Abstract
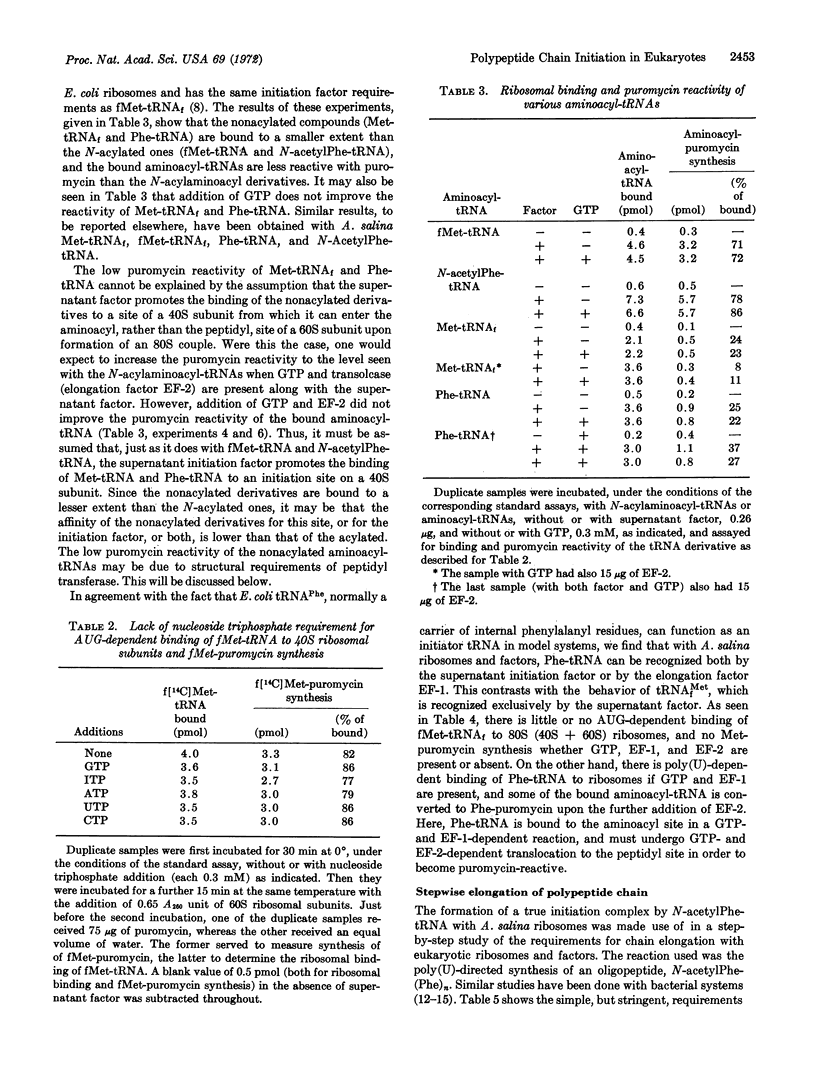
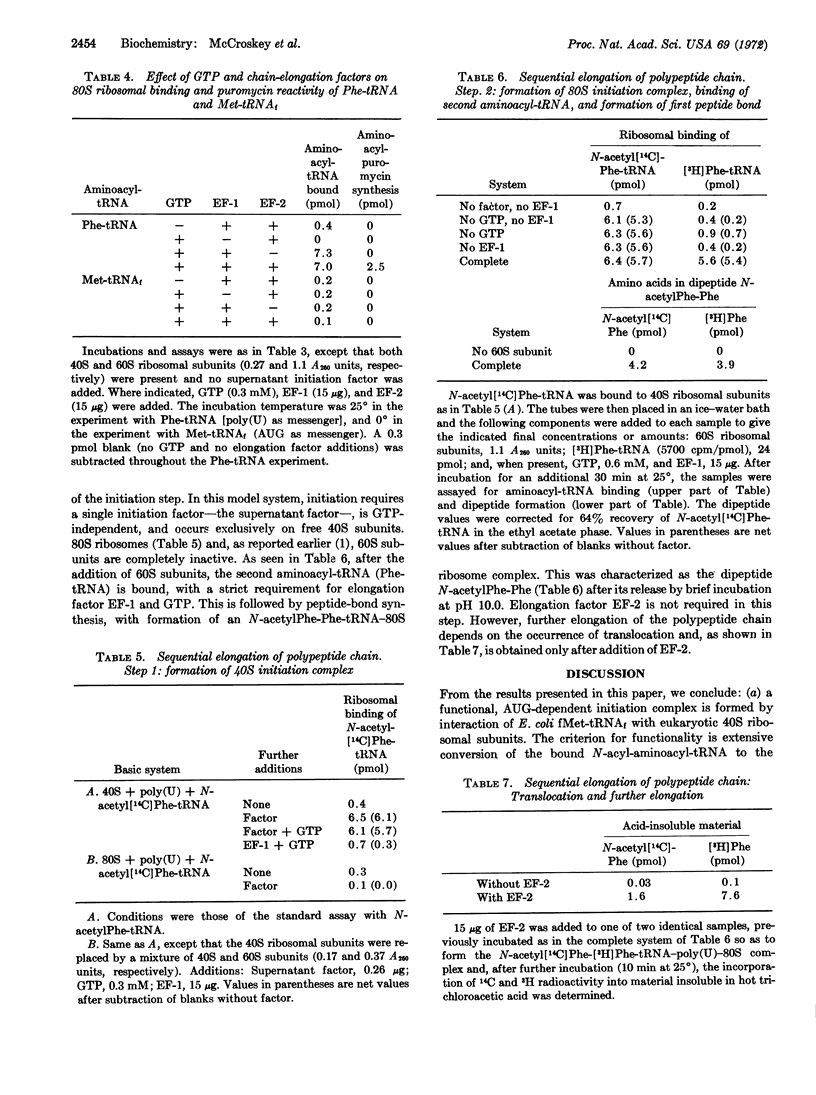
The supernatant initiation factor from Artemia salina embryos promotes, besides the AUG-dependent binding of fMet-tRNAf, the poly(U)-dependent binding of N-acetylPhe-tRNA to 40S ribosomal subunits; the bound N-acylaminoacyl-tRNA reacts directly with puromycin upon addition of 60S subunits. Both the binding reaction and the synthesis of N-acylaminoacyl-puromycin occur in the absence of GTP or other ribonucleoside triphosphates. To a smaller extent, the factor also mediates the 40S ribosomal binding of Met-tRNAf and Phe-tRNA; in this case, the bound aminoacyl-tRNA is less reactive with puromycin. After the poly(U)- and supernatant factor-dependent binding of N-acetylPhe-tRNA to 40S subunits at low Mg2+ concentration, binding of a second aminoacyl-tRNA (Phe-tRNA), with ensuing formation of the first peptide bond, is dependent upon the addition of the 60S subunit, elongation factor EF-1, and GTP. Further growth of the polypeptide chain requires translocation and is, therefore, dependent upon the addition of elongation factor EF-2. As with the Escherichia coli system, once requirements for translation of the third codon have been met, no further additions are necessary for elongation of a peptide chain.
Keywords: Artemia salina, embryos, cysts, brine-shrimp eggs, poly(U)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ciferri O., Parisi B., Perani A., Grandi M. Different specificity of yeast transfer enzymes for Escherichia coli ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1968 Nov 14;37(3):529–533. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crystal R. G., Anderson W. F. Initiation of hemoglobin synthesis: comparison of model reactions that use artificial templates with those using natural messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):706–711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erbe R. W., Leder P. Initiation and protein synthesis: translation of di- and tri-codon messengers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jun 10;31(5):798–803. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90633-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erbe R. W., Nau M. M., Leder P. Translation and translocation of defined RNA messengers. J Mol Biol. 1969 Feb 14;39(3):441–460. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasior E., Moldave K. Evidence for a soluble protein factor specific for the interaction between aminoacylated transfer RNA's and the 40 s subunit of mammalian ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1972 May 28;66(3):391–402. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90422-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasior E., Rao P., Moldave K. The interaction of aminoacyl-tRNA and N-acylaminoacyl-tRNA with ribosomes and ribosomal subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 16;254(2):331–340. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90841-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Beaudet A. L., Caskey C. T. Peptide chain termination with mammalian release factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):99–106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haenni A. L., Chapeville F. The behaviour of acetylphenylalanyl soluble ribonucleic acid in polyphenylalanine synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jan 18;114(1):135–148. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haenni A. L., Lucas-Lenard J. Stepwise synthesis of a tripeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1363–1369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krisko I., Gordon J., Lipmann F. Studies on the interchangeability of one of the mammalian and bacterial supernatant factors in protein biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6117–6123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leader D. P., Klein-Bremhaar H., Wool I. G. Distribution of initiation factors in cell fractions from mammalian tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 14;46(1):215–224. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90652-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leader D. P., Wool I. G. Partial purification and characterization of an initiation factor from rat liver which promotes the binding of phenylalanyl-tRNA to 40 -S ribosomal subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 24;262(3):360–370. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90274-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Nau M. M. Initiation of protein synthesis. 3. Factor-GTP-codon-dependent binding of F-met-tRNA to ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Aug;58(2):774–781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.2.774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leis J. P., Keller E. B. Protein chain initiation by methionyl-tRNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jul 27;40(2):416–421. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas-Lenard J., Lipmann F. Initiation of polyphenylalanine synthesis by N-acetylphenylalanyl-SRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Apr;57(4):1050–1057. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.4.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas-Lenard J. Protein biosynthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:409–448. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.002205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A. Tobacco mosaic virus ribonucleic acid-dependent amino acid incorporation in a wheat embryo system in vitro. Formation of a ribosome-messenger "initiation" complex. J Biol Chem. 1970 Mar 10;245(5):962–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monro R. E., Cerná J., Marcker K. A. Ribosome-catalyzed peptidyl transfer: substrate specificity at the P-site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Nov;61(3):1042–1049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.3.1042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravel J. M., Shorey R. L., Garner C. W., Dawkins R. C., Shive W. The role of an aminoacyl-tRNA-GTP-protein complex in polypeptide synthesis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:321–330. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafritz D. A., Laycock D. G., Crystal R. G., Anderson W. F. Requirement for GTP in the initiation process on reticulocyte ribosomes and ribosomal subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2246–2251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafritz D. A., Prichard P. M., Gilbert J. M., Merrick W. C., Anderson W. F. Separation of reticulocyte initiation factor M 2 activity into two components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):983–987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez D., Battaner E., Neth R., Heller G., Monro R. E. The function of 80 S ribosomal subunits and effects of some antibiotics. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:369–375. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M., Ochoa S. A supernatant factor involved in initiation complex formation with eukaryotic ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3059–3063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M., Ochoa S. Polypeptide chain initiation in eukaryotes: functional identity of supernatant factor from various sources. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1796–1799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


