Abstract
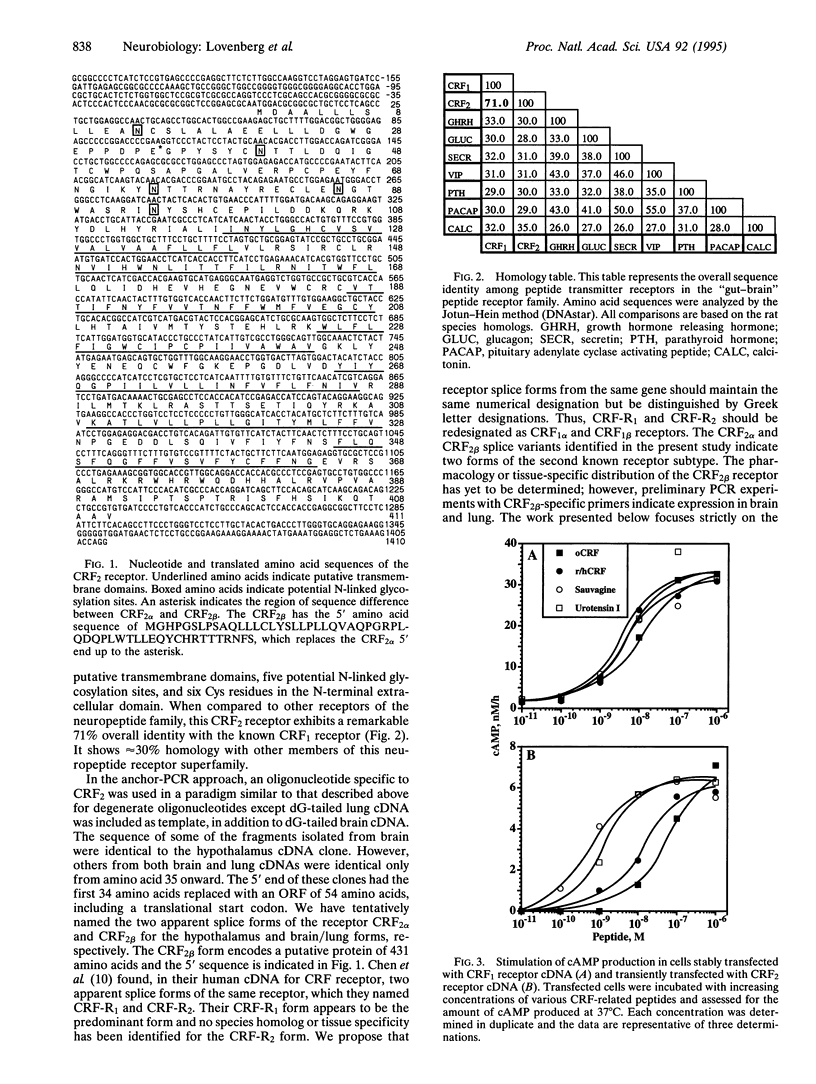
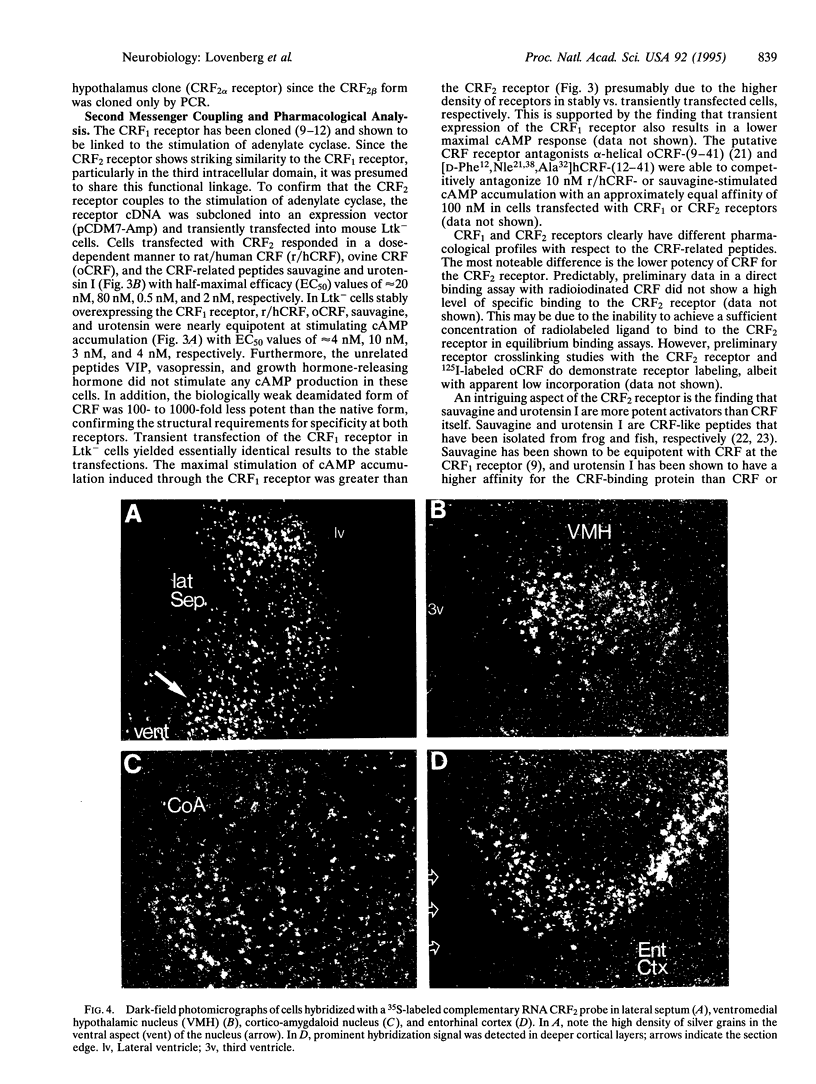
The present study reports the isolation of a cDNA clone that encodes a second member of the corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) receptor family, designated as the CRF2 receptor. The cDNA was identified using oligonucleotides of degenerate sequence in a PCR paradigm. A PCR fragment obtained from rat brain was utilized to isolate a full-length cDNA from a rat hypothalamus cDNA library that encoded a 411-amino acid protein with approximately 70% identity to the known CRF1 receptor over the entire coding region. When expressed in mouse Ltk- cells, this receptor stimulates cAMP production in response to CRF and known CRF-like agonists. CRF and the nonmammalian CRF-related peptides sauvagine and urotensin I stimulate adenylate cyclase activity in a dose-dependent manner with a rank order of potency different from that of the CRF1 receptor: sauvagine > urotensin > or = rat/human CRF > ovine CRF. Tissue distribution analysis of the mRNAs by reverse transcriptase-PCR shows CRF2 receptor mRNA is present in rat brain and detectable in lung and heart. In situ hybridization studies indicate specific expression within the brain in the ventromedial nuclei of the hypothalamus, the lateral septum, the amygdala, and entorhinal cortex, but there is unremarkable expression in the pituitary. An additional splice variant of the CRF2 receptor with a different N-terminal domain has been identified by PCR, encoding a putative protein of 431 amino acids. Thus, the data demonstrate the presence of another functional CRF receptor, with significant differences in the pharmacological profile and tissue distribution from the CRF1 receptor, which would predict important functional differences between the two receptors.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida O. F., Hassan A. H., Holsboer F. Intrahypothalamic neuroendocrine actions of corticotropin-releasing factor. Ciba Found Symp. 1993;172:151–172. doi: 10.1002/9780470514368.ch8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battaglia G., Webster E. L., De Souza E. B. Characterization of corticotropin-releasing factor receptor-mediated adenylate cyclase activity in the rat central nervous system. Synapse. 1987;1(6):572–581. doi: 10.1002/syn.890010610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behan D. P., Potter E., Sutton S., Fischer W., Lowry P. J., Vale W. W. Corticotropin-releasing factor-binding protein. A putative peripheral and central modulator of the CRF family of neuropeptides. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 Oct 29;697:1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb49918.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton D. R., Hoffman D. K., Lederis K., Rivier J. A comparison of the behavioral effects of CRF, sauvagine and urotensin I. Brain Res. 1984 Jun 25;304(2):201–205. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90322-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. P., Pearse R. V., 2nd, O'Connell S., Rosenfeld M. G. Identification of a seven transmembrane helix receptor for corticotropin-releasing factor and sauvagine in mammalian brain. Neuron. 1993 Dec;11(6):1187–1195. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90230-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R., Lewis K. A., Perrin M. H., Vale W. W. Expression cloning of a human corticotropin-releasing-factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):8967–8971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.8967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn A. J., Berridge C. W. Physiological and behavioral responses to corticotropin-releasing factor administration: is CRF a mediator of anxiety or stress responses? Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1990 May-Aug;15(2):71–100. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(90)90012-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlander M. G., Lovenberg T. W., Baron B. M., de Lecea L., Danielson P. E., Racke M., Slone A. L., Siegel B. W., Foye P. E., Cannon K. Two members of a distinct subfamily of 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors differentially expressed in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3452–3456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold P. W., Loriaux D. L., Roy A., Kling M. A., Calabrese J. R., Kellner C. H., Nieman L. K., Post R. M., Pickar D., Gallucci W. Responses to corticotropin-releasing hormone in the hypercortisolism of depression and Cushing's disease. Pathophysiologic and diagnostic implications. N Engl J Med. 1986 May 22;314(21):1329–1335. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198605223142101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederis K., Letter A., McMaster D., Moore G., Schlesinger D. Complete amino acid sequence of urotensin I, a hypotensive and corticotropin-releasing neuropeptide from Catostomus. Science. 1982 Oct 8;218(4568):162–165. doi: 10.1126/science.6981844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libert F., Parmentier M., Lefort A., Dinsart C., Van Sande J., Maenhaut C., Simons M. J., Dumont J. E., Vassart G. Selective amplification and cloning of four new members of the G protein-coupled receptor family. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):569–572. doi: 10.1126/science.2541503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovenberg T. W., Erlander M. G., Baron B. M., Racke M., Slone A. L., Siegel B. W., Craft C. M., Burns J. E., Danielson P. E., Sutcliffe J. G. Molecular cloning and functional expression of 5-HT1E-like rat and human 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2184–2188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemeroff C. B., Owens M. J., Bissette G., Andorn A. C., Stanley M. Reduced corticotropin releasing factor binding sites in the frontal cortex of suicide victims. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1988 Jun;45(6):577–579. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1988.01800300075009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens M. J., Nemeroff C. B. Physiology and pharmacology of corticotropin-releasing factor. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Dec;43(4):425–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin M. H., Donaldson C. J., Chen R., Lewis K. A., Vale W. W. Cloning and functional expression of a rat brain corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) receptor. Endocrinology. 1993 Dec;133(6):3058–3061. doi: 10.1210/endo.133.6.8243338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter E., Behan D. P., Linton E. A., Lowry P. J., Sawchenko P. E., Vale W. W. The central distribution of a corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF)-binding protein predicts multiple sites and modes of interaction with CRF. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):4192–4196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.4192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter E., Sutton S., Donaldson C., Chen R., Perrin M., Lewis K., Sawchenko P. E., Vale W. Distribution of corticotropin-releasing factor receptor mRNA expression in the rat brain and pituitary. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 13;91(19):8777–8781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.19.8777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivier J., Rivier C., Vale W. Synthetic competitive antagonists of corticotropin-releasing factor: effect on ACTH secretion in the rat. Science. 1984 May 25;224(4651):889–891. doi: 10.1126/science.6326264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenzel-Poore M. P., Heldwein K. A., Stenzel P., Lee S., Vale W. W. Characterization of the genomic corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) gene from Xenopus laevis: two members of the CRF family exist in amphibians. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Oct;6(10):1716–1724. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.10.1448118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vita N., Laurent P., Lefort S., Chalon P., Lelias J. M., Kaghad M., Le Fur G., Caput D., Ferrara P. Primary structure and functional expression of mouse pituitary and human brain corticotrophin releasing factor receptors. FEBS Lett. 1993 Nov 29;335(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80427-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]