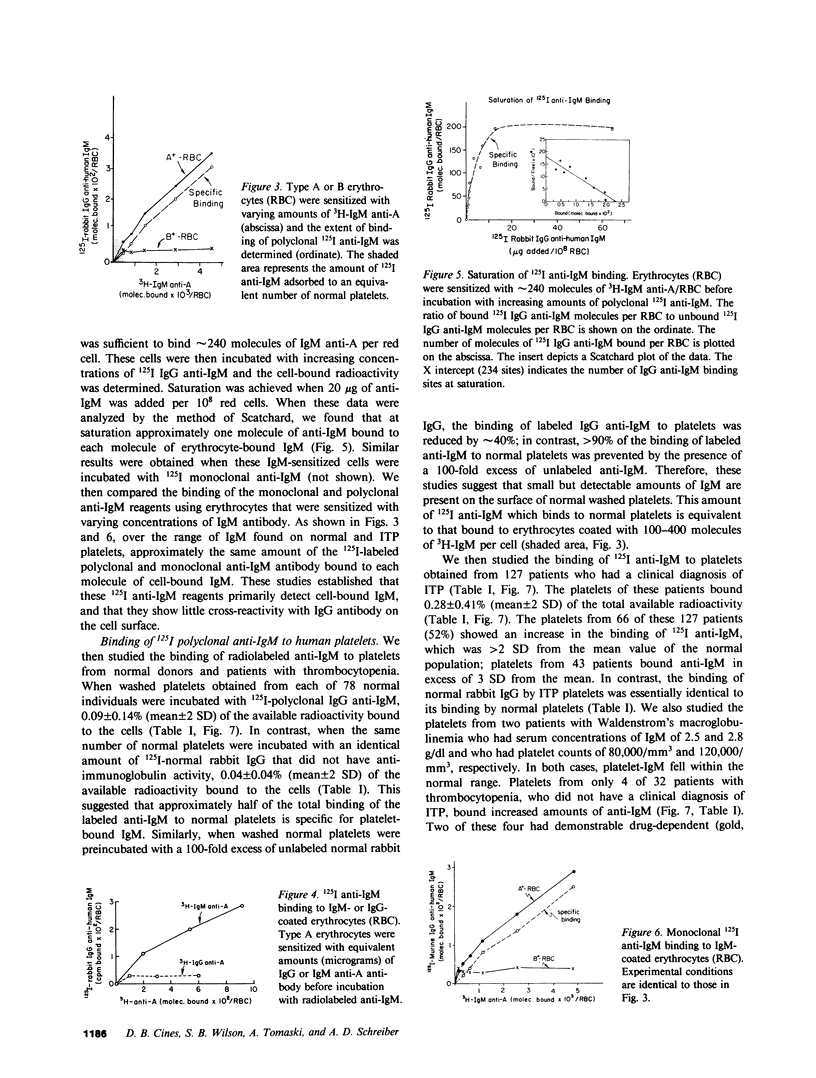
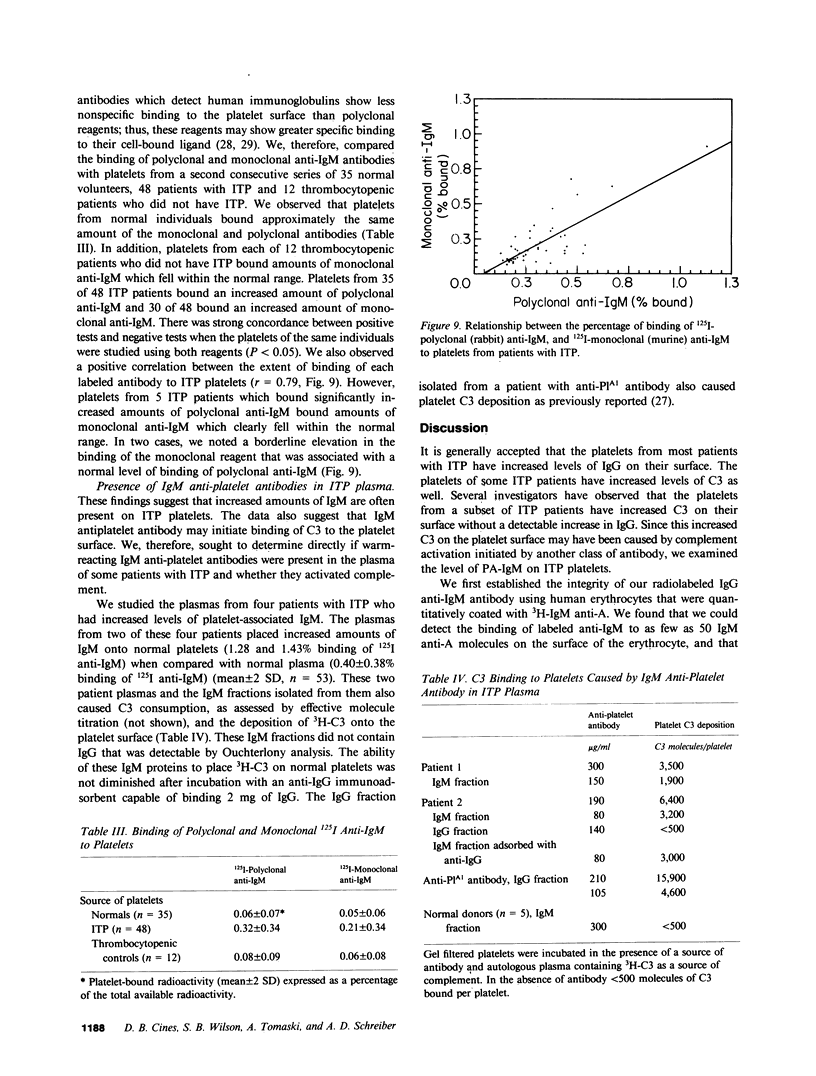
Abstract
The clinical course and response to therapy of patients with immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) are not completely determined by the level of IgG present on the platelet surface. It is possible that antibodies of other immunoglobulin classes also play a role in platelet destruction in some of these patients. Therefore, we studied 175 patients with ITP for the presence of IgM anti-platelet antibodies using radiolabeled polyclonal or monoclonal anti-IgM. We observed that 57% of patients with clinical ITP had increased levels of IgM on their platelets, compared with normal controls and patients with thrombocytopenia who did not have ITP (less than 10%), (P less than 0.01). We obtained similar results using either radiolabeled polyclonal or monoclonal anti-IgM, reagents whose integrity was first characterized using erythrocytes coated with defined amounts of IgM antibody. Among patients with increased platelet-IgM there was a significant correlation both with the presence of increased platelet-C3 as well as the amount of platelet-C3 (P less than 0.01, r = 0.53). We demonstrated the presence of warm-reacting IgM anti-platelet antibodies in the plasma of two of these patients who were further studied. The isolated IgM fraction from these two plasmas was able to activate complement and place 3H-C3 on normal platelets. These studies demonstrate the presence of warm-reacting IgM anti-platelet antibodies in some patients with ITP. They suggest that the binding of complement to platelets by IgM antibodies may initiate platelet clearance as well as enhance the effect of IgG antibodies in ITP.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bussel J. B., Kimberly R. P., Inman R. D., Schulman I., Cunningham-Rundles C., Cheung N., Smithwick E. M., O'Malley J., Barandun S., Hilgartner M. W. Intravenous gammaglobulin treatment of chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 1983 Aug;62(2):480–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung N. K., Hilgartner M. W., Schulman I., McFall P., Glader B. E. Platelet-associated immunoglobulin G in childhood idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. J Pediatr. 1983 Mar;102(3):366–370. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80650-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cines D. B., Schreiber A. D. Effect of anti-P1A1 antibody on human platelets. I. The role of complement. Blood. 1979 Apr;53(4):567–577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cines D. B., Schreiber A. D. Immune thrombocytopenia. Use of a Coombs antiglobulin test to detect IgG and C3 on platelets. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jan 18;300(3):106–111. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197901183000302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGE J. T., MITCHELL C., HANAHAN D. J. The preparation and chemical characteristics of hemoglobin-free ghosts of human erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Jan;100:119–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R., Rosse W., Ebbert L. Quantitative determination of antibody in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Correlation of serum and platelet-bound antibody with clinical response. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jan 30;292(5):230–236. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197501302920503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Follea G., Mandrand B., Dechavanne M. Simultaneous enzymo-immunologic assays of platelet associated IgG, IgM and C3. A useful tool in assessment of immune thrombocytopenias. Thromb Res. 1982 May 15;26(4):249–258. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90289-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer C. H., Wirtz G. H., Renfer L., Gresham H. D., Tack B. F. Large scale isolation of functionally active components of the human complement system. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3995–4006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauch T. W., Rosse W. F. Platelet-bound complement (C3) in immune thrombocytopenia. Blood. 1977 Dec;50(6):1129–1136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelton J. G., Powers P. J., Carter C. J. A prospective study of the usefulness of the measurement of platelet-associated IgG for the diagnosis of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 1982 Oct;60(4):1050–1053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelton J. G., Steeves K. The amount of platelet-bound albumin parallels the amount of IgG on washed platelets from patients with immune thrombocytopenia. Blood. 1983 Oct;62(4):924–927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernoff M., Malan E. Platelet antibody levels do not correlate with response to therapy in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Br J Haematol. 1983 Apr;53(4):559–562. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb07307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightsey A. L., Jr, Koenig H. M., McMillan R., Stone J. R., Jr Platelet-associated immunoglobulin G in childhood idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. J Pediatr. 1979 Feb;94(2):201–204. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80823-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwin S. D., Balaban S., Eyster M. E. Gm allotype preference in erythrocyte IgG antibodies of patients with autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Blood. 1973 Aug;42(2):241–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LoBuglio A. F., Court W. S., Vinocur L., Maglott G., Shaw G. M. Immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Use of a 125I-labeled antihuman IgG monoclonal antibody to quantify platelet-bound IgG. N Engl J Med. 1983 Aug 25;309(8):459–463. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198308253090804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath K. M., Stuart J. J., Richards F., 2nd Correlation between serum IgG, platelet membrane IgG, and platelet function in hypergammaglobulinaemic states. Br J Haematol. 1979 Aug;42(4):585–591. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1979.tb01171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller-Eckhardt C., Kayser W., Mersch-Baumert K., Mueller-Eckhardt G., Breidenbach M., Kugel H. G., Graubner M. The clinical significance of platelet-associated IgG: a study on 298 patients with various disorders. Br J Haematol. 1980 Sep;46(1):123–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1980.tb05942.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller-Eckhardt C., Mueller-Eckhardt G., Kayser W., Voss R. M., Wegner J., Küenzlen E. Platelet associated IgG, platelet survival, and platelet sequestration in thrombocytopenic states. Br J Haematol. 1982 Sep;52(1):49–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1982.tb03860.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers T. J., Kim B. K., Steiner M., Baldini M. G. Platelet-associated complement C3 in immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 1982 May;59(5):1023–1028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nel J. D., Stevens K., Mouton A., Pretorius F. J. Platelet-bound IgM in autoimmune thrombocytopenia. Blood. 1983 Jan;61(1):119–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawha J., Giuliani D., Morse B. S. Platelet-associated IgM levels in thrombocytopenia. Vox Sang. 1983;45(2):97–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1983.tb01893.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfueller S. L., Cosgrove L., Firkin B. G., Tew D. Relationship of raised platelet IgG in thrombocytopenia to total platelet protein content. Br J Haematol. 1981 Oct;49(2):293–302. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1981.tb07226.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosse W. F., Devine D. V., Ware R. Reactions of immunoglobulin G-binding ligands with platelets and platelet-associated immunoglobulin G. J Clin Invest. 1984 Feb;73(2):489–496. doi: 10.1172/JCI111235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. D., Frank M. M. Role of antibody and complement in the immune clearance and destruction of erythrocytes. I. In vivo effects of IgG and IgM complement-fixing sites. J Clin Invest. 1972 Mar;51(3):575–582. doi: 10.1172/JCI106846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G. M., Axelson J., Maglott J. G., LoBuglio A. F. Quantification of platelet-bound IgG by 125I-Staphylococcal protein A in immune thrombocytopenic purpura and other thrombocytopenic disorders. Blood. 1984 Jan;63(1):154–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varon D., Karpatkin S. A monoclonal anti-platelet antibody with decreased reactivity for autoimmune thrombocytopenic platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6992–6995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veenhoven W. A., Van der Schans G. S., Nieweg H. O. Platelet antibodies in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Mar;39(3):645–651. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winiarski J., Holm G. Platelet associated immunoglobulins and complement in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Jul;53(1):201–207. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods V. L., Jr, Oh E. H., Mason D., McMillan R. Autoantibodies against the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex in patients with chronic ITP. Blood. 1984 Feb;63(2):368–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Boxtel C. J., Oosterhof F., Engelfriet C. P. Immunofluorescence microphotometry for the detection of platelet antibodies. III. Demonstration of autoantibodies against platelets. Scand J Immunol. 1975;4(7):657–672. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1975.tb02674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Leeuwen E. F., van der Ven J. T., Engelfriet C. P., von dem Borne A. E. Specificity of autoantibodies in autoimmune thrombocytopenia. Blood. 1982 Jan;59(1):23–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von dem Borne A. E., Helmerhorst F. M., van Leeuwen E. F., Pegels H. G., von Riesz E., Engelfriet C. P. Autoimmune thrombocytopenia: detection of platelet autoantibodies with the suspension immunofluorescence test. Br J Haematol. 1980 Jun;45(2):319–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1980.tb07151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


