Abstract
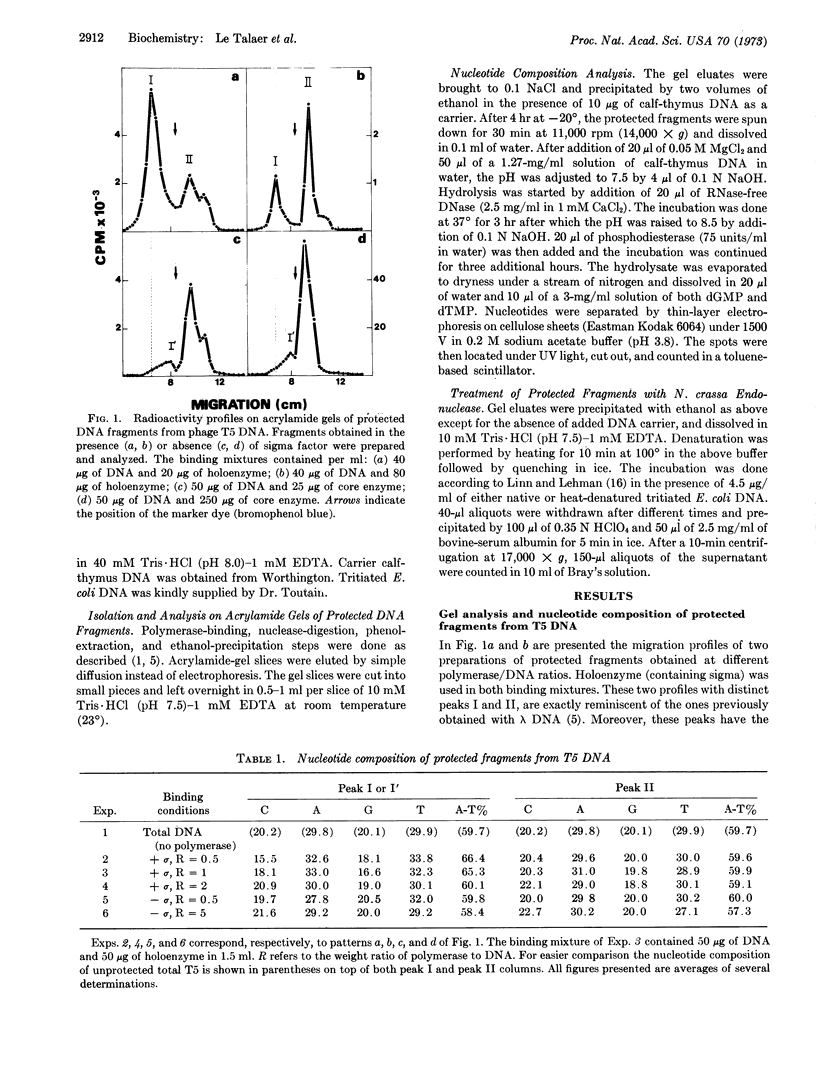
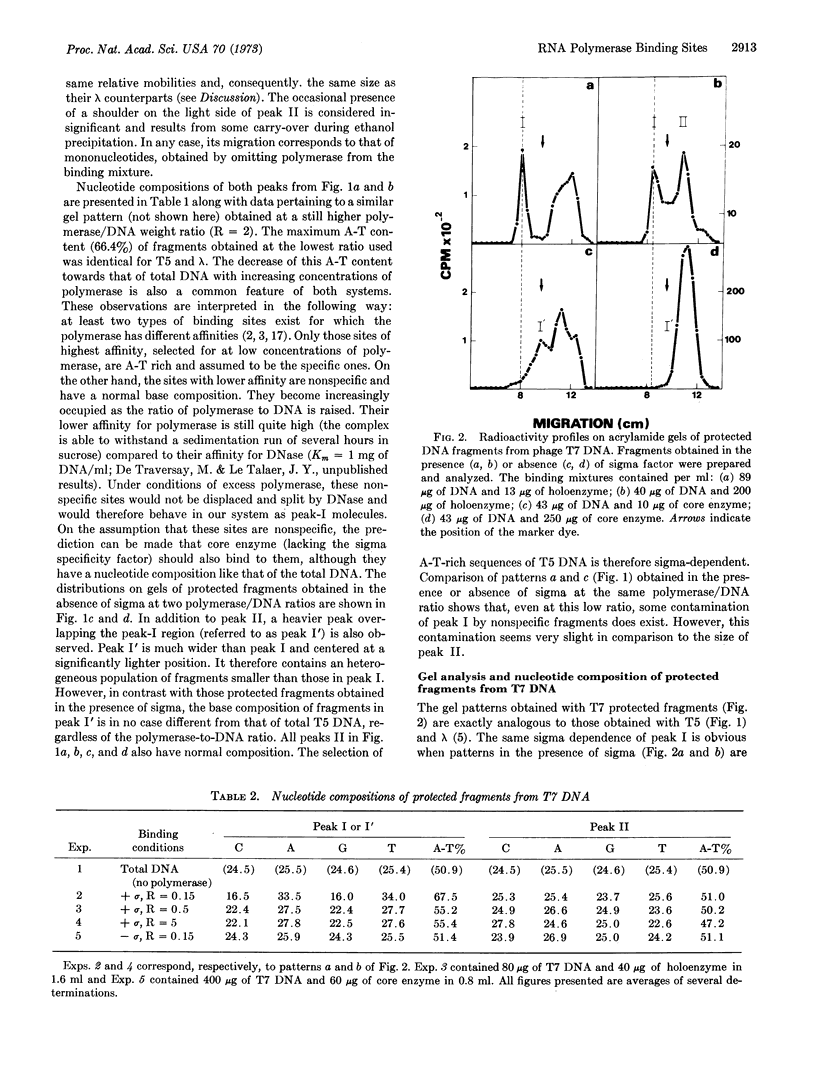
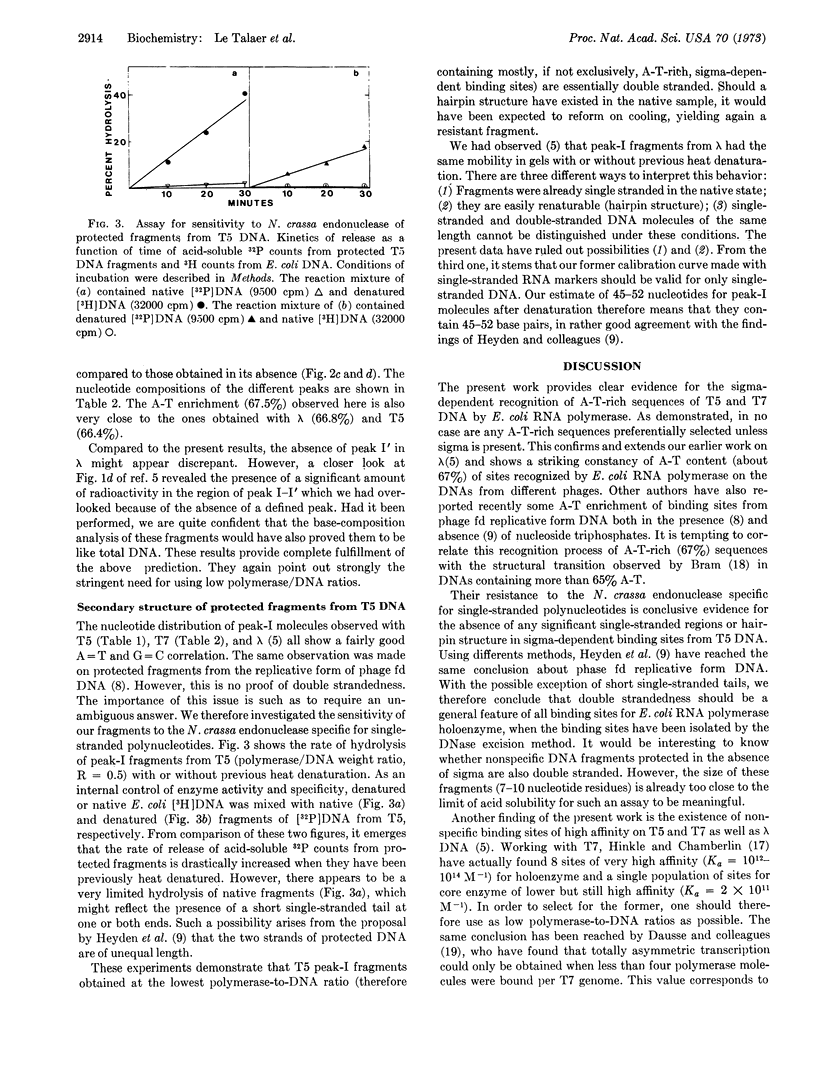
Previous isolation and analysis of E. coli RNA polymerase (EC 2.7.7.6) binding sites on λ DNA had demonstrated the existence of a sigma-dependent process of recognition of A-T-rich DNA sequences. We have now extended this finding to T5 and T7 DNA and häve provided evidence for the double-strandedness of the isolated binding sites. The possible equation of these sites to the genetically defined promoters is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babinet C. A new method for the purification of RNA-polymerase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Mar 21;26(6):639–644. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(67)80119-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bautz E. K., Bautz F. A. Initiation of RNA synthesis: the function of sigma in the binding of RNA polymerase to promoter sites. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1219–1222. doi: 10.1038/2261219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Dahlberg J. E., Boettiger J. K., Fiandt M., Szybalski W. Distance from a promoter mutation to an RNA synthesis startpoint on bacteriophage lambda DNA. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jun 21;237(77):232–236. doi: 10.1038/newbio237232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Dahlberg J. E. RNA synthesis startpoints in bacteriophage lambda: are the promoter and operator transcribed? Nat New Biol. 1972 Jun 21;237(77):227–232. doi: 10.1038/newbio237227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram S. The function of the structure of DNA in chromosomes. Biochimie. 1972;54(8):1005–1011. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(72)80051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R. A new method for the large scale purification of Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6160–6167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dausse J. P., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Interaction of RNA polymerase from Escherichia coli with DNA. Selection of initiation sites on T 7 DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Mar 15;26(1):43–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01737.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyden B., Nüsslein C., Schaller H. Single RNA polymerase binding site isolated. Nat New Biol. 1972 Nov 1;240(96):9–12. doi: 10.1038/newbio240009a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle D. C., Chamberlin M. J. Studies of the binding of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase to DNA. I. The role of sigma subunit in site selection. J Mol Biol. 1972 Sep 28;70(2):157–185. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90531-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones O. W., Berg P. Studies on the binding of RNA polymerase to polynucleotides. J Mol Biol. 1966 Dec 28;22(2):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90126-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANNI Y. T. Invasion by bacteriophage T5. III. Stages revealed by changes in susceptibility of early complexes to abortive infection. Virology. 1961 Oct;15:127–135. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90229-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINN S., LEHMAN I. R. AN ENDONUCLEASE FROM NEUROSPORA CRASSA SPECIFIC FOR POLYNUCLEOTIDES LACKING AN ORDERED STRUCTURE. I. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF THE ENZYME. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1287–1293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Talaer J. Y., Jeanteur P. Discrimination by tRNA of two types of isolated binding sites for E. Coli RNA-polymerase on phage lambda DNA. FEBS Lett. 1972 Dec 15;28(3):305–308. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80737-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Talaer J. Y., Jeanteur P. Preferential binding of E. coli RNA-polymerase to A-T rich sequences of bacteriophage lambda DNA. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jan 30;12(5):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Talaer J. Y., Jeanteur P. Purification and base composition analysis of phage lambda early promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3211–3215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LePecq J. B., Baldwin R. L. The starting point and direction of lambda DNA replication. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:609–620. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto T., Sugiura M., Takanami M. RNA polymerase binding sites of phage fd replicative form DNA. Nat New Biol. 1972 May 24;237(73):108–109. doi: 10.1038/newbio237108a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saucier J. M., Wang J. C. Angular alteration of the DNA helix by E. coli RNA polymerase. Nat New Biol. 1972 Oct 11;239(93):167–170. doi: 10.1038/newbio239167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stead N. W., Jones O. W. Stability of RNA polymerase--DNA complexes. J Mol Biol. 1967 May 28;26(1):131–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90267-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


