Abstract
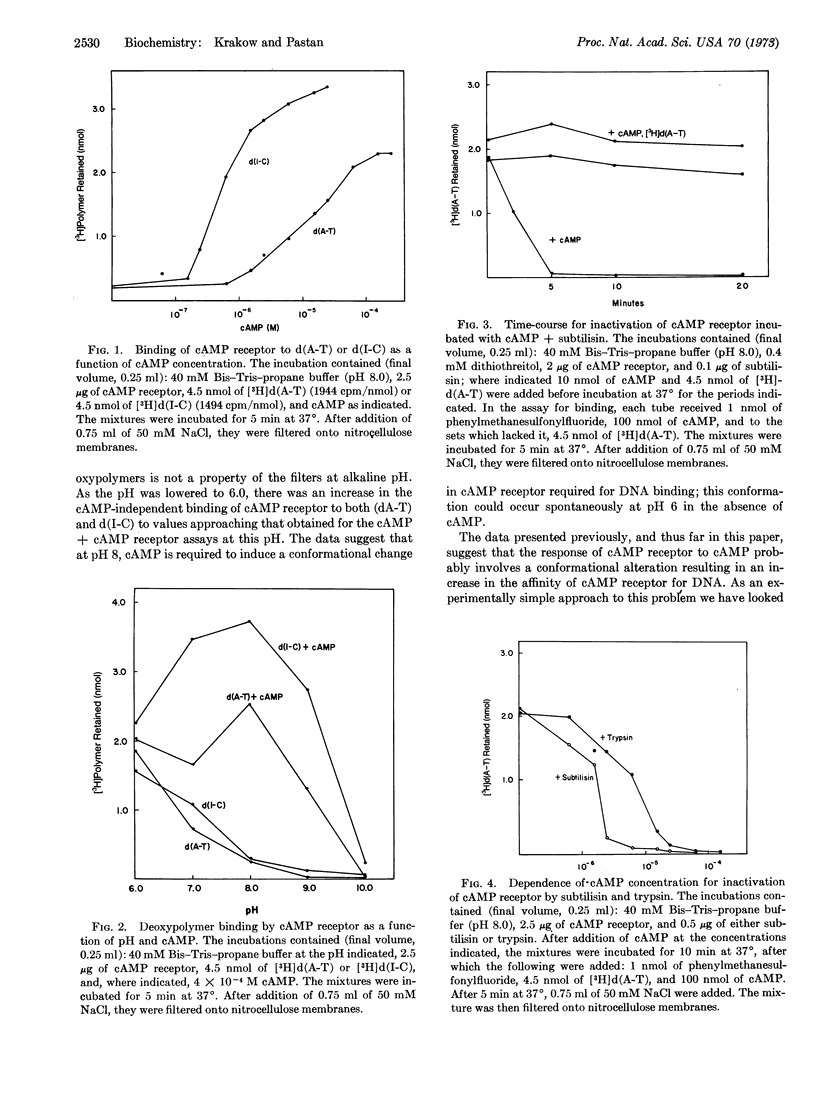
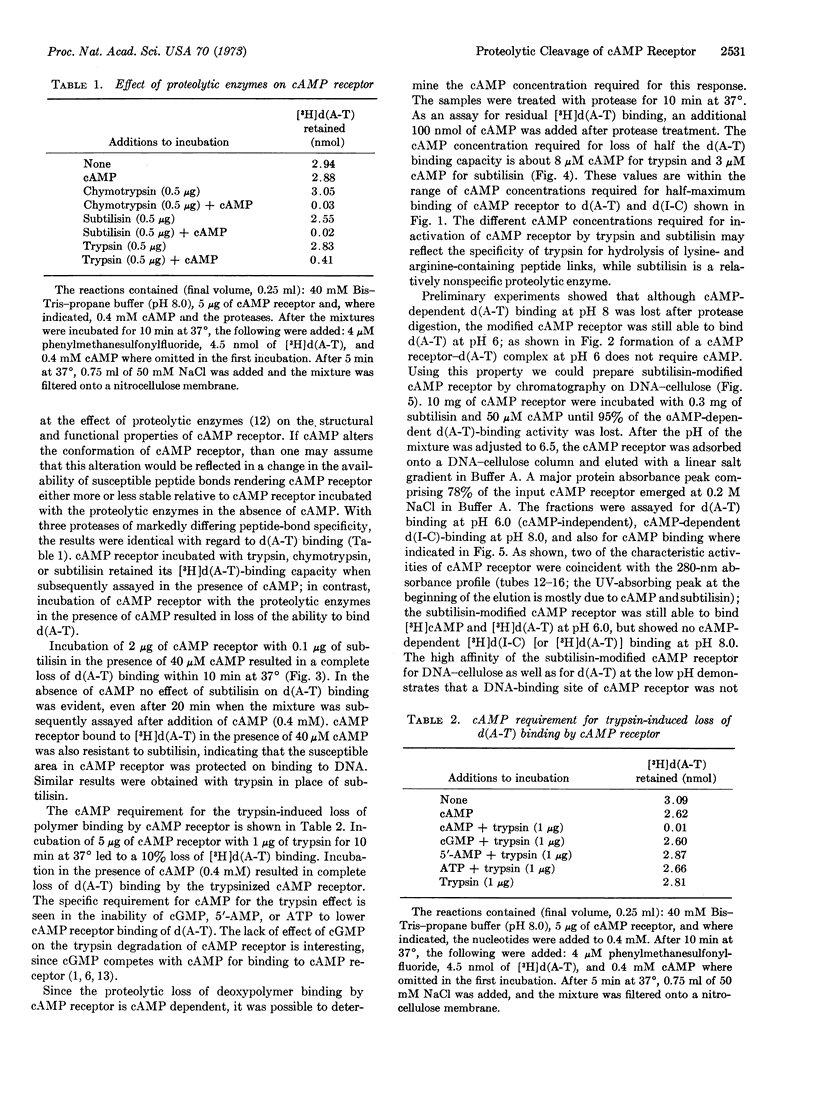
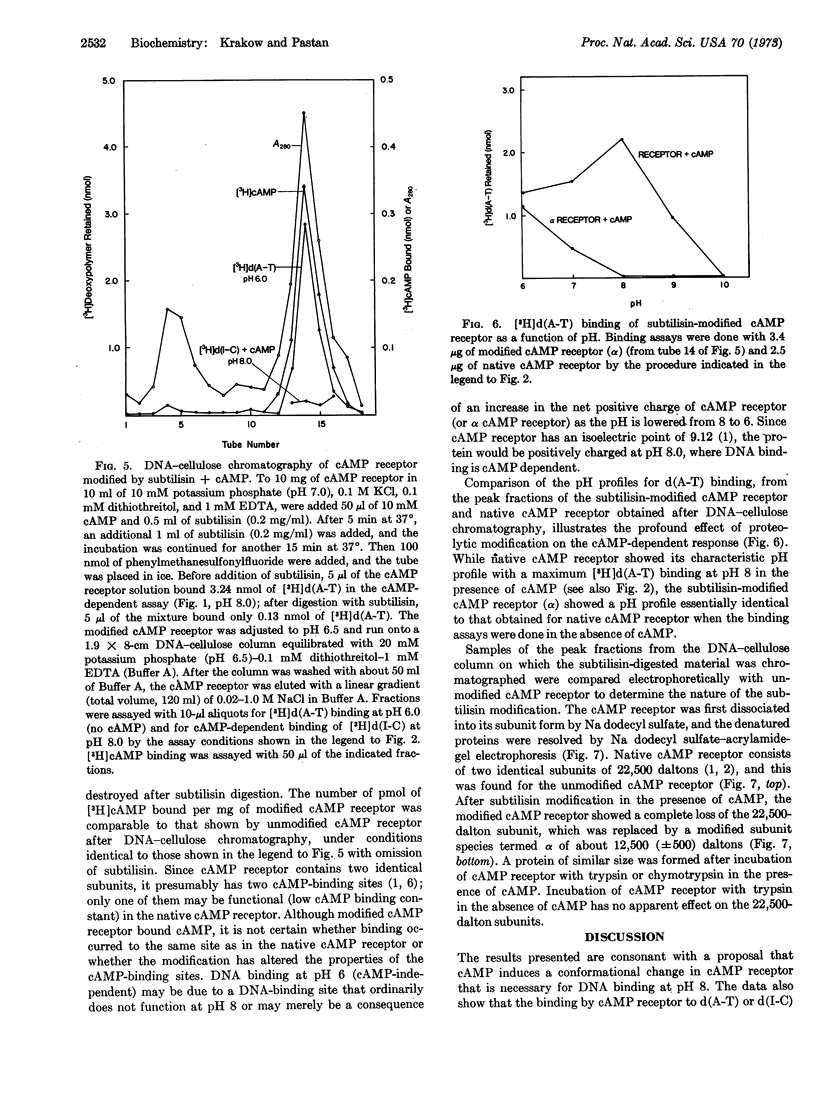
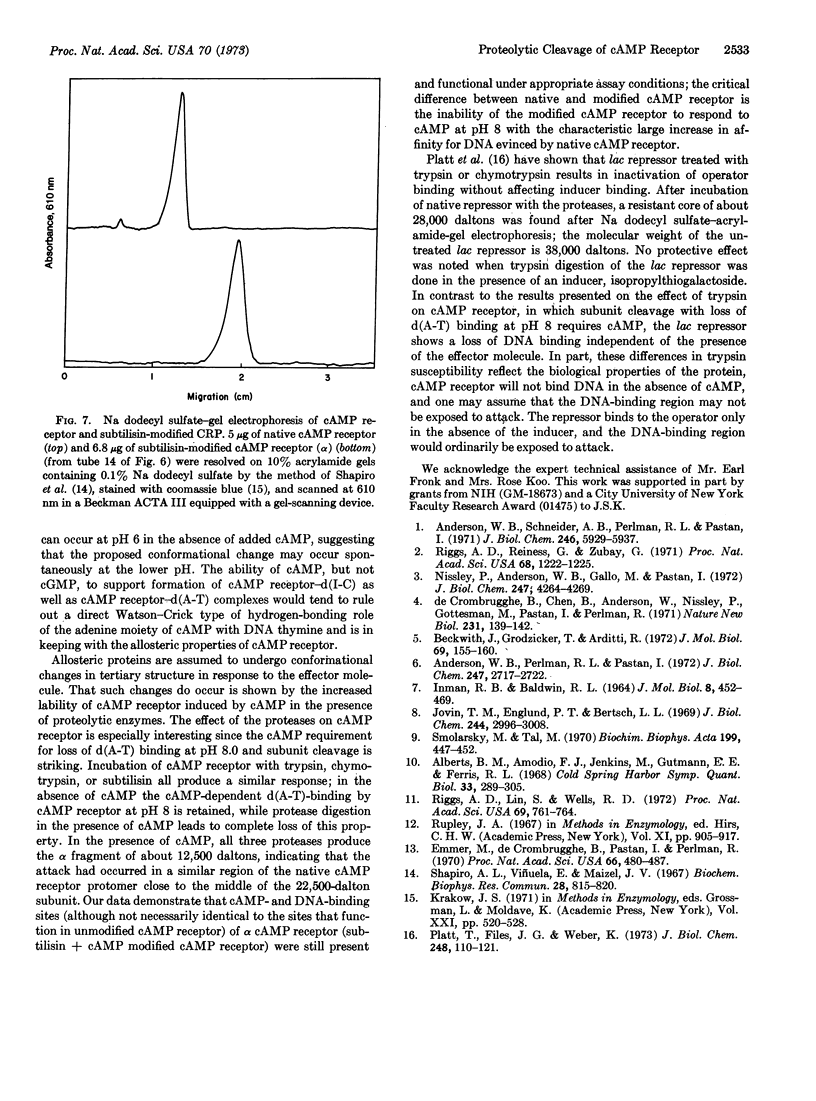
The cAMP receptor requires cAMP for DNA binding at pH 8.0 but shows cAMP-independent DNA binding at pH 6.0. Incubation of the cAMP receptor with proteolytic enzymes in the presence of cAMP results in loss of DNA-binding ability at pH 8, while it is still able to bind cAMP and DNA at pH 6. Incubation with proteolytic enzyme in the absence of cAMP does not affect the DNA-binding properties of the cAMP receptor. After proteolysis in the presence of cAMP, analysis by sodium dodecyl sulfateacrylamide-gel electrophoresis shows that the 22,500-dalton subunit characteristic of the untreated protein has been completely replaced by a 12,500-dalton fragment.
Keywords: binding assay, DNA-cellulose chromatography, conformation
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts B. M., Amodio F. J., Jenkins M., Gutmann E. D., Ferris F. L. Studies with DNA-cellulose chromatography. I. DNA-binding proteins from Escherichia coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:289–305. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson W. B., Perlman R. L., Pastan I. Effect of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate analogues on the activity of the cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate receptor in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2717–2722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckwith J., Grodzicker T., Arditti R. Evidence for two sites in the lac promoter region. J Mol Biol. 1972 Aug 14;69(1):155–160. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90031-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Crombrugghe B., Chen B., Anderson W., Nissley P., Gottesman M., Pastan I., Perlman R. Lac DNA, RNA polymerase and cyclic AMP receptor protein, cyclic AMP, lac repressor and inducer are the essential elements for controlled lac transcription. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 2;231(22):139–142. doi: 10.1038/newbio231139a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmer M., deCrombrugghe B., Pastan I., Perlman R. Cyclic AMP receptor protein of E. coli: its role in the synthesis of inducible enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):480–487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INMAN R. B., BALDWIN R. L. HELIX--RANDOM COIL TRANSITIONS IN DNA HOMOPOLYMER PAIRS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Apr;8:452–469. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jovin T. M., Englund P. T., Bertsch L. L. Enzymatic synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. XXVI. Physical and chemical studies of a homogeneous deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 10;244(11):2996–3008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissley P., Anderson W. B., Gallo M., Pastan I., Perlman R. L. The binding of cyclic adenosine monophosphate receptor to deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 10;247(13):4264–4269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T., Files J. G., Weber K. Lac repressor. Specific proteolytic destruction of the NH 2 -terminal region and loss of the deoxyribonucleic acid-binding activity. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):110–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Lin S., Wells R. D. Lac repressor binding to synthetic DNAs of defined nucleotide sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):761–764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Reiness G., Zubay G. Purification and DNA-binding properties of the catabolite gene activator protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1222–1225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolarsky M., Tal M. Novel method for measuring polyuridylic acid binding to ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 18;199(2):447–452. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90087-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


