Abstract
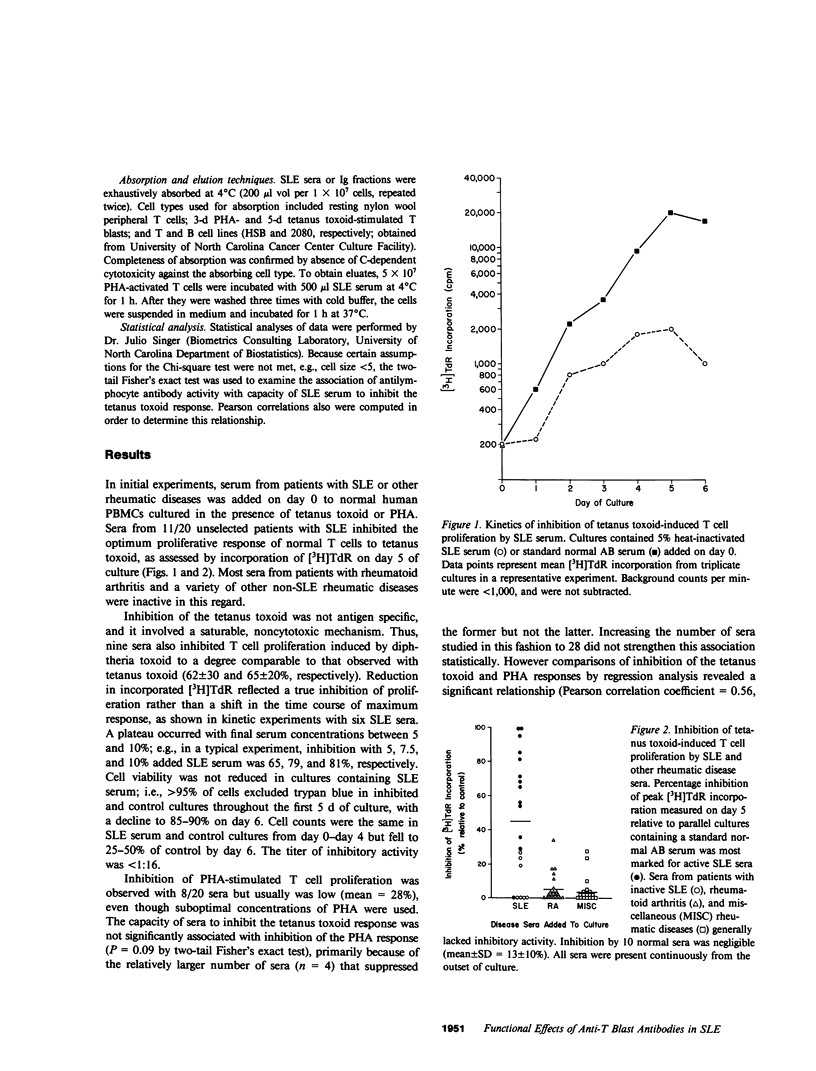
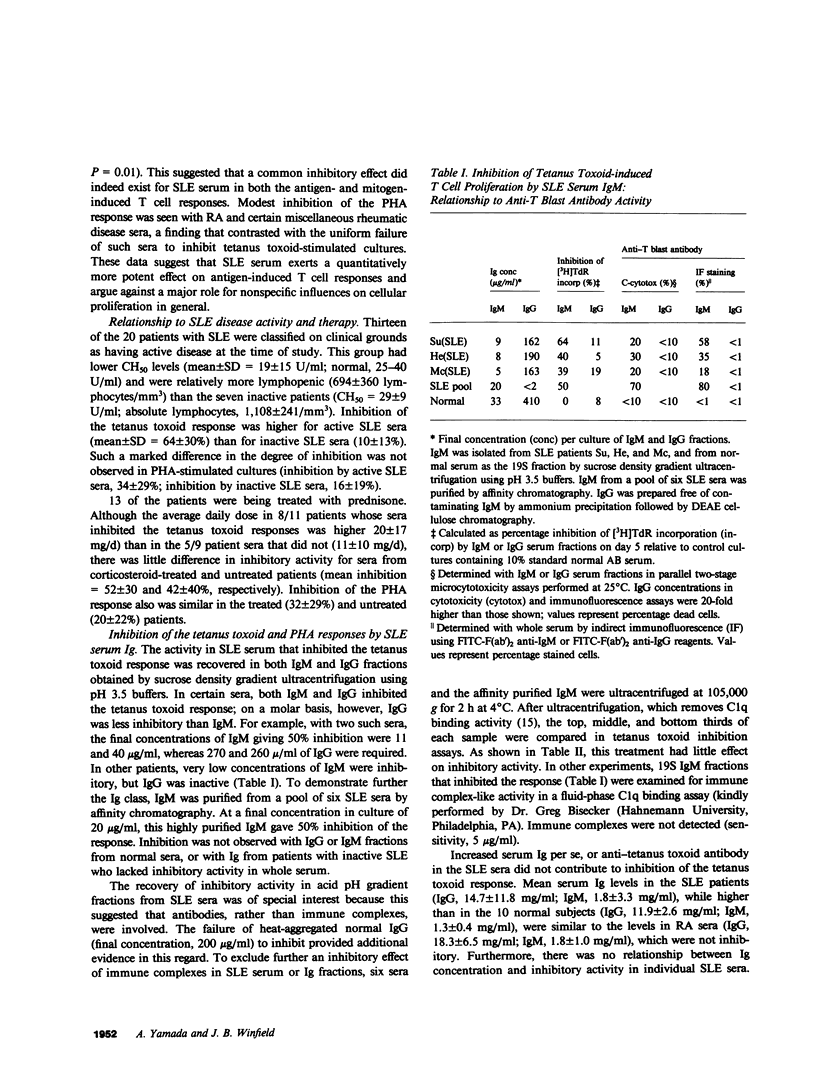
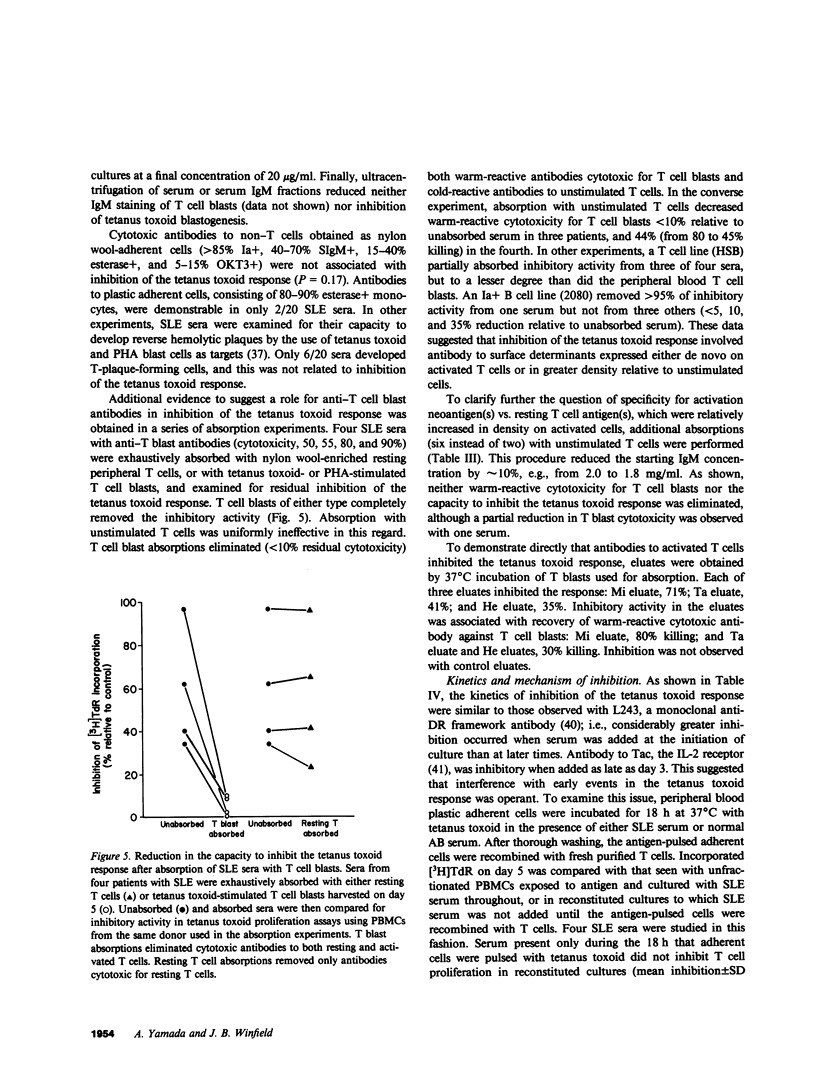
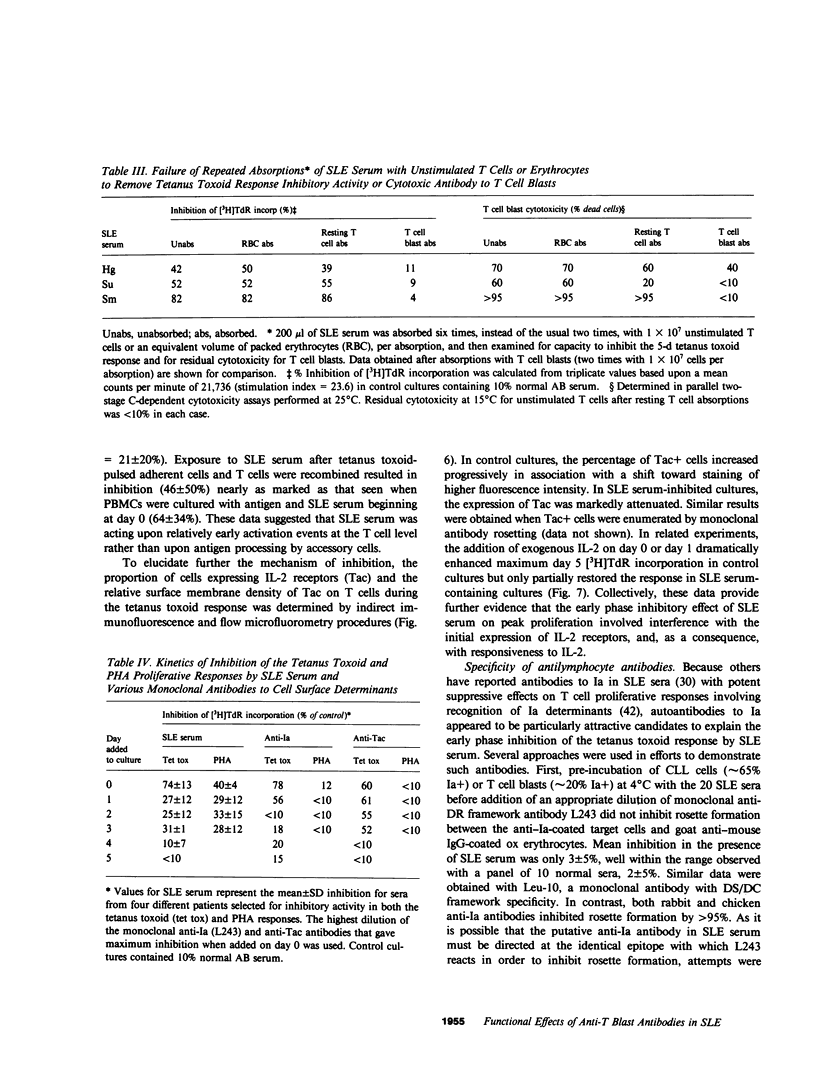
One of the fundamental immunologic characteristics of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a depressed T cell proliferative response to various specific and nonspecific stimuli. Both intrinsic cellular defect(s) and inhibitory influences of humoral factors, e.g., antilymphocyte autoantibodies or immune complexes, have been postulated to underly this functional abnormality. Because patient serum can induce SLE-like T cell dysfunction in normal cells, an extrinsic mechanism is probably responsible, but the nature and site of action of this humoral activity has not been defined. This laboratory recently described a novel antibody specific for activated T cells in SLE, which raised the possibility that suppression of T cell proliferation by SLE serum involved antibodies directed to surface determinants expressed during the process of activation. In experiments to examine this concept further, relatively warm-reactive antibodies to T cell blasts were found to inhibit strongly the well-characterized T cell response to tetanus toxoid. These antibodies were distinct from conventional cold-reactive IgM antibodies to resting T cells, which exhibited little inhibitory activity. Inhibition involved noncytotoxic effects on early activation events at the level of the responding T cell, which markedly reduced the expression of receptors for interleukin 2. Inhibitory effects on antigen-pulsed macrophages or on T cells already committed to proliferate were not demonstrable. Anti-T blast antibodies were characteristic of active SLE and were detected only occasionally in patients with inactive disease or non-SLE rheumatic disorders. Although the exact antigenic specificity was not identified, considerable evidence was obtained against the presence of antibodies to Ia and certain other surface determinants of functional relevance. Our observations concerning the suppressive effects of anti-T blast antibodies in SLE serum on the T cell response to tetanus toxoid should provide new insight into mechanisms of in vivo T cell dysfunction in this and other immunologic disorders.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biddison W. E., Rao P. E., Talle M. A., Goldstein G., Shaw S. Possible involvement of the T4 molecule in T cell recognition of class II HLA antigens: evidence from studies of proliferative responses to SB antigens. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):152–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnihan B., Jasin H. E. Suppressor function of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in normal individuals and in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):106–116. doi: 10.1172/JCI108607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budman D. R., Merchant E. B., Steinberg A. D., Doft B., Gershwin M. E., Lizzio E., Reeves J. P. Increased spontaneous activity of antibody-forming cells in the peripheral blood of patients with active SLE. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Apr;20(3):829–833. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. W., Kung P. C., Gingras S. P., Goldstein G. Does OKT3 monoclonal antibody react with an antigen-recognition structure on human T cells? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1805–1808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. L., Litvin D. A., Winfield J. B. Association between endogenously activated T cells and immunoglobulin-secreting B cells in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Feb;25(2):168–173. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFreitas E. C., Chesnut R. W., Grey H. M., Chiller J. M. Macrophage-dependent activation of antigen-specific T cells requires antigen and a soluble monokine. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):23–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Steinberg A. D., Haynes B. F., Whalen G. Immunoregulatory aberrations in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1473–1479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geha R. S., Milgrom H., Broff M., Alpert S., Martin S., Yunis E. J. Effect of anti-HLA antisera on macrophage-T-cell interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):4038–4041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.4038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg W. W., Finkelman F. D., Lipsky P. E. Circulating and pokeweed mitogen-induced immunoglobulin-secreting cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Jan;35(1):76–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glinski W., Gershwin M. E., Steinberg A. D. Fractionation of cells on a discontinuous Ficoll gradient. Study of subpopulations of human T cells using anti-T-cell antibodies from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1976 Mar;57(3):604–614. doi: 10.1172/JCI108316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. The chromic chloride method of coupling antigens to erythrocytes: definition of some important parameters. J Immunol Methods. 1976;10(1):61–66. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb A. B., Lahita R. G., Chiorazzi N., Kunkel H. G. Immune function in systemic lupus erythematosus. Impairment of in vitro T-cell proliferation and in vivo antibody response to exogenous antigen. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):885–892. doi: 10.1172/JCI109388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunther G. R., Wang J. L., Edelman G. M. The kinetics of cellular commitment during stimulation of lymphocytes by lectins. J Cell Biol. 1974 Aug;62(2):366–377. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.2.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschberg H., Hirschberg T., Nousiainen H., Braathen L. R., Jaffe E. The effects of corticosteroids on the antigen presenting properties of human monocytes and endothelial cells. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 Jun;23(3):577–585. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz D. A., Cousar J. B. A relationship between impaired cellular immunity humoral suppression of lymphocyte function and severity of systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1975 Jun;58(6):829–835. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90639-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz D. A., Garrett M. A., Craig A. H. Serum effects of mitogenic reactivity in subjects with systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis and scleroderma. Technical considerations and lack of correlation with anti-lymphocyte antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Jan;27(1):100–110. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasin H. E., Ziff M. Immunoglobulin synthesis by peripheral blood cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 May-Jun;18(3):219–228. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karsh J., Dorval G., Osterland C. K. Natural cytotoxicity in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1981 Jun;19(3):437–446. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(81)90086-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai S., Steinberg A. D., Green I. Antibodies to T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus can induce antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity against human T cells. J Clin Invest. 1981 Mar;67(3):605–614. doi: 10.1172/JCI110074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampson L. A., Levy R. Two populations of Ia-like molecules on a human B cell line. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):293–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. C., Whalen G., Fauci A. S. Antigen-induced human T cell help. Precursor frequency, radiation sensitivity, and allogeneic effects. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):636–647. doi: 10.1172/JCI111013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linker-Israeli M., Bakke A. C., Kitridou R. C., Gendler S., Gillis S., Horwitz D. A. Defective production of interleukin 1 and interleukin 2 in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2651–2655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkowitz S., Greene W. C., Rubin A. L., Novogrodsky A., Stenzel K. H. Expression of receptors for interleukin 2: Role in the commitment of T lymphocytes to proliferate. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):31–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litvin D. A., Cohen P. L., Winfield J. B. Characterization of warm-reactive IgG anti-lymphocyte antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Relative specificity for mitogen-activated T cells and their soluble products. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):181–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyawaki T., Yachie A., Uwadana N., Ohzeki S., Nagaoki T., Taniguchi N. Functional significance of Tac antigen expressed on activated human T lymphocytes: Tac antigen interacts with T cell growth factor in cellular proliferation. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2474–2478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Reinherz E. L., Distaso J. A., Steinberg A. D., Schlossman S. F. Relationship between systemic lupus erythematosus T cell subsets, anti-T cell antibodies, and T cell functions. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):689–700. doi: 10.1172/JCI111261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardiello S., Pizzella T., Russo M., Galanti B. Esterase staining of monocytes in suspensions of Ficoll-Paque isolated mononuclear cells. J Immunol Methods. 1982;52(1):111–114. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90356-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okudaira K., Searles R. P., Ceuppens J. L., Goodwin J. S., Williams R. C., Jr Anti-Ia reactivity in sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jan;69(1):17–24. doi: 10.1172/JCI110428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okudaira K., Searles R. P., Goodwin J. S., Williams R. C., Jr Antibodies in the sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus that block the binding of monoclonal anti-Ia to Ia-positive targets also inhibit the autologous mixed lymphocyte response. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):582–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okudaira K., Searles R. P., Tanimoto K., Horiuchi Y., Williams R. C., Jr T lymphocyte interaction with immunoglobulin G antibody in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1982 Apr;69(4):1026–1038. doi: 10.1172/JCI110506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios R., Martinez-Maza O. Is the E receptor on human T lymphocytes a "negative signal receptor"? J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2479–2485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qvigstad E., Thorsby E. Class-II HLA restriction of antigen-specific human T-lymphocyte clones. Evidence of restriction elements on both DR and MT molecules. Scand J Immunol. 1983 Oct;18(4):299–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1983.tb01801.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Hussey R. E., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody blocking human T cell function. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Oct;10(10):758–762. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830101006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal C. J., Franklin E. C. Depression of cellular-mediated immunity in systemic lupus erythematosus. relation to disease activity. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 May-Jun;18(3):207–217. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagawa A., Abdou N. I. Suppressor-cell antibody in systemic lupus erythematosus. Possible mechanism for suppressor-cell dysfunction. J Clin Invest. 1979 Mar;63(3):536–539. doi: 10.1172/JCI109333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Kotani H., Takada S., Murakawa Y., Ueda Y. A defect in the suppressor circuits among OKT4+ cell populations in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus occurs independently of a defect in the OKT8+ suppressor T cell function. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):753–761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Steinberg A. D., Green I. Failure of autologous mixed lymphocyte reactions between T and non-T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3464–3468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Steinberg A. D., Green I. Studies of immune functions of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. I. Dysfunction of suppressor T-cell activity related to impaired generation of, rather than response to, suppressor cells. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Jul-Aug;21(6):657–664. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Steinberg A. D., Reeves J. P., Green I. Studies of immune functions of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Complement-dependent immunoglobulin M anti-thymus-derived cell antibodies preferentially inactivate suppressor cells. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):954–965. doi: 10.1172/JCI109396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Steinberg A. D., Reeves J. P., Green I. Studies of immune functions of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. T-cell subsets and antibodies to T-cell subsets. J Clin Invest. 1979 Nov;64(5):1260–1269. doi: 10.1172/JCI109581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxon A., Barnett E. Human auto-antiidiotypes regulating T cell-mediated reactivity to tetanus toxoid. J Clin Invest. 1984 Feb;73(2):342–348. doi: 10.1172/JCI111218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheinberg M. A., Cathcart E. S. Antibody-dependent direct cytotoxicity of human lymphocytes. I. Studies on peripheral blood lymphocytes and sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 May;24(2):317–322. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J., Chin W., Friou G. J., Cooper S. M., Harding B., Hill R. L., Quismorio F. P. Reduced antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 May;20(2):187–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searles R. P., Messner R. P., Hermanson S. M. Antilymphocyte antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis: increased reactivity against activated lymphocytes. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1981 Aug;20(2):246–254. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(81)90183-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman S. L., Cathcart E. S. Natural killing in systemic lupus erythematosus: inhibitory effects of serum. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Oct;17(2):219–226. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocker J. W., Garotta G., Hausmann B., Trucco M., Ceppellini R. Separation of human cells bearing HLA-DR antigens using a monoclonal antibody rosetting method. Tissue Antigens. 1979 Mar;13(3):212–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1979.tb00786.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsokos G. C., Balow J. E. Cytotoxic responses to alloantigens in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Immunol. 1981 Oct;1(4):208–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00915138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Beller D. I., Lu C. Y., Allen P. M. Antigen presentation: comments on its regulation and mechanism. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):1–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernet P., Kunkel H. G. Antibodies to a specific surface antigen of T cells in human sera inhibiting mixed leukocyte culture reactions. J Exp Med. 1973 Oct 1;138(4):1021–1026. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.4.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Jr, Bankhurst A. D., Montaño J. D. IgG antilymphocyte antibodies in SLE detected by 125I protein A. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 Nov-Dec;19(6):1261–1270. doi: 10.1002/art.1780190606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfield J. B., Lobo P. I., Singer A. Significance of anti-lymphocyte antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Jun;21(5 Suppl):S215–S221. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfield J. B., Winchester R. J., Kunkel H. G. Association of cold-reactive antilymphocyte antibodies with lymphopenia in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Nov-Dec;18(6):587–594. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfield J. B., Winchester R. J., Wernet P., Fu S. M., Kunkel H. G. Nature of cold-reactive antibodies to lymphocyte surface determinants in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Jan-Feb;18(1):1–8. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfield J. B., Winchester R. J., Wernet P., Kunkel H. G. Specific concentration of antilymphocyte antibodies in the serum cryoprecipitates of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Mar;19(3):399–406. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu D. T., Winchester R. J., Fu S. M., Gibofsky A., Ko H. S., Kunkel H. G. Peripheral blood Ia-positive T cells. Increases in certain diseases and after immunization. J Exp Med. 1980 Jan 1;151(1):91–100. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


