Abstract
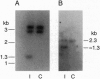
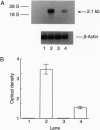
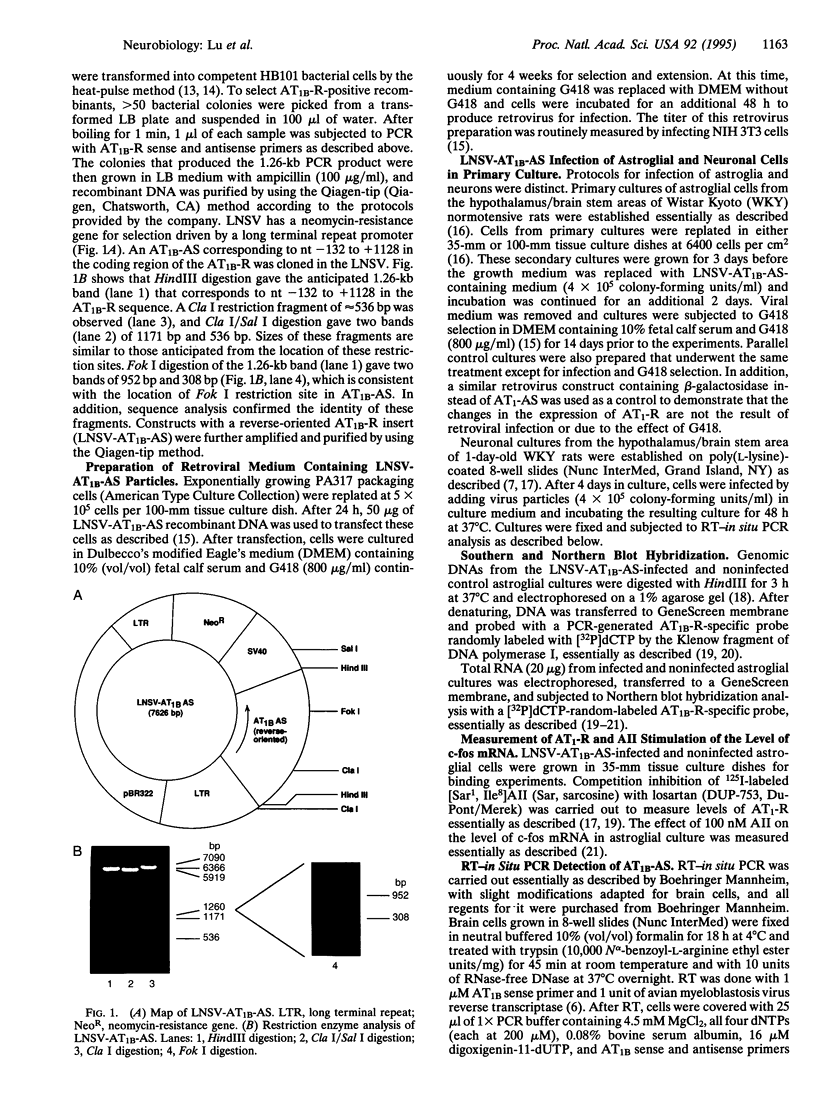
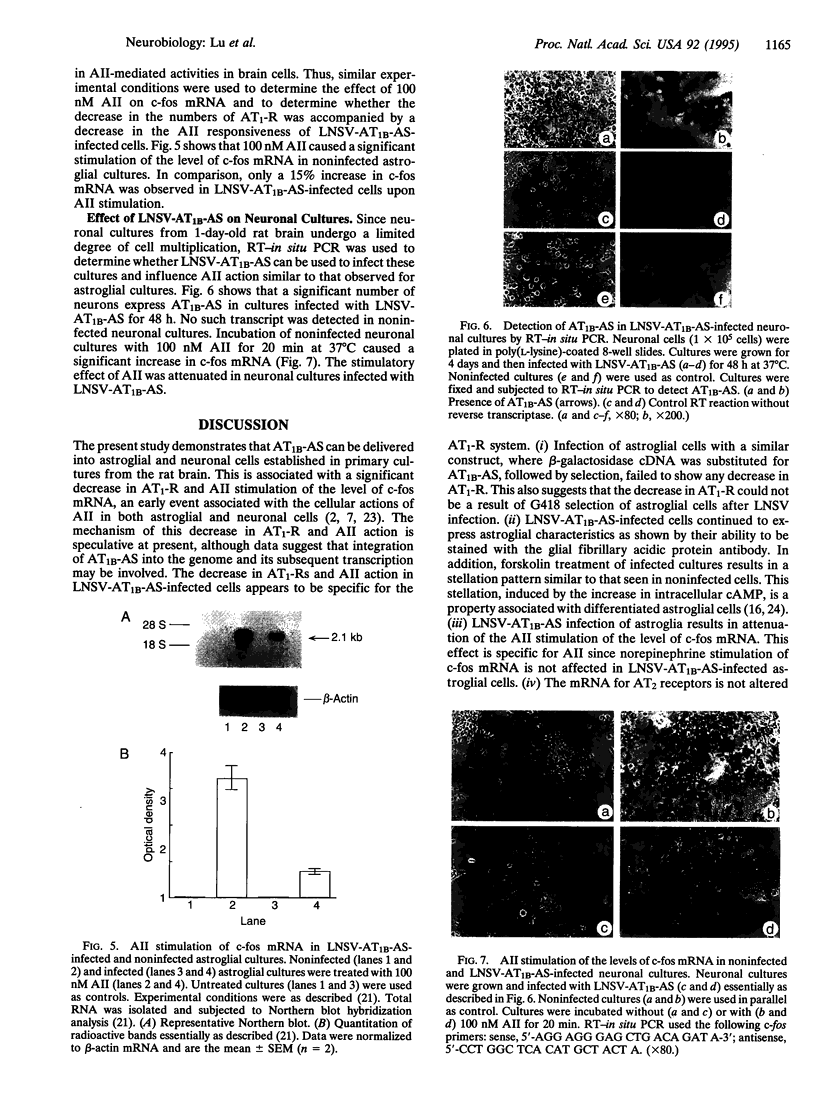
The AT1-R has been implicated in many cellular and physiological actions of angiotensin II (AII) in the brain. A retrovirus vector (LNSV) containing an AT1B-R antisense sequence (AT1B-AS) (termed LNSV-AT1B-AS) was constructed and used to determine the feasibility of using viral-mediated gene transfer to control AT1-Rs and AII actions in astroglial and neuronal cells in primary cultures from rat brain. Briefly, a 1.26-kb antisense sequence corresponding to nt -132 to +1128 of AT1-R cDNA was cloned into the LNSV vector, the vector was transfected into PA317 cells, and transfected cells were selected in G418. Incubation of brain cells with culture medium containing LNSV-AT1B-AS viral particles showed that AT1B-AS was integrated into the genome and transcribed in brain cells. This was associated with a significant decrease in AT1-Rs and in the AII-stimulated increase of c-fos mRNA, a measure of AT1-R function. These observations show that the AT1B-AS gene can be transferred into astroglial cells in culture by LNSV and that such a transfer inhibits AT1-Rs and the AII stimulation of cellular activities. In addition, the usefulness of this approach to study AII-dependent pathophysiology in primary neuronal cultures from brain, in particular, is established.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyurko R., Wielbo D., Phillips M. I. Antisense inhibition of AT1 receptor mRNA and angiotensinogen mRNA in the brain of spontaneously hypertensive rats reduces hypertension of neurogenic origin. Regul Pept. 1993 Dec 10;49(2):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(93)90438-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Rosman G. J. Improved retroviral vectors for gene transfer and expression. Biotechniques. 1989 Oct;7(9):980-2, 984-6, 989-90. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuovo G. J., Forde A., MacConnell P., Fahrenwald R. In situ detection of PCR-amplified HIV-1 nucleic acids and tumor necrosis factor cDNA in cervical tissues. Am J Pathol. 1993 Jul;143(1):40–48. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. A., Jr, Shiverick K. T., Ogilvie S., Buhi W. C., Raizada M. K. Angiotensin II induces secretion of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 and a tissue metalloprotease inhibitor-related protein from rat brain astrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1928–1932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. A., Jr, Shiverick K. T., Ogilvie S., Buhi W. C., Raizada M. K. Developmental expression of rat insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 by astrocytic glial cells in culture. Endocrinology. 1991 Aug;129(2):1066–1074. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-2-1066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens G. C., Boyd C. J. Expressing antisense P0 RNA in Schwann cells perturbs myelination. Development. 1991 Jun;112(2):639–649. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.2.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raizada M. K., Lu D., Tang W., Kurian P., Sumners C. Increased angiotensin II type-1 receptor gene expression in neuronal cultures from spontaneously hypertensive rats. Endocrinology. 1993 Apr;132(4):1715–1722. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.4.8462471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raizada M. K., Rydzewski B., Lu D., Sumners C. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor-mediated stimulation of c-fos gene expression in astroglial cultures. Am J Physiol. 1993 Oct;265(4 Pt 1):C1046–C1049. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.4.C1046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raizada M. K., Sumners C., Lu D. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor mRNA levels in the brains of normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Neurochem. 1993 May;60(5):1949–1952. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb13426.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai R. R., He P. F., Yang X. D., Ma L. Y., Guo Y. F., Reilly J. J., Moga C. N., Fluharty S. J. Intracerebroventricular administration of AT1 receptor antisense oligonucleotides inhibits the behavioral actions of angiotensin II. J Neurochem. 1994 May;62(5):2053–2056. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.62052053.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Hong G. F., Hill D. F., Petersen G. B. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 25;162(4):729–773. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90546-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steckelings U. M., Bottari S. P., Unger T. Angiotensin receptor subtypes in the brain. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Sep;13(9):365–368. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90110-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steckelings U., Lebrun C., Qadri F., Veltmar A., Unger T. Role of brain angiotensin in cardiovascular regulation. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1992;19 (Suppl 6):S72–S79. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199219006-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumners C., Tang W., Zelezna B., Raizada M. K. Angiotensin II receptor subtypes are coupled with distinct signal-transduction mechanisms in neurons and astrocytes from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7567–7571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verity A. N., Bredesen D., Vonderscher C., Handley V. W., Campagnoni A. T. Expression of myelin protein genes and other myelin components in an oligodendrocytic cell line conditionally immortalized with a temperature-sensitive retrovirus. J Neurochem. 1993 Feb;60(2):577–587. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03188.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang R. H., Jin H., Chen S. J., Wyss J. M., Oparil S. Blocking hypothalamic AT1 receptors lowers blood pressure in salt-sensitive rats. Hypertension. 1992 Dec;20(6):755–762. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.20.6.755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelezna B., Rydzewski B., Lu D., Olson J. A., Shiverick K. T., Tang W., Sumners C., Raizada M. K. Angiotensin-II induction of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene expression in astroglial cells of normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rat brain. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Dec;6(12):2009–2017. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.12.1491687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]