Abstract
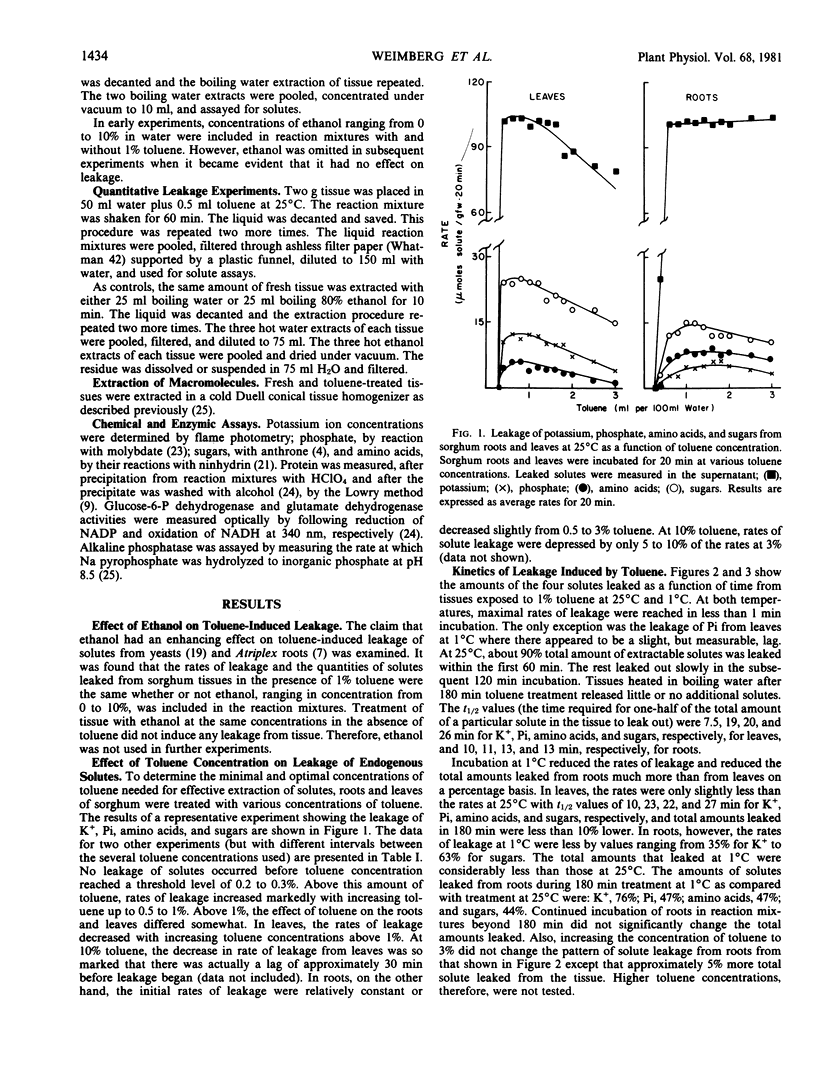
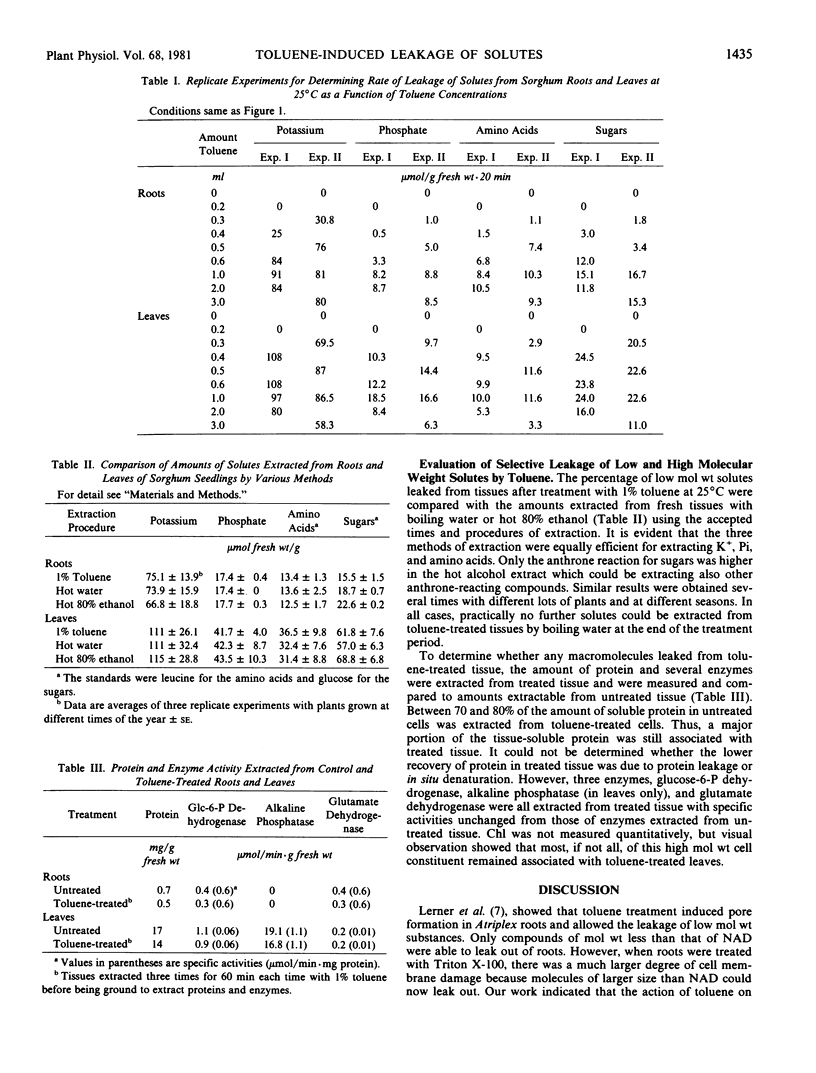
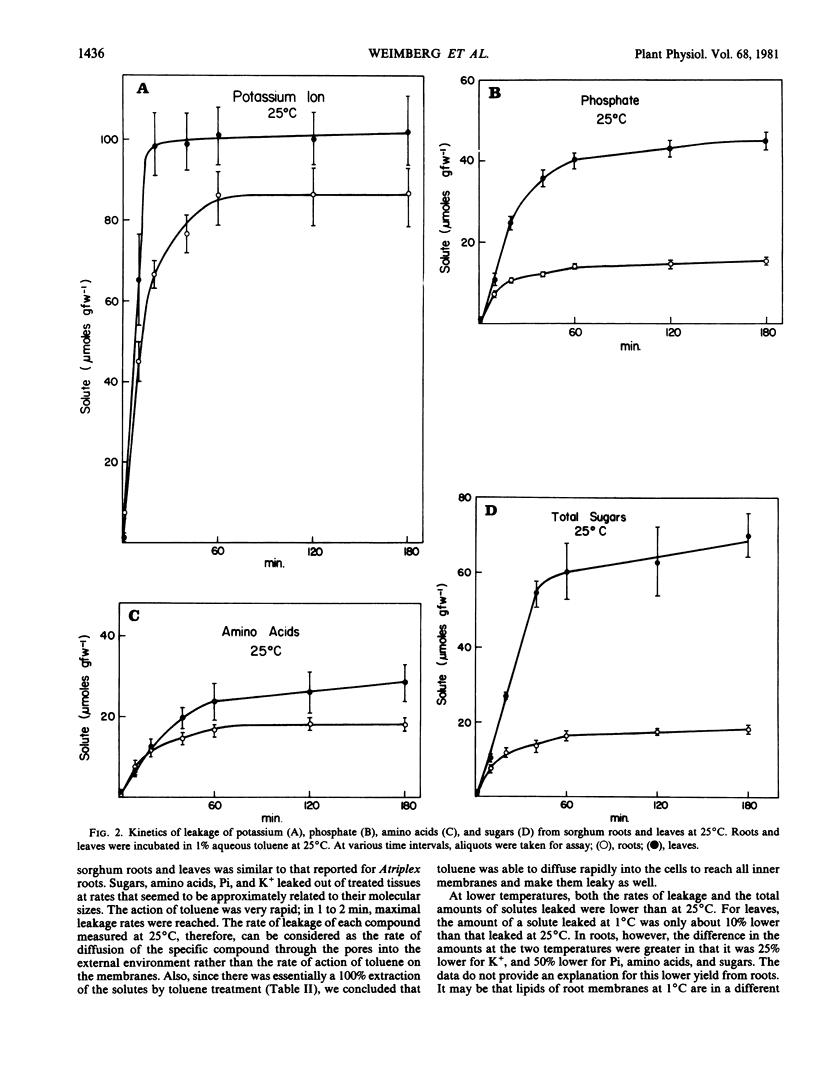
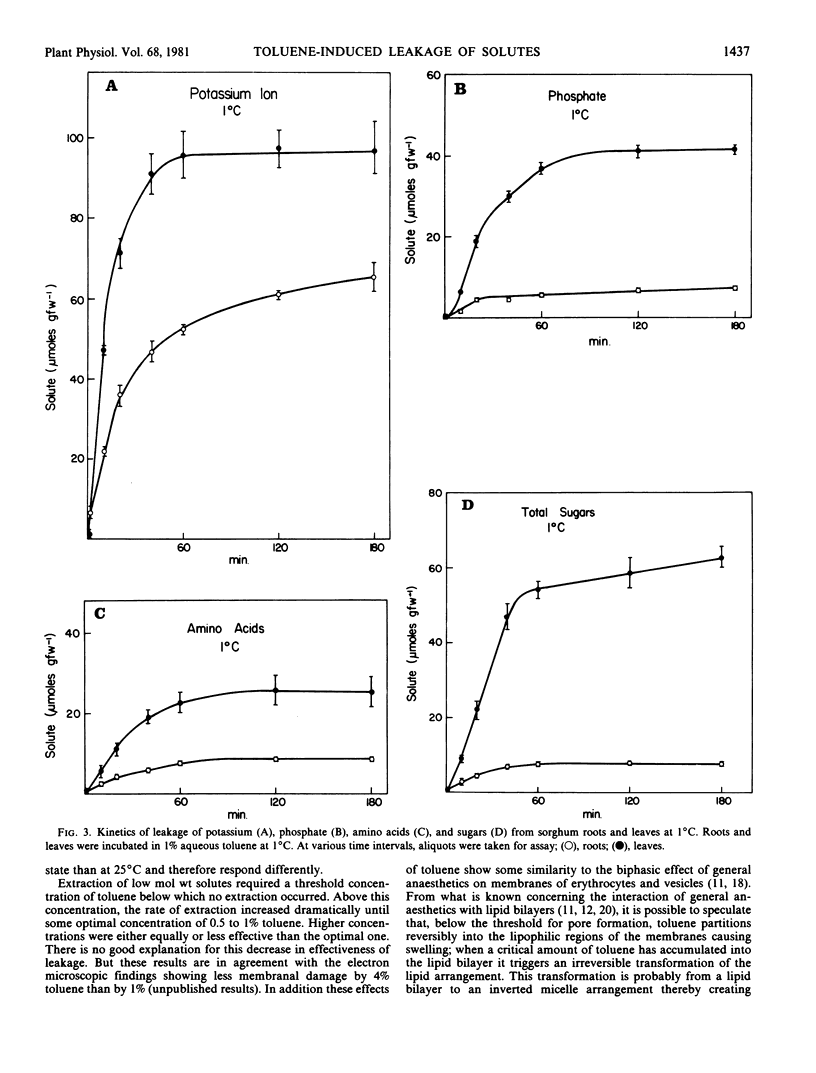
The relationship between toluene concentration and the rate of leakage of solutes from toluene-treated roots and leaves of Sorghum bicolor, L. Moench, was studied to determine the effect of toluene on plant cell membranes. A threshold concentration of 0.2% toluene was needed to induce leakage. Maximal leakage rates were obtained with 0.5% toluene. Low molecular weight solutes, such as amino acids, sugars, and inorganic ions, leaked from treated tissue, while macromolecules, such as protein were retained. The rates at which the low molecular weight solutes diffused from treated cells decreased with increasing molecular weight. At 25°C, treatment of roots and leaves with 0.5% toluene resulted in the quasi-quantitative leakage of solutes within 180 minutes. At 1°C, roots and leaves differed in their response to toluene. The rates of leakage from roots at 1°C were much lower and the total amounts much smaller than at 25°C, while in leaves the difference between the two temperatures was very small.
The procedure of treating tissues with 0.5% toluene for 180 minutes at 25°C proved to be a rapid and simple technique for quantitative extraction of water-soluble, low molecular weight solutes from plant cells into the extracting medium while macromolecular constituents are retained inside the cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basabe J. R., Lee C. A., Weiss R. L. Enzyme assays using permeabilized cells of Neurospora. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jan 15;92(2):356–360. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90670-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gachelin G. A new assay of the phosphotransferase system in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Feb 21;34(4):382–387. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90392-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilderman R. H., Goldblatt P. J., Deutscher M. P. Preparation and characterization of liver cells made permeable to macromolecules by treatment with toluene. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4796–4801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. W., DeMoss J. A. Effects of toluene on Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1420–1425. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1420-1425.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVIN D. H., THANG M. N., GRUNBERG-MANAGO M. SYNTHESIS IN VIVO OF POLYNUCLEOTIDE PHOSPHORYLASE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. I. EFFECT OF AMINO ACIDS ON POLYNUCLEOTIDE PHOSPHORYLASE ACTIVITY IN A CHLORAMPHENICOL-INHIBITED SYSTEM. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Dec 20;76:558–571. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner H. R., Ben-Bassat D., Reinhold L., Poljakoff-Mayber A. Induction of "pore" formation in plant cell membranes by toluene. Plant Physiol. 1978 Feb;61(2):213–217. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.2.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlib M. A., Shannon W. A., Jr, Srere P. A. Measurement of matrix enzyme activity in isolated mitochondria made permeable with toluene. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jan 30;178(2):396–407. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90209-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe J. C., Burgen A. S. Relaxation of anaesthetics in the presence of cyto-membranes. Nature. 1968 Nov 9;220(5167):587–588. doi: 10.1038/220587a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mordoh J., Hirota Y., Jacob F. On the process of cellular division in Escherichia coli. V. Incorporation of deoxynucleoside triphosphates by DNA thermosensitive mutants of Escherichia coli also lacking DNA polymerase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):773–778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses R. E., Richardson C. C. Replication and repair of DNA in cells of Escherichia coli treated with toluene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):674–681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnam S. L., Koch A. L. Complications in the simplest cellular enzyme assay: lysis of Escherichia coli for the assay of beta-galactosidase. Anal Biochem. 1975 Feb;63(2):350–360. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90357-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano R., Gancedo J. M., Gancedo C. Assay of yeast enzymes in situ. A potential tool in regulation studies. Eur J Biochem. 1973 May 2;34(3):479–482. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02783.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swissa M., Weinhouse H., Benziman M. Activities of citrate synthase and other enzymes of Acetobacter xylinum in situ and in vitro. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 1;153(2):499–501. doi: 10.1042/bj1530499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAUSSKY H. H., SHORR E. A microcolorimetric method for the determination of inorganic phosphorus. J Biol Chem. 1953 Jun;202(2):675–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimberg R. Effect of growth in highly salinized media on the enzymes of the photosynthetic apparatus in pea seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1975 Jul;56(1):8–12. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.1.8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimberg R. Enzyme levels in pea seedlings grown on highly salinized media. Plant Physiol. 1970 Sep;46(3):466–470. doi: 10.1104/pp.46.3.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitzman P. D. Behaviour of enzymes at high concentration. Use of permeabilised cells in the study of enzyme activity and its regulation. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jun 1;32(2):247–250. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80843-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Smet M. J., Kingma J., Witholt B. The effect of toluene on the structure and permeability of the outer and cytoplasmic membranes of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jan 4;506(1):64–80. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90435-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


