Abstract
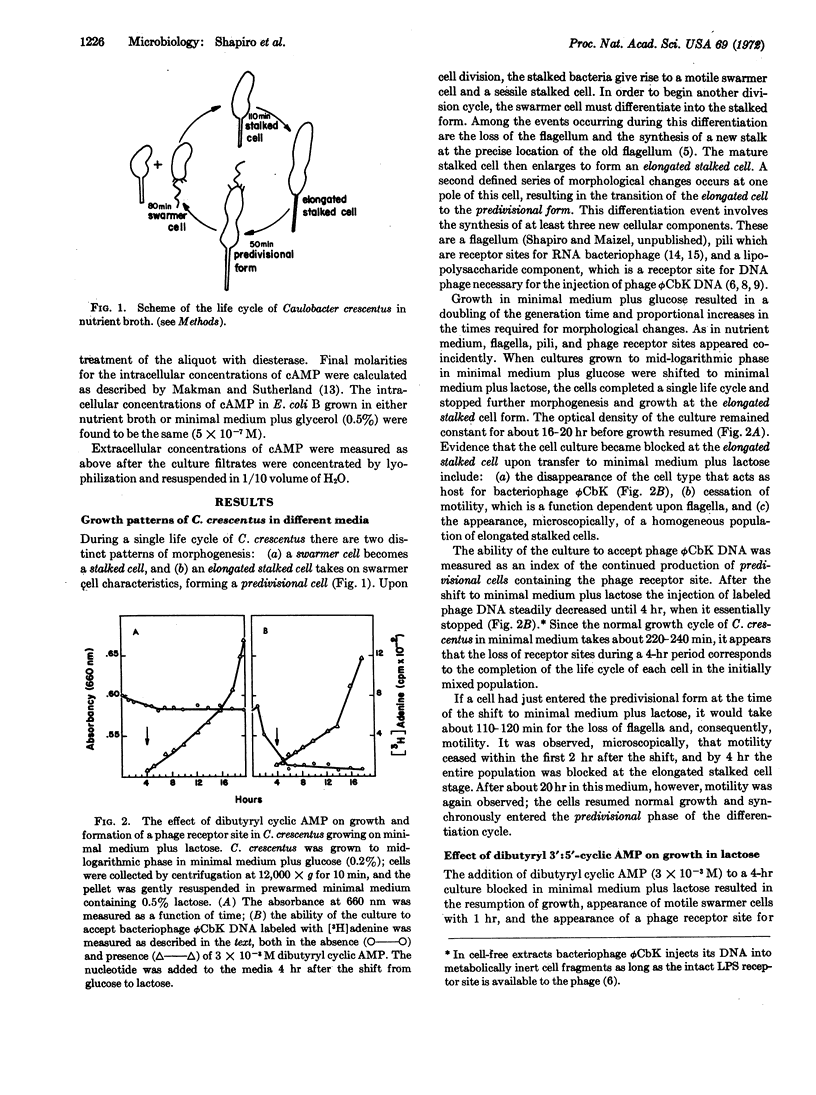
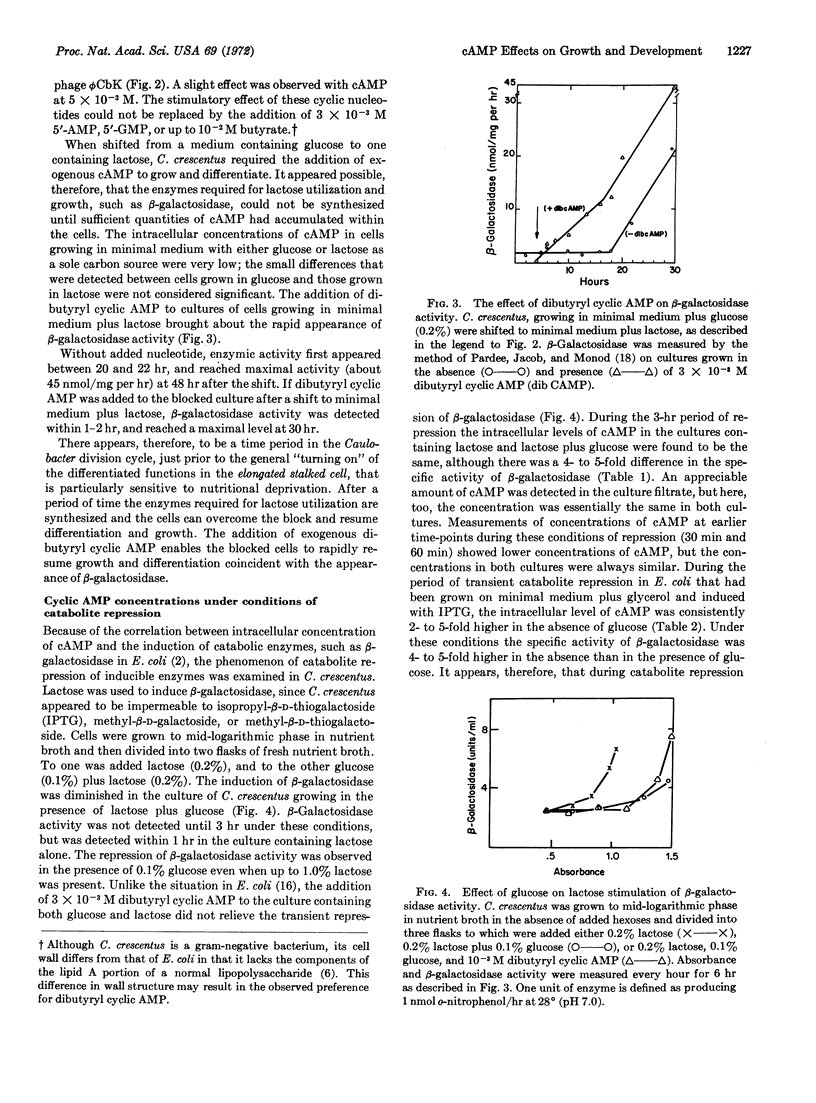
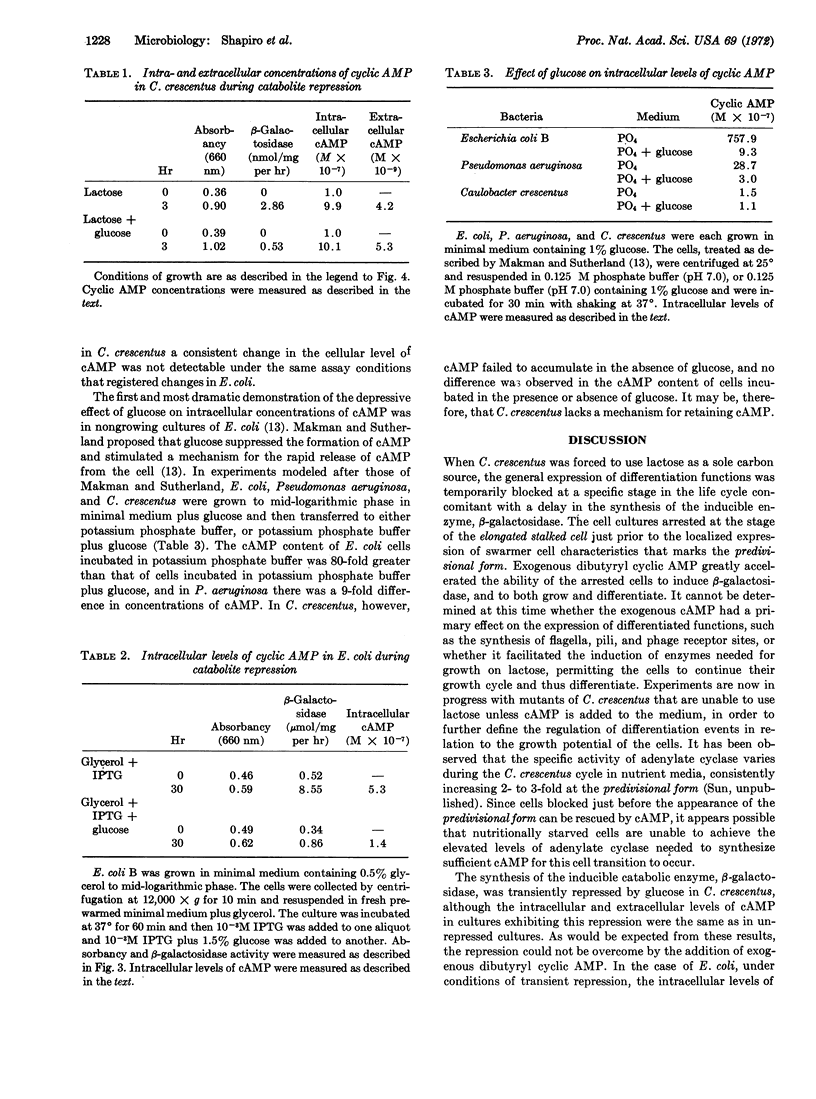
Caulobacter crescentus goes through a series of morphological changes during its life cycle, including the coincident expression of synthesis of flagella, pili, and receptor sites for DNA bacteriophage. Upon transfer of a mixed population of cells to medium containing lactose as the sole carbon source, these changes were blocked for about 20 hr until β-galactosidase activity became apparent. The addition of dibutyryl cyclic AMP to the blocked cultures brought about the resumption of cell differentiation, growth, and the appearance of β-galactosidase activity within 1 hr. Unlike Escherichia coli, the intracellular and extracellular concentrations of cyclic AMP in C. crescentus did not vary under several growth conditions, including catabolite repression. It would appear, therefore, that although there is an effect of cyclic AMP on the induction of β-galactosidase and differentiation in C. crescentus, regulation of these processes occurs without consistent changes in the cellular level of this nucleotide.
Keywords: β-galactosidase, Escherichia coli, cyclic AMP, catabolite repression
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agabian-Keshishian N., Shapiro L. Bacterial differentiation and phage infection. Virology. 1971 Apr;44(1):46–53. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90151-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agabian-Keshishian N., Shapiro L. Stalked bacteria: properties of deoxriybonucleic acid bacteriophage phiCbK. J Virol. 1970 Jun;5(6):795–800. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.6.795-800.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appleman M. M., Birnbaumer L., Torres H. N. Factors affecting the activity of muscle glycogen synthetase. 3. The reaction with adenosine triphosphate Mg++, and cyclic 3'5'-adenosine monophosphate. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Sep 26;116(1):39–43. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN-BAZIRE G., SISTROM W. R., STANIER R. Y. Kinetic studies of pigment synthesis by non-sulfur purple bacteria. J Cell Physiol. 1957 Feb;49(1):25–68. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030490104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Crombrugghe B., Perlman R. L., Varmus H. E., Pastan I. Regulation of inducible enzyme synthesis in Escherichia coli by cyclic adenosine 3', 5'-monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 10;244(21):5828–5835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobrogosz W. J., Hamilton P. B. The role of cyclic AMP in chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jan 22;42(2):202–207. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90088-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. A protein binding assay for adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):305–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goren E. N., Rosen O. M. The effect of nucleotides and a nondialyzable factor on the hydrolysis of cyclic AMP by a cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase from beef heart. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Feb;142(2):720–723. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90540-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAKMAN R. S., SUTHERLAND E. W. ADENOSINE 3',5'-PHOSPHATE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1309–1314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POINDEXTER J. S. BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES AND CLASSIFICATION OF THE CAULOBACTER GROUP. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Sep;28:231–295. doi: 10.1128/br.28.3.231-295.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Perlman R. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate in bacteria. Science. 1970 Jul 24;169(3943):339–344. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3943.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robison G. A., Butcher R. W., Sutherland E. W. Cyclic AMP. Annu Rev Biochem. 1968;37:149–174. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.37.070168.001053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J. M. Observations on the adsorption of Caulobacter bacteriophages containing ribonucleic acid. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Nov;45(2):347–353. doi: 10.1099/00221287-45-2-347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro L., Agabian-Keshishian N., Bendis I. Bacterial differentiation. Science. 1971 Sep 3;173(4000):884–892. doi: 10.1126/science.173.4000.884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro L., Agabian-Keshishian N. Specific Assay for Differentiation in the Stalked Bacterium Caulobacter crescentus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):200–203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota T., Gots J. S. Requirement of adenosine 3', 5'-cyclic phosphate for flagella formation in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1970 Aug;103(2):513–516. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.2.513-516.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


