Abstract
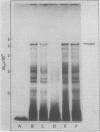
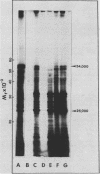
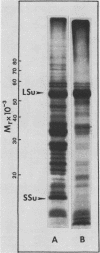
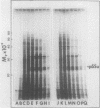
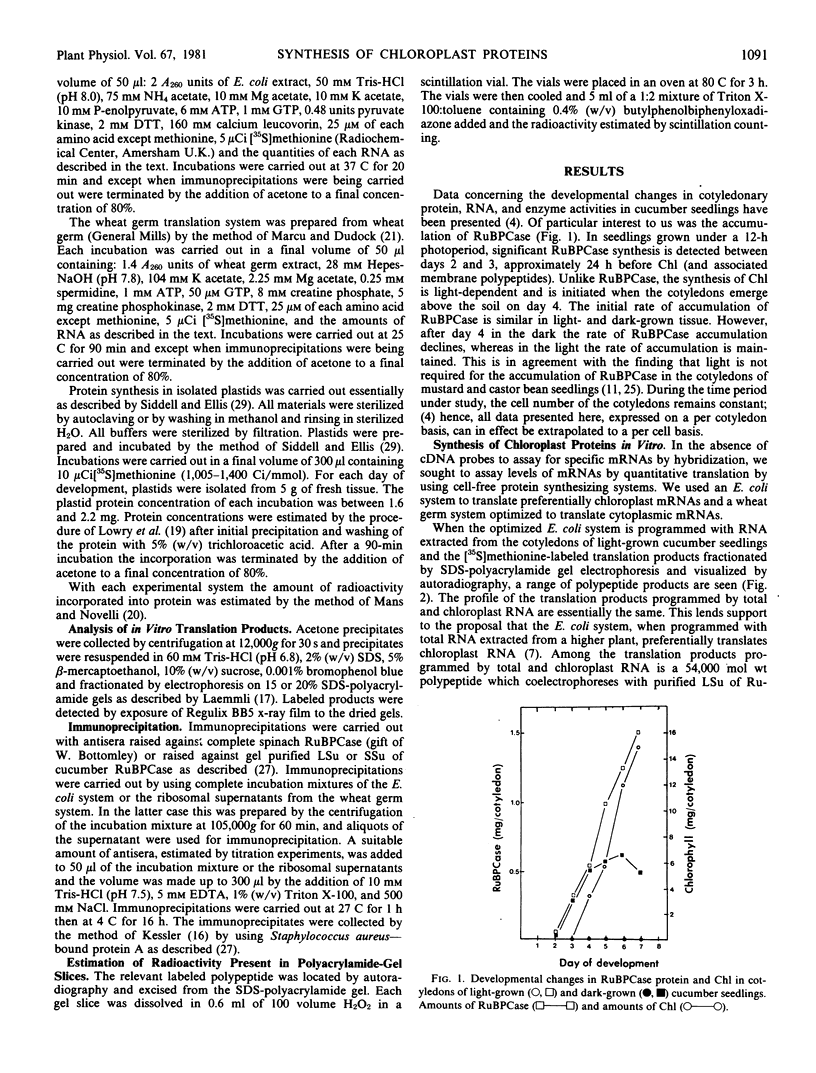
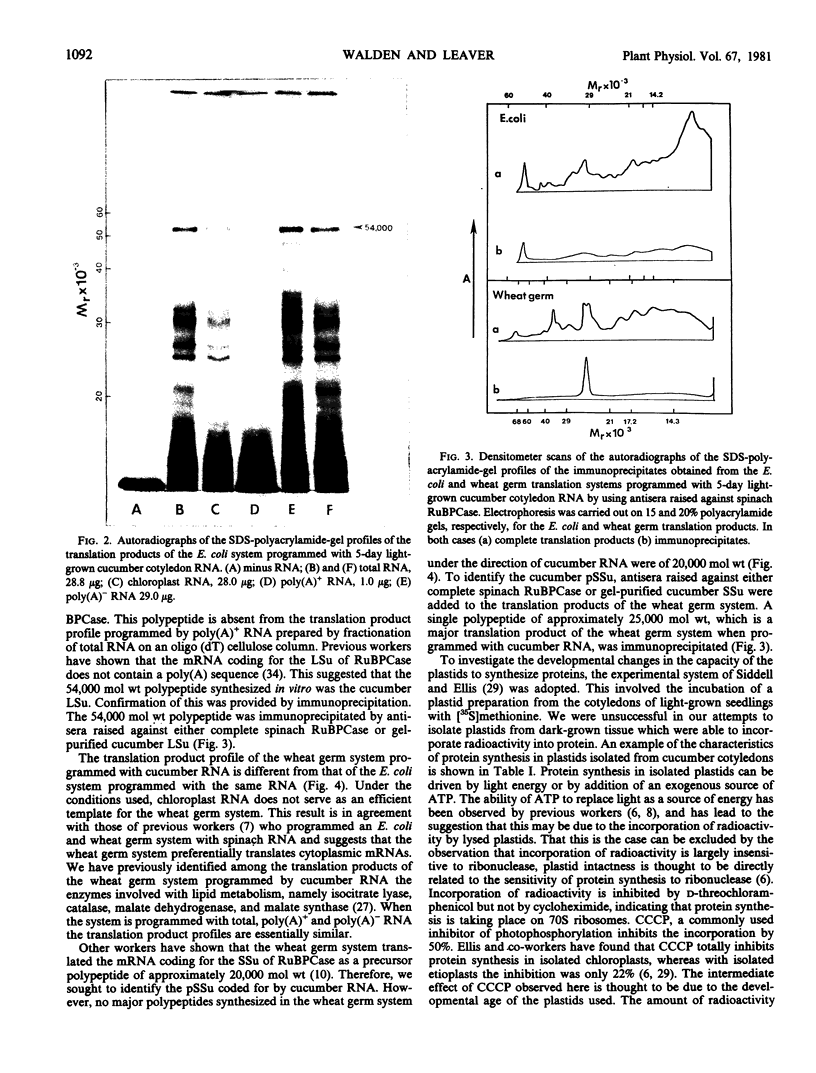
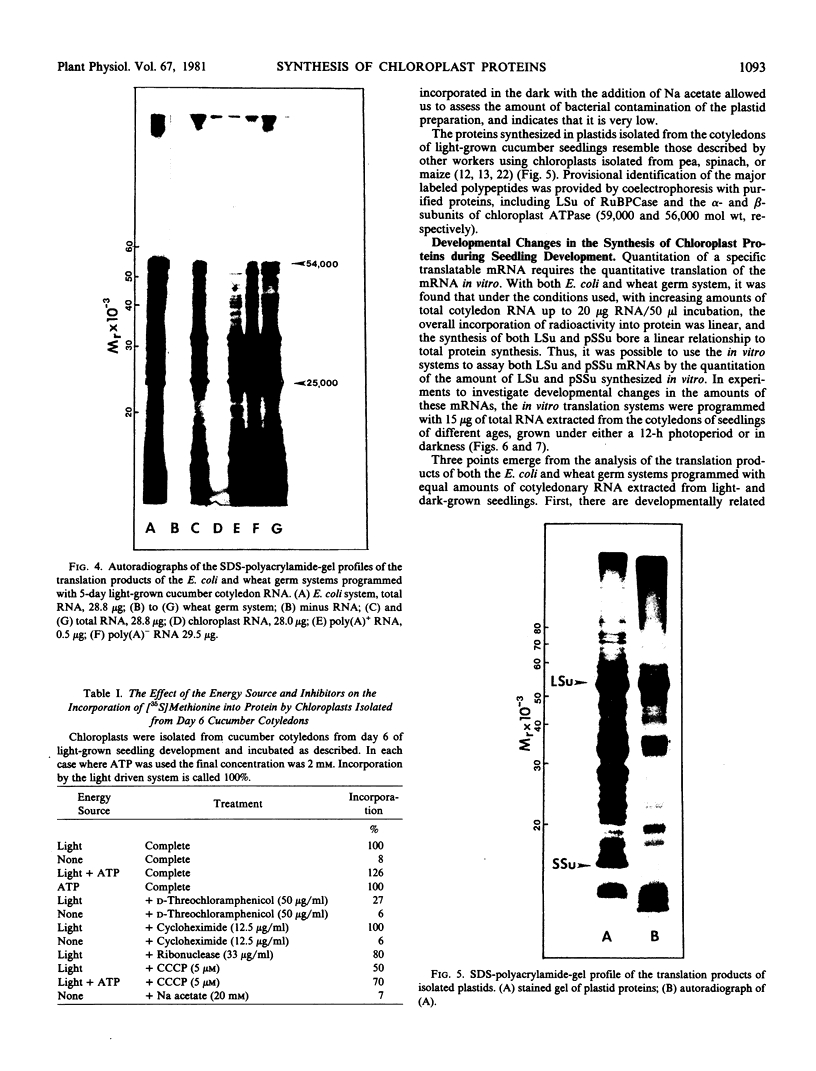
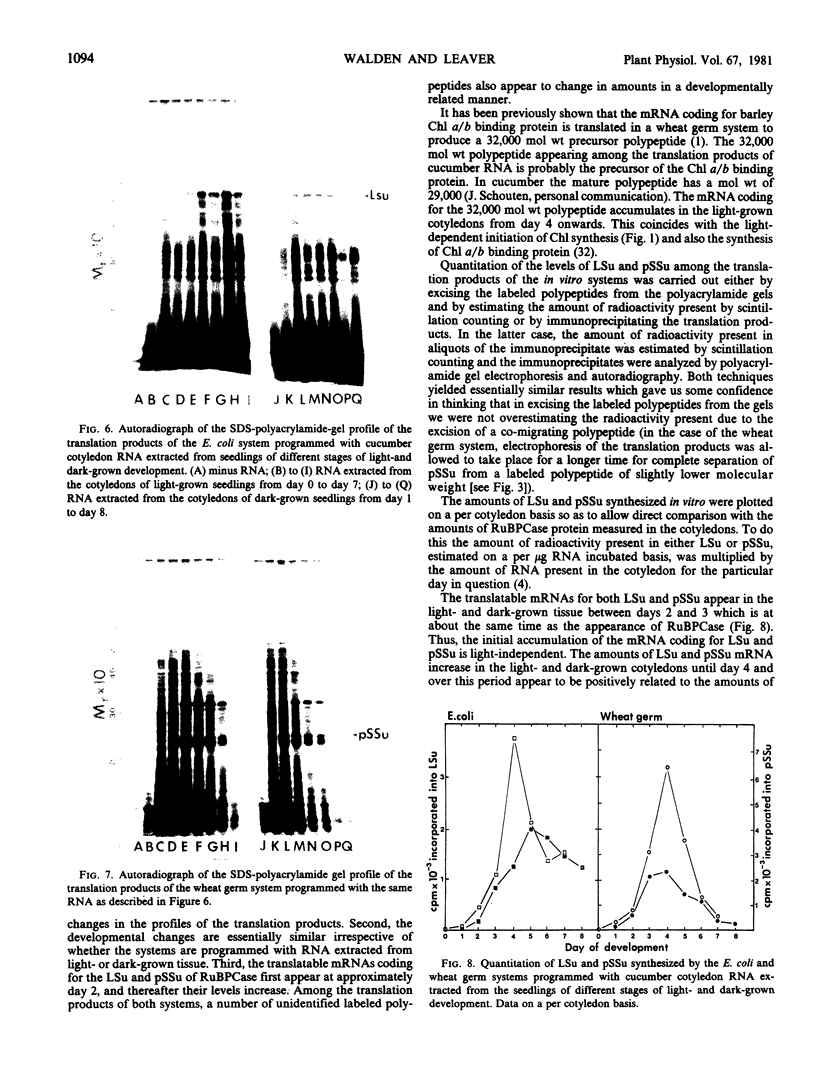
Cell-free protein synthesizing systems have been used to study the developmental changes in the synthesis of chloroplast proteins in the cotyledons of cucumber seedlings grown in the light or in the dark. Escherichia coli and wheat germ in vitro protein synthesizing systems have been used to assay the changes in the levels of the mRNA's coding for ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase (RuBPCase). The large subunit of cucumber RuBPCase has been identified among the translation products of the E. coli system. The wheat germ system translates the cucumber mRNA coding for the small subunit of RuBPCase to produce a 25,000 molecular weight precursor polypeptide. Plastids isolated from light-grown cotyledons were used to study developmental changes in their capacity to synthesize protein. The data obtained indicate that in the light there is an initial 48-hour period of accumulation of the mRNA's coding for the large and small subunits of RuBPCase, coupled with an increase in the capacity of the isolated plastids to synthesize protein. This is followed by a decline. This decline is not reflected in the accumulation of RuBPCase in the cotyledons which remains constant over the period of study.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apel K., Kloppstech K. The plastid membranes of barley (Hordeum vulgare). Light-induced appearance of mRNA coding for the apoprotein of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):581–588. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12273.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnon D. I. COPPER ENZYMES IN ISOLATED CHLOROPLASTS. POLYPHENOLOXIDASE IN BETA VULGARIS. Plant Physiol. 1949 Jan;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1104/pp.24.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedbrook J. R., Link G., Coen D. M., Bogorad L. Maize plastid gene expressed during photoregulated development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3060–3064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley W., Higgins T. J., Whitfeld P. R. Differential recognition of chloroplast and cytoplasmic messenger RNA by 70S and 80S ribosomal systems. FEBS Lett. 1976 Mar 15;63(1):120–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80207-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley W., Spencer D., Whitfeld P. R. Protein synthesis in isolated spinach chloroplasts: comparison of light-driven and ATP-driven synthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Sep;164(1):106–117. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua N. H., Schmidt G. W. Post-translational transport into intact chloroplasts of a precursor to the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6110–6114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobberstein B., Blobel G., Chua N. H. In vitro synthesis and processing of a putative precursor for the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1082–1085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dockerty A., Lord J. M., Merrett M. J. Development of ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase in castor bean cotyledons. Plant Physiol. 1977 Jun;59(6):1125–1127. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.6.1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grebanier A. E., Steinback K. E., Bogorad L. Comparison of the Molecular Weights of Proteins Synthesized by Isolated Chloroplasts with Those Which Appear during Greening in Zea mays. Plant Physiol. 1979 Mar;63(3):436–439. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.3.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley M. R., Wheeler A., Ellis R. J. Protein synthesis in chloroplasts. V. Translation of messenger RNA for the large subunit of fraction I protein in a heterologous cell-free system. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 5;91(1):67–77. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90372-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman J. G., Moorman A. F., Verkley F. N. In vitro synthesis of chloroplast ferredoxin as a high molecular weight precursor in a cell-free protein synthesizing system from wheat germs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jun 29;82(4):1121–1131. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90303-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leaver C. J., Ingle J. The molecular integrity of chloroplast ribosomal ribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1971 Jun;123(2):235–243. doi: 10.1042/bj1230235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K., Dudock B. Characterization of a highly efficient protein synthesizing system derived from commercial wheat germ. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Nov;1(11):1385–1397. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.11.1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendiola-Morgenthaler L. R., Morgenthaler J. J., Price C. A. Synthesis of coupling factor CF1 protein by isolated spinach chloroplasts. FEBS Lett. 1976 Feb 1;62(1):96–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt G. W., Devillers-Thiery A., Desruisseaux H., Blobel G., Chua N. H. NH2-terminal amino acid sequences of precursor and mature forms of the ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Cell Biol. 1979 Dec;83(3):615–622. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.3.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddell S. G., Ellis R. J. Protein synthesis in chloroplasts. Characteristics and products of protein synthesis in vitro in etioplasts and developing chloroplasts from pea leaves. Biochem J. 1975 Mar;146(3):675–685. doi: 10.1042/bj1460675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverthorne J., Ellis R. J. Protein synthesis in chloroplasts. VIII. Differential synthesis of chloroplast proteins during spinach leaf development. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Apr 30;607(2):319–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler A. M., Hartley M. R. Major mRNA species from spinach chloroplasts do not contain poly(A). Nature. 1975 Sep 4;257(5521):66–67. doi: 10.1038/257066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]