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10279–10283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J., Edgington T. E. Synthesis of a fibrinolytic activator and inhibitor by endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3903–3907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad R. L., Uhteg L. C., Vogel C. N., Kingdon H. S., Mann K. G. Preparation and partial characterization of two forms of bovine thrombin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Sep 16;66(2):482–489. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90536-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyberg T., Galdal K. S., Evensen S. A., Prydz H. Cellular cooperation in endothelial cell thromboplastin synthesis. Br J Haematol. 1983 Jan;53(1):85–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb01989.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney W. C., Kurachi K., Hermodson M. A. Formation and dissociation of the covalent complexes between trypsin and two homologous inhibitors, alpha 1-antitrypsin and antithrombin III. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Apr;105(3):545–552. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04531.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K. G. Prothrombin. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:123–156. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45016-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miletich J. P., Jackson C. M., Majerus P. W. Interaction of coagulation factor Xa with human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):4033–4036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.4033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J., Johnson A. J., Karpatkin M. H., Puszkin S. Methods for the production of clinically effective intermediate- and high-purity factor-VIII concentrates. Br J Haematol. 1971 Jul;21(1):1–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb03413.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odegård O. R., Abildgaard U., Lie M., Miller-Andersson M. Inactivation of bovine and human thrombin and factor Xa by antithrombin III studied with amidolytic methods. Thromb Res. 1977 Aug;11(2):205–261. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers G. M., Broze G. J., Jr, Shuman M. A. The number of receptors for factor VII correlates with the ability of cultured cells to initiate coagulation. Blood. 1984 Feb;63(2):434–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers G. M., Shuman M. A. Prothrombin is activated on vascular endothelial cells by factor Xa and calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):7001–7005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.7001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. D., Damus P. S. The purification and mechanism of action of human antithrombin-heparin cofactor. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6490–6505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosing J., Tans G., Govers-Riemslag J. W., Zwaal R. F., Hemker H. C. The role of phospholipids and factor Va in the prothrombinase complex. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):274–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. M., Drillings M., Kisiel W., Nawroth P., Nossel H. L., LaGamma K. S. Activation of factor IX bound to cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):913–917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. M., Drillings M., Nossel H. L., Hurlet-Jensen A., LaGamma K. S., Owen J. Binding of factors IX and IXa to cultured vascular endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4119–4123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. M., Nossel H. L., Owen J. Acquired antibody to factor XI in a patient with congenital factor XI deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jun;69(6):1270–1276. doi: 10.1172/JCI110566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki L. A., Thompson A. R. Factor IX antigen by a rapid staphylococcal protein A-membrane binding radioimmunoassay: results in haemophilia B patients and carriers and in fetal samples. Br J Haematol. 1982 Apr;50(4):673–682. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1982.tb01968.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy P. B., Nesheim M. E., Mann K. G. Coordinate binding of factor Va and factor Xa to the unstimulated platelet. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):743–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy P. B., Peterson J. M., Nesheim M. E., McDuffie F. C., Mann K. G. Interaction of coagulation factor V and factor Va with platelets. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10354–10361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weksler B. B., Marcus A. J., Jaffe E. A. Synthesis of prostaglandin I2 (prostacyclin) by cultured human and bovine endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3922–3926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dieijen G., Tans G., Rosing J., Hemker H. C. The role of phospholipid and factor VIIIa in the activation of bovine factor X. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3433–3442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


