Abstract
We have used Fourier transform nuclear magnetic resonance methods to measure the spin-lattice and transverse relaxation times at 220 MHz of the choline N-methyl and the fatty-acid α-carbonyl, allyl, vinyl, methylene, and methyl protons of sonicated egg-yolk lecithin. Over the temperature range investigated the T1 values were, in general, similar to, but different from, one another, suggesting that the relaxation rates of all of the fatty-acid protons are not determined solely by spin-diffusion to a heat sink. Arrhenius plots of the T1 data gave activation energies similar to those for the barriers to internal rotation in alkanes. The values of the transverse relaxation rate, T2, showed a relatively large variation among the proton resonances; about 20% of the methylene protons had a T2 of 56 msec, while the remaining protons relaxed according to a distribution of values all shorter than 20 msec. Such a distribution of relaxation times is envisioned to arise from a distribution of correlation times stemming from complex motions in which extended angular excursions of the fatty acid chain are coupled to trans→gauche conformational transitions.
Keywords: PMR, nuclear relaxation, Fourier transform NMR
Full text
PDF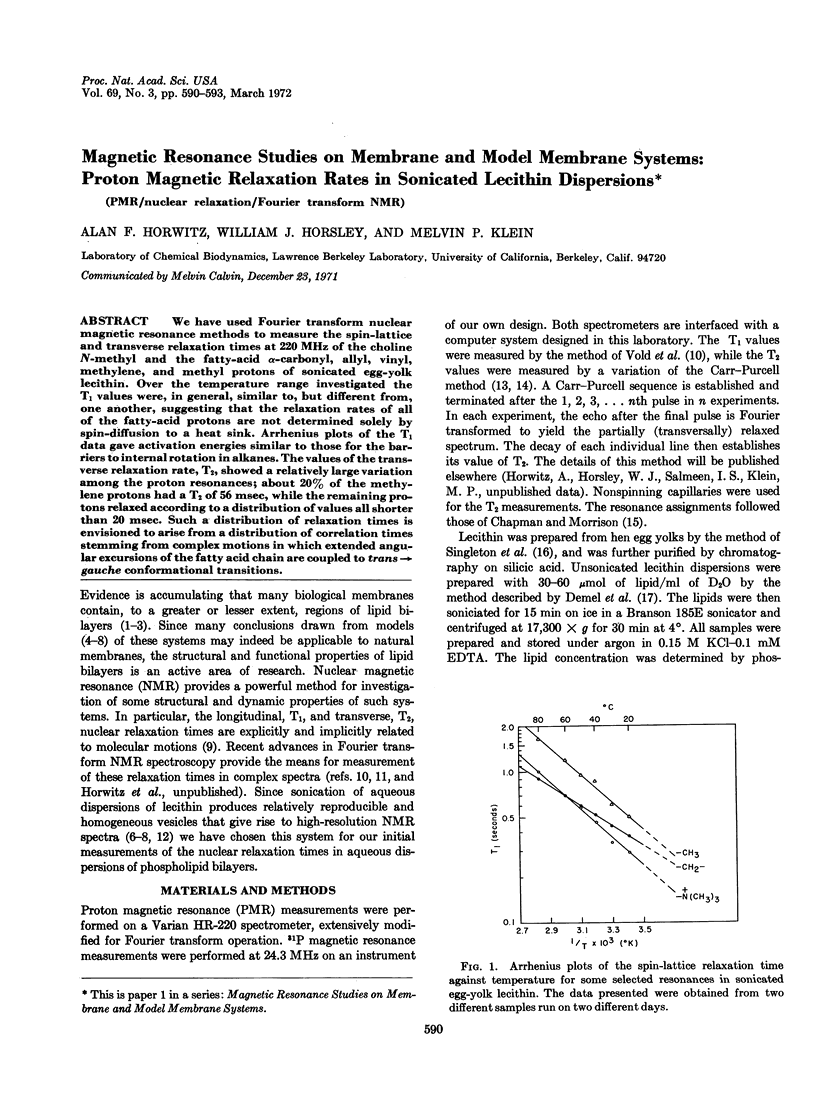



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATTWOOD D., SAUNDEES L. A LIGHT-SCATTERING STUDY OF ULTRASONICALLY IRRADIATED LECITHIN SOLS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Apr 5;98:344–350. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90126-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. I., Feigenson G. W., Seiter C. H. Nuclear relaxation studies of lecithin bilayers. Nature. 1971 May 14;231(5298):110–112. doi: 10.1038/231110a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman D., Morrison A. Physical studies of phospholipids. IV. High resolution nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of phospholipids and related substances. J Biol Chem. 1966 Nov 10;241(21):5044–5052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demel R. A., Kinsky S. C., Kinsky C. B., van Deenen L. L. Effects of temperature and cholesterol on the glucose permeability of liposomes prepared with natural and synthetic lecithins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jun 11;150(4):655–665. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henn F. A., Thompson T. E. Synthetic lipid bilayer membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1969;38:241–262. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.38.070169.001325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. Studies on phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Formation and physical characteristics. Biochemistry. 1969 Jan;8(1):344–352. doi: 10.1021/bi00829a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. A. The detection of oxidation in liposome preparations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 8;210(3):486–489. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClare C. W. An accurate and convenient organic phosphorus assay. Anal Biochem. 1971 Feb;39(2):527–530. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90443-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe J. C., Birdsall N. J., Feeney J., Lee A. G., Levine Y. K., Partington P. 13 C NMR spectra of lecithin vesicles and erythrocyte membranes. Nature. 1971 Sep 17;233(5316):199–201. doi: 10.1038/233199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothfield L., Finkelstein A. Membrane biochemistry. Annu Rev Biochem. 1968;37:463–496. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.37.070168.002335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGLETON W. S., GRAY M. S., BROWN M. L., WHITE J. L. CHROMATOGRAPHICALLY HOMOGENEOUS LECITHIN FROM EGG PHOSPHOLIPIDS. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1965 Jan;42:53–56. doi: 10.1007/BF02558256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheard B. Internal mobility in phospholipids. Nature. 1969 Sep 6;223(5210):1057–1059. doi: 10.1038/2231057a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Engelman D. M. Current models for the structure of biological membranes. J Cell Biol. 1969 Sep;42(3):613–646. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.3.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins M. H., Blaurock A. E., Engelman D. M. Bilayer structure in membranes. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 17;230(11):72–76. doi: 10.1038/newbio230072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


