Abstract
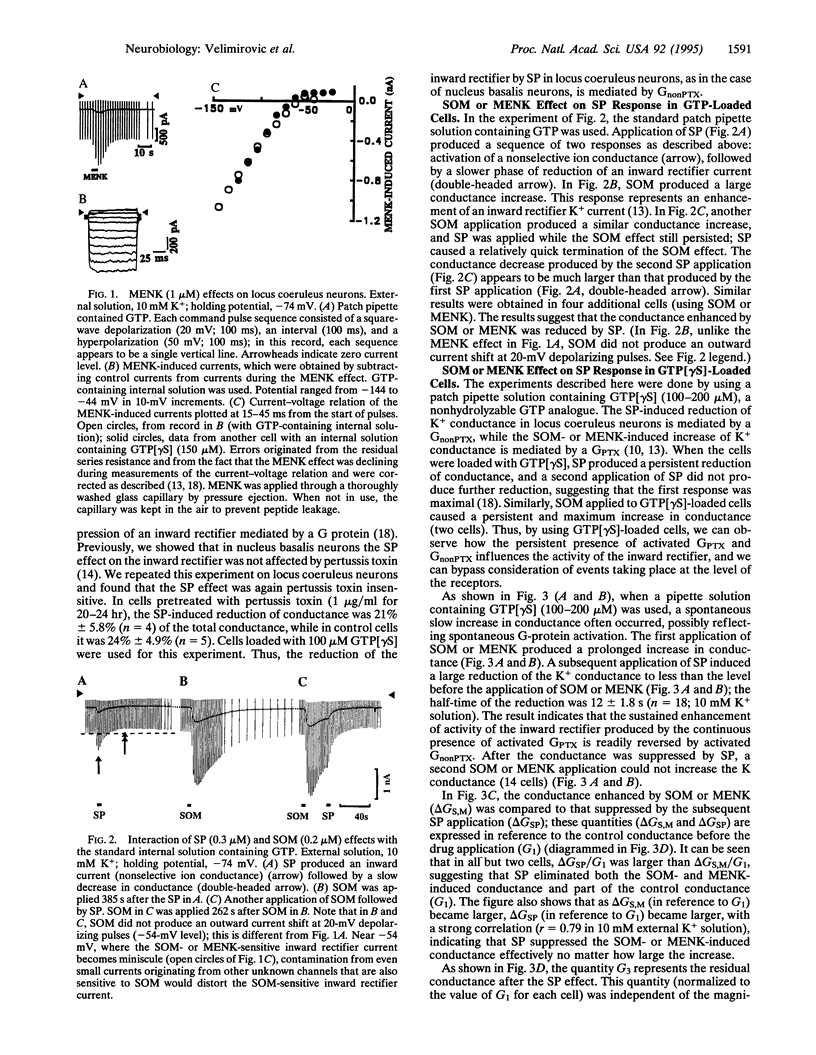
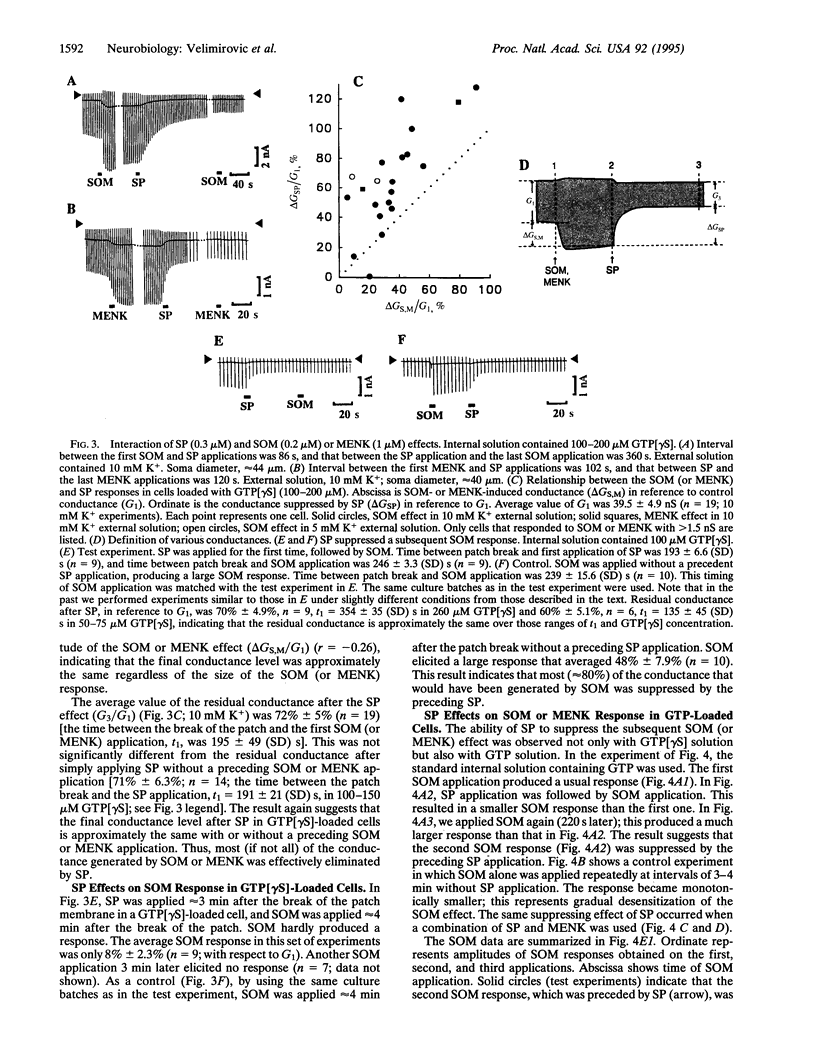
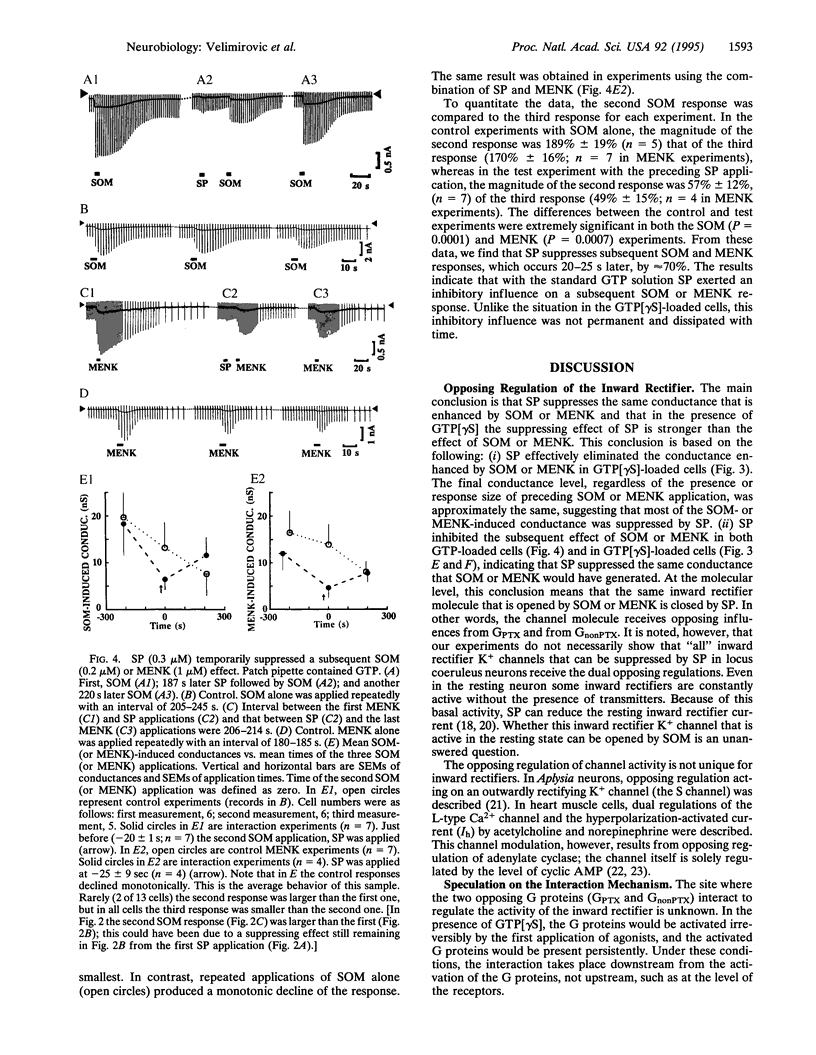
In locus coeruleus neurons, substance P (SP) suppresses an inwardly rectifying K+ current via a pertussis toxin-insensitive guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein; GnonPTX), whereas somatostatin (SOM) or [Met]enkephalin (MENK) enhances it via a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein (GPTX). The interaction of the SP and the SOM (or MENK) effects was studied in cultured locus coeruleus neurons. In neurons loaded with guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate (GTP[gamma S]), application of SOM (or MENK) evoked a persistent increase in the inward rectifier K+ conductance. A subsequent application of SP suppressed this conductance to a level less than that before the SOM (or MENK) application; the final conductance level was independent of the magnitude of the SOM (or MENK) response. This suppression by SP was persistent, and a subsequent SOM (or MENK) application did not reverse it. When SP was applied to GTP[gamma S]-loaded cells first, subsequent SOM elicited only a small response. In GTP-loaded neurons, application of SP temporarily suppressed the subsequent SOM- (or MENK)-induced conductance increase. These results suggest that the same inward rectifier molecule that responds to an opening signal from GPTX also responds to a closing signal from GnonPTX. The closing signal is stronger than the opening signal.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belardetti F., Kandel E. R., Siegelbaum S. A. Neuronal inhibition by the peptide FMRFamide involves opening of S K+ channels. Nature. 1987 Jan 8;325(7000):153–156. doi: 10.1038/325153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitwieser G. E., Szabo G. Uncoupling of cardiac muscarinic and beta-adrenergic receptors from ion channels by a guanine nucleotide analogue. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):538–540. doi: 10.1038/317538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dascal N., Schreibmayer W., Lim N. F., Wang W., Chavkin C., DiMagno L., Labarca C., Kieffer B. L., Gaveriaux-Ruff C., Trollinger D. Atrial G protein-activated K+ channel: expression cloning and molecular properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10235–10239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D., Tromba C. Muscarinic control of the hyperpolarization-activated current (if) in rabbit sino-atrial node myocytes. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:493–510. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farkas R. H., Nakajima S., Nakajima Y. Neurotensin excites basal forebrain cholinergic neurons: ionic and signal-transduction mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 29;91(7):2853–2857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.7.2853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischmeister R., Hartzell H. C. Mechanism of action of acetylcholine on calcium current in single cells from frog ventricle. J Physiol. 1986 Jul;376:183–202. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Jaffe L. A. Electrical properties of egg cell membranes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1979;8:385–416. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.08.060179.002125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Nakajima S., Nakajima Y. Somatostatin induces an inward rectification in rat locus coeruleus neurones through a pertussis toxin-sensitive mechanism. J Physiol. 1988 Dec;407:177–198. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyano K., Velimirovic B. M., Grigg J. J., Nakajima S., Nakajima Y. Two signal transduction mechanisms of substance P-induced depolarization in locus coeruleus neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 1993 Sep 1;5(9):1189–1197. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1993.tb00973.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo Y., Baldwin T. J., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Primary structure and functional expression of a mouse inward rectifier potassium channel. Nature. 1993 Mar 11;362(6416):127–133. doi: 10.1038/362127a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo Y., Reuveny E., Slesinger P. A., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Primary structure and functional expression of a rat G-protein-coupled muscarinic potassium channel. Nature. 1993 Aug 26;364(6440):802–806. doi: 10.1038/364802a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuko S., Nakajima Y., Nakajima S., Yamaguchi K. Noradrenergic neurons from the locus ceruleus in dissociated cell culture: culture methods, morphology, and electrophysiology. J Neurosci. 1986 Nov;6(11):3229–3241. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-11-03229.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihara S., North R. A., Surprenant A. Somatostatin increases an inwardly rectifying potassium conductance in guinea-pig submucous plexus neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Sep;390:335–355. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake M., Christie M. J., North R. A. Single potassium channels opened by opioids in rat locus ceruleus neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3419–3422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima Y., Nakajima S., Inoue M. Pertussis toxin-insensitive G protein mediates substance P-induced inhibition of potassium channels in brain neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3643–3647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Williams J. T., Surprenant A., Christie M. J. Mu and delta receptors belong to a family of receptors that are coupled to potassium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5487–5491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffinger P. J., Martin J. M., Hunter D. D., Nathanson N. M., Hille B. GTP-binding proteins couple cardiac muscarinic receptors to a K channel. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):536–538. doi: 10.1038/317536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen K. Z., North R. A. Substance P opens cation channels and closes potassium channels in rat locus coeruleus neurons. Neuroscience. 1992 Sep;50(2):345–353. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90428-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi W. X., Bunney B. S. Neurotensin modulates autoreceptor mediated dopamine effects on midbrain dopamine cell activity. Brain Res. 1991 Mar 15;543(2):315–321. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90043-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B., Stanfield P. R. A potential- and time-dependent blockade of inward rectification in frog skeletal muscle fibres by barium and strontium ions. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:169–191. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield P. R., Nakajima Y., Yamaguchi K. Substance P raises neuronal membrane excitability by reducing inward rectification. Nature. 1985 Jun 6;315(6019):498–501. doi: 10.1038/315498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trussell L. O., Jackson M. B. Dependence of an adenosine-activated potassium current on a GTP-binding protein in mammalian central neurons. J Neurosci. 1987 Oct;7(10):3306–3316. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-10-03306.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi K., Nakajima Y., Nakajima S., Stanfield P. R. Modulation of inwardly rectifying channels by substance P in cholinergic neurones from rat brain in culture. J Physiol. 1990 Jul;426:499–520. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



