Abstract
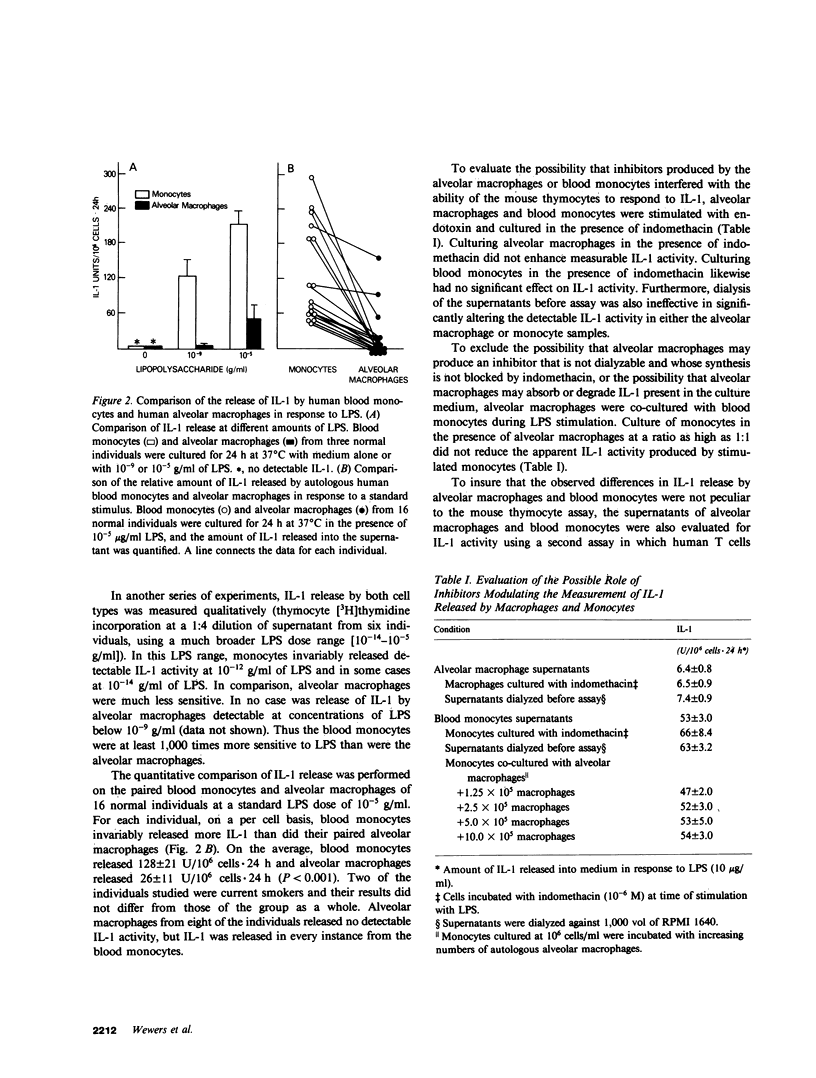
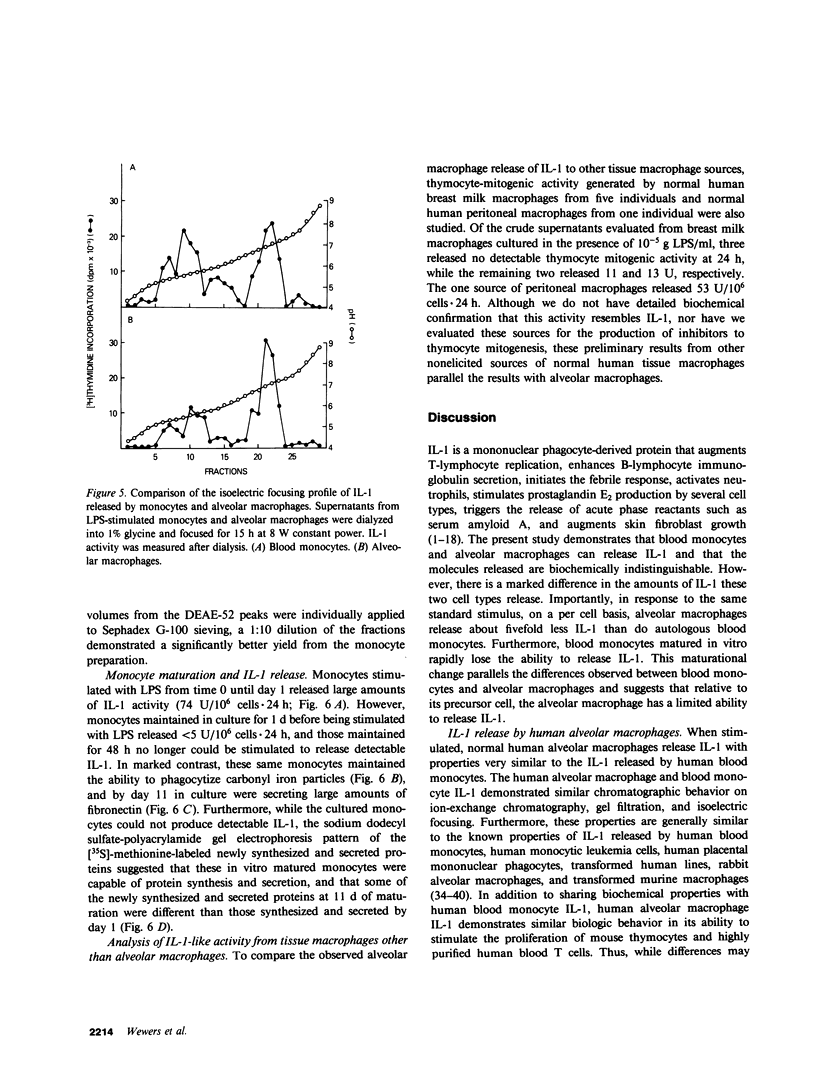
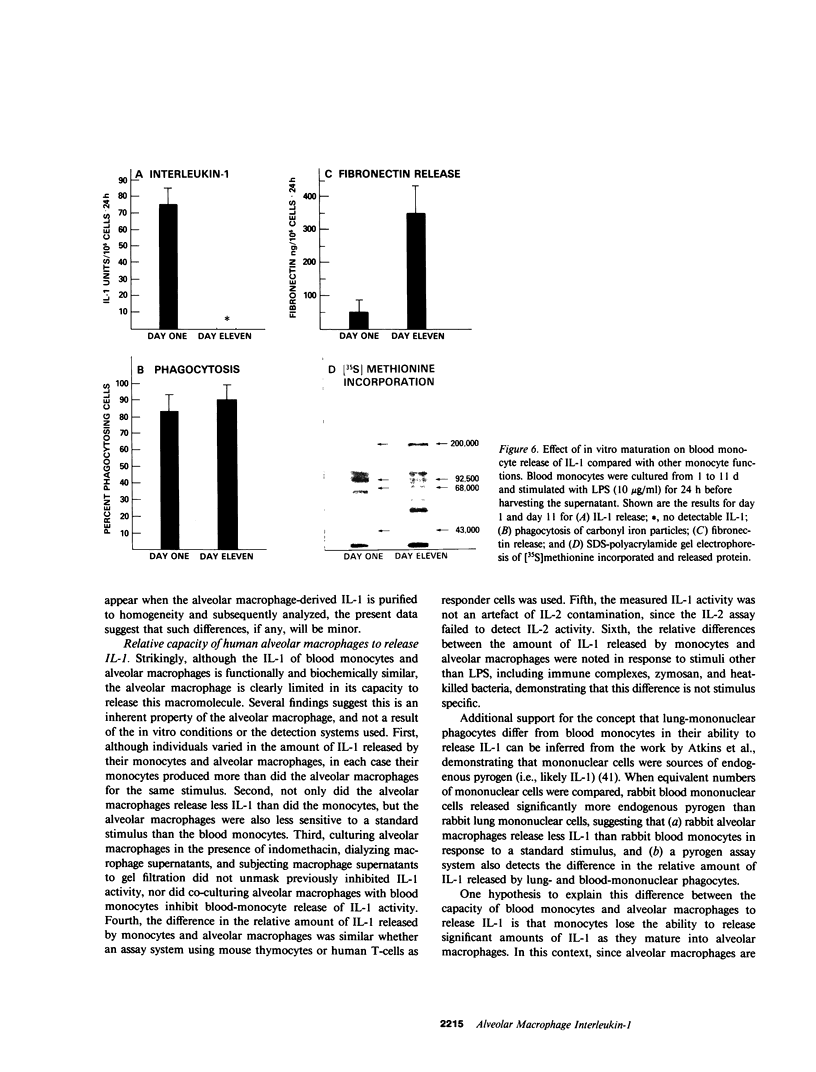
Interleukin-1 (IL-1) is a mediator released by stimulated mononuclear phagocytes that is thought to play an important role in modulating T and B lymphocyte activation as well as in contributing to the febrile response and other inflammatory processes. Circulating mononuclear phagocytes, blood monocytes, readily release IL-1 when stimulated. However, the ability of lung mononuclear phagocytes, alveolar macrophages, to dispose of the large daily burden of inhaled antigens without stimulating an inflammatory response suggests that the release of IL-1 by alveolar macrophages may differ significantly from that of blood monocytes. To evaluate this hypothesis, normal autologous alveolar macrophages, obtained by bronchoalveolar lavage, were compared with blood monocytes for their ability to release IL-1 in response to a standard stimulus, lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Alveolar macrophages were found to be at least 1,000 times less sensitive to LPS than blood monocytes. Furthermore, alveolar macrophages released significantly less IL-1 than blood monocytes (26 +/- 11 vs. 128 +/- 21 U/10(6) cells X 24 h, respectively, after stimulation with 10 micrograms/ml of LPS, P less than 0.001). This difference was not due to the release of substances by macrophages, which inhibited lymphocyte proliferation in response to IL-1, or to degradation of IL-1 by macrophages. Culturing macrophages in the presence of indomethacin and dialysis of macrophage supernatants did not affect the difference, and culturing macrophages with monocytes did not decrease detectable IL-1 activity from the monocytes. The IL-1 produced by the two cell types was indistinguishable by anion-exchange chromatography, gel filtration, and isoelectric focusing. In addition, consistent with the findings for alveolar macrophages, macrophages generated by the in vitro maturation of blood monocytes were also deficient in their ability to release IL-1. These findings suggest that if the population of alveolar macrophages obtained by bronchoalveolar lavage represents the total in vivo population of alveolar macrophages, although normal human macrophages are capable of IL-1 release, they are relatively limited in this ability, and this limitation seems to be linked to the maturational state of the mononuclear phagocyte. These observations may explain, in part, the ability of alveolar macrophages to clear the airspaces of foreign antigens without extensive activation of other pulmonary inflammatory and immune effector cells.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alitalo K., Hovi T., Vaheri A. Fibronectin is produced by human macrophages. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):602–613. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins E., Bodel P., Francis L. Release of an endogenous pyrogen in vitro from rabbit mononuclear cells. J Exp Med. 1967 Aug 1;126(2):357–384. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blussé van Oud Alblas A., van der Linden-Schrever B., van Furth R. Origin and kinetics of pulmonary macrophages during an inflammatory reaction induced by intravenous administration of heat-killed bacillus Calmette-Guérin. J Exp Med. 1981 Aug 1;154(2):235–252. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.2.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blyden G., Handschumacher R. E. Purification and properties of human lymphocyte activating factor (LAF). J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1631–1638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler R. H., Revoltella R. P., Musiani P., Piantelli M. Constitutive production of Interleukin-1 by the human continuous cell line, CM-S. Cell Immunol. 1983 Jun;78(2):368–374. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90291-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFreitas E. C., Chesnut R. W., Grey H. M., Chiller J. M. Macrophage-dependent activation of antigen-specific T cells requires antigen and a soluble monokine. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):23–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demenkoff J. H., Ansfield M. J., Kaltreider H. B., Adam E. Alveolar macrophage suppression of canine bronchoalveolar lymphocytes: the role of prostaglandin E2 in the inhibition of mitogen-responses. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1365–1370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Marnoy S. O., Rosenwasser L. J. Role of arachidonate metabolism in the immunoregulatory function of human leukocytic pyrogen/lymphocyte-activating factor/interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):890–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff G. W., Atkins E. The detection of endotoxin by in vitro production of endogenous pyrogen: comparison with limulus amebocyte lysate gelation. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Aug 13;52(3):323–331. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ettensohn D. B., Roberts N. J., Jr Human alveolar macrophage support of lymphocyte responses to mitogens and antigens. Analysis and comparison with autologous peripheral-blood-derived monocytes and macrophages. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Sep;128(3):516–522. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.3.516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn A., Finke J. H., Hilfiker M. L. Placental mononuclear phagocytes as a source of interleukin-1. Science. 1982 Oct 29;218(4571):475–477. doi: 10.1126/science.6981846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gery I., Gershon R. K., Waksman B. H. Potentiation of the T-lymphocyte response to mitogens. I. The responding cell. J Exp Med. 1972 Jul 1;136(1):128–142. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard M., Mizel S. B., Lachman L., Ansel J., Johnson B., Paul W. E. Role of interleukin 1 in anti-immunoglobulin-induced B cell proliferation. J Exp Med. 1983 May 1;157(5):1529–1543. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.5.1529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Gadek J. E., Kawanami O., Ferrans V. J., Crystal R. G. Inflammatory and immune processes in the human lung in health and disease: evaluation by bronchoalveolar lavage. Am J Pathol. 1979 Oct;97(1):149–206. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempner M. S., Dinarello C. A., Gallin J. I. Human leukocytic pyrogen induces release of specific granule contents from human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1330–1336. doi: 10.1172/JCI109050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempner M. S., Dinarello C. A., Henderson W. R., Gallin J. I. Stimulation of neutrophil oxygen-dependent metabolism by human leukocytic pyrogen. J Clin Invest. 1979 Oct;64(4):996–1002. doi: 10.1172/JCI109566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn J. H., Halushka P. V., LeRoy E. C. Mononuclear cell modulation of connective tissue function: suppression of fibroblast growth by stimulation of endogenous prostaglandin production. J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;65(2):543–554. doi: 10.1172/JCI109698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachman L. B., Moore J. O., Metzgar R. S. Preparation and characterization of lymphocyte-activating factor (LAF) from acute monocytic and myelomonocytic leukemia cells. Cell Immunol. 1978 Nov;41(1):199–206. doi: 10.1016/s0008-8749(78)80040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Evans R. L., Lipinski M., Cunningham-Rundles C., Good R. A., Herzenberg L. A. Evolutionary conservation of surface molecules that distinguish T lymphocyte helper/inducer and cytotoxic/suppressor subpopulations in mouse and man. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):310–323. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. C., Wong M., McIntyre D. Characterization of macrophage subpopulations responsive to activation by endotoxin and lymphokines. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2474–2479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizel A. L., Mehta S. R., Ford R. J., Lachman L. B. Effect of interleukin 1 on human thymocytes and purified human T cells. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):470–475. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayernik D. G., Ul-Haq A., Rinehart J. J. Differentiation-associated alteration in human monocyte-macrophage accessory cell function. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2156–2160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer M. S., Oppenheim J. J. Bidirectional amplification of macrophage-lymphocyte interactions: enhanced lymphocyte activation factor production by activated adherent mouse peritoneal cells. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):77–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B., Ben-Zvi A. Studies on the role of lymphocyte-activating factor (Interleukin 1) in antigen-induced lymph node lymphocyte proliferation. Cell Immunol. 1980 Sep 1;54(2):382–389. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90218-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B., Dayer J. M., Krane S. M., Mergenhagen S. E. Stimulation of rheumatoid synovial cell collagenase and prostaglandin production by partially purified lymphocyte-activating factor (interleukin 1). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2474–2477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B., Oppenheim J. J., Rosentreich D. L. Characterization of lymphocyte-activating factor (LAF) produced by a macrophage cell line, P388D1. II. Biochemical characterization of LAF induced by activated T cells and LPS. J Immunol. 1978 May;120(5):1504–1508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy P. A., Simon P. L., Willoughby W. F. Endogenous pyrogens made by rabbit peritoneal exudate cells are identical with lymphocyte-activating factors made by rabbit alveolar macrophages. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2498–2501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musson R. A., Shafran H., Henson P. M. Intracellular levels and stimulated release of lysosomal enzymes from human peripheral blood monocytes and monocyte-derived macrophages. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1980 Sep;28(3):249–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman S. L., Musson R. A., Henson P. M. Development of functional complement receptors during in vitro maturation of human monocytes into macrophages. J Immunol. 1980 Nov;125(5):2236–2244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkston P., Bitterman P. B., Crystal R. G. Spontaneous release of interleukin-2 by lung T lymphocytes in active pulmonary sarcoidosis. N Engl J Med. 1983 Apr 7;308(14):793–800. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198304073081401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennard S. I., Hunninghake G. W., Bitterman P. B., Crystal R. G. Production of fibronectin by the human alveolar macrophage: mechanism for the recruitment of fibroblasts to sites of tissue injury in interstitial lung diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7147–7151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Lipsky P. E. The role of monocytes in pokeweed mitogen-stimulated human B cell activation: separate requirements for intact monocytes and a soluble monocyte factor. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1341–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenwasser L. J., Dinarello C. A. Ability of human leukocytic pyrogen to enhance phytohemagglutinin induced murine thymocyte proliferation. Cell Immunol. 1981 Sep 1;63(1):134–142. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90034-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salahuddin S. Z., Markham P. D., Gallo R. C. Establishment of long-term monocyte suspension cultures from normal human peripheral blood. J Exp Med. 1982 Jun 1;155(6):1842–1857. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.6.1842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scala G., Oppenheim J. J. Antigen presentation by human monocytes: evidence for stimulant processing and requirement for interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1160–1166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J. A., Mizel S. B., Cohen D., Green I. Interleukin 1, a potential regulator of fibroblast proliferation. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2177–2182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon P. L., Willoughby W. F. The role of subcellular factors in pulmonary immune function: physicochemical characterization of two distinct species of lymphocyte-activating factor produced by rabbit alveolar macrophages. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1534–1541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A., Gilbride K. J., Favata M. F. Lymphocyte activating factor promotes T-cell growth factor production by cloned murine lymphoma cells. Nature. 1980 Oct 30;287(5785):853–855. doi: 10.1038/287853a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sztein M. B., Vogel S. N., Sipe J. D., Murphy P. A., Mizel S. B., Oppenheim J. J., Rosenstreich D. L. The role of macrophages in the acute-phase response: SAA inducer is closely related to lymphocyte activating factor and endogenous pyrogen. Cell Immunol. 1981 Sep 1;63(1):164–176. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich F. Studies of lymphocyte activating factor from alveolar macrophages. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1977 Jan;21(1):33–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner M. S., Bianco C., Nussenzweig V. Enhanced binding of neuraminidase-treated sheep erythrocytes to human T lymphocytes. Blood. 1973 Dec;42(6):939–946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whisler R. L., Newhouse Y. G., Lachman L. B. Heterogeneity of human monocyte subsets in the promotion of B cell colonies and the role of interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):455–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. D., Cameron P. M. The relationship between bacterial endotoxin and human B cell-activating factor. J Immunol. 1978 Jul;121(1):53–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



