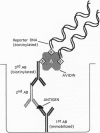
Abstract
Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) is an important mediator in many pathophysiologic processes, both in the central nervous system (CNS) and in the periphery. For this study, we have designed a very sensitive immuno-PCR detection system to investigate the time course of TNF-alpha induction in the rat cerebrospinal fluid after intracerebroventricular administration of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Immuno-PCR combines antibody specificity with PCR signal amplification and provides a sensitivity in the picomolar range. The enhanced sensitivity of this assay allowed the detection of TNF-alpha in the cerebrospinal fluid as early as 15 min after intracerebroventricular administration of LPS. The present results suggest that the ventricular compartment of the CNS, although confined within the blood-brain barrier, is highly responsive to proinflammatory stimuli such as LPS administration. Insight into the molecular mechanisms underlying this compartmentalization could be key to the pathology and treatment of many CNS diseases, especially the meningitides.
Full text
PDF
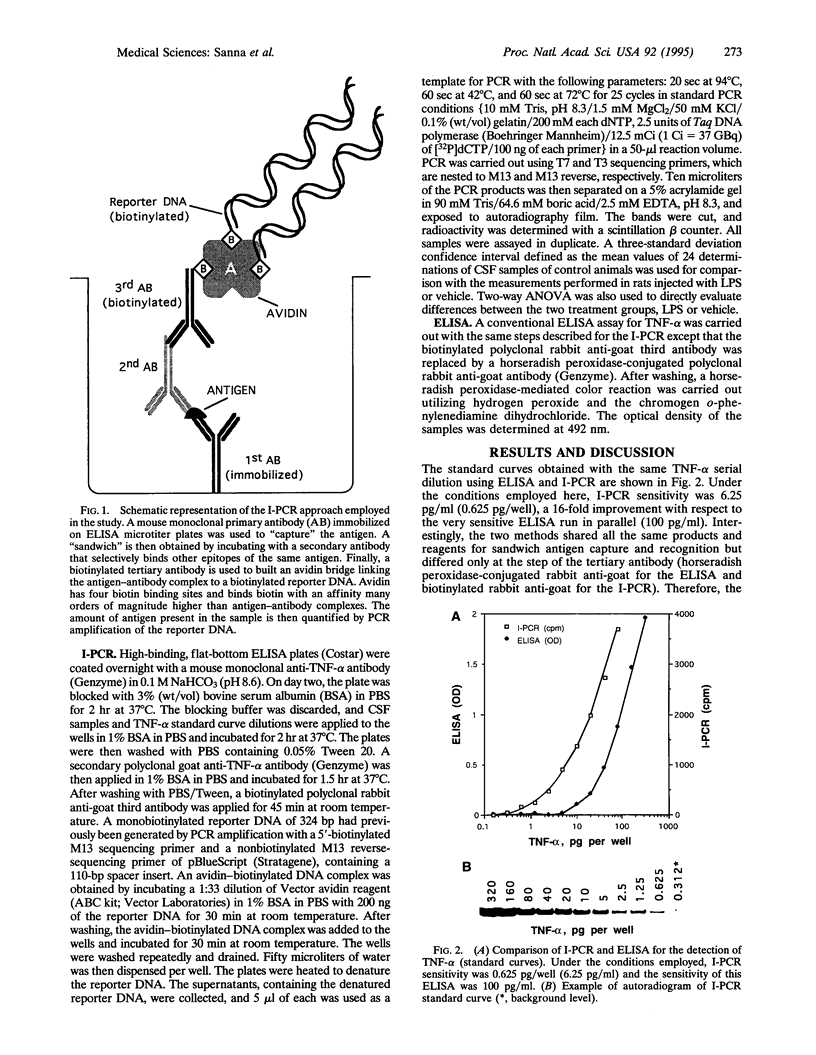
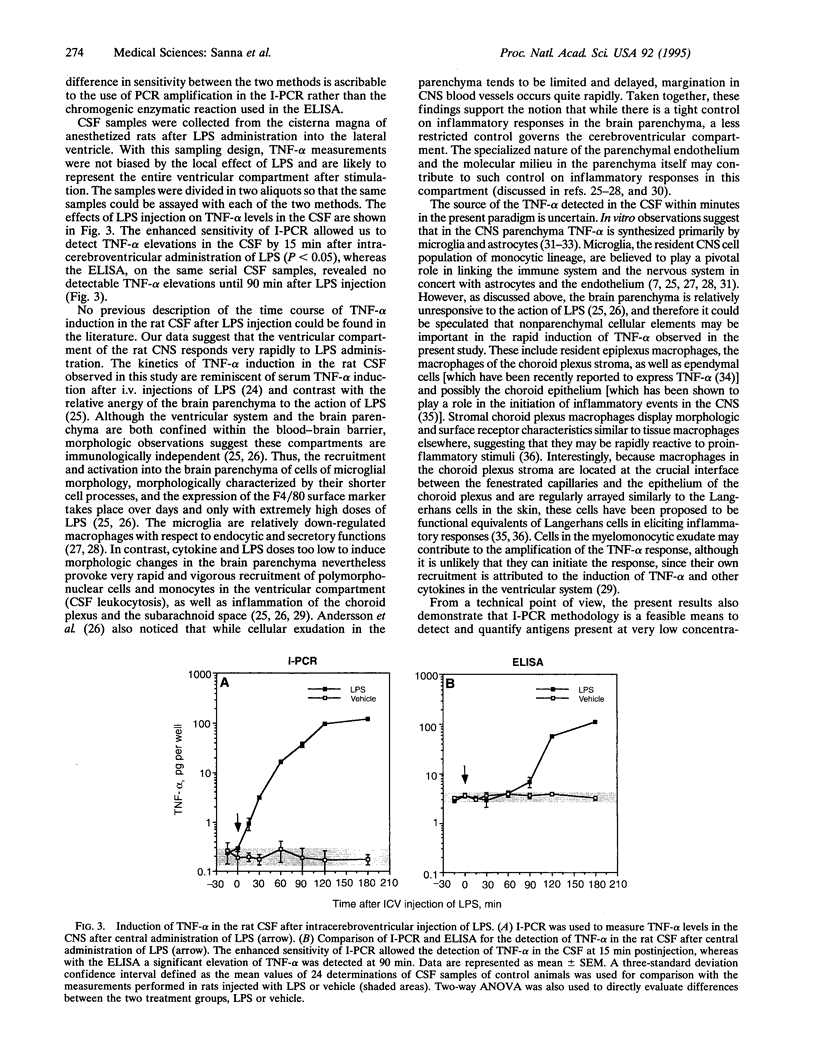

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson P. B., Perry V. H., Gordon S. The acute inflammatory response to lipopolysaccharide in CNS parenchyma differs from that in other body tissues. Neuroscience. 1992;48(1):169–186. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90347-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer J., Strauss S., Schreiter-Gasser U., Ganter U., Schlegel P., Witt I., Yolk B., Berger M. Interleukin-6 and alpha-2-macroglobulin indicate an acute-phase state in Alzheimer's disease cortices. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jul 8;285(1):111–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80737-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B. A., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor: production, distribution, and metabolic fate in vivo. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3972–3977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Tumor necrosis, cachexia, shock, and inflammation: a common mediator. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:505–518. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971 Sep;8(9):871–874. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90454-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espevik T., Nissen-Meyer J. A highly sensitive cell line, WEHI 164 clone 13, for measuring cytotoxic factor/tumor necrosis factor from human monocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Dec 4;95(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90322-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flick D. A., Gifford G. E. Comparison of in vitro cell cytotoxic assays for tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Mar 30;68(1-2):167–175. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90147-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransen L., Van der Heyden J., Ruysschaert R., Fiers W. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor: its effect and its synergism with interferon-gamma on a variety of normal and transformed human cell lines. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1986 Apr;22(4):419–426. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(86)90107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frei K., Leist T. P., Meager A., Gallo P., Leppert D., Zinkernagel R. M., Fontana A. Production of B cell stimulatory factor-2 and interferon gamma in the central nervous system during viral meningitis and encephalitis. Evaluation in a murine model infection and in patients. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):449–453. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo P., Frei K., Rordorf C., Lazdins J., Tavolato B., Fontana A. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection of the central nervous system: an evaluation of cytokines in cerebrospinal fluid. J Neuroimmunol. 1989 Jul;23(2):109–116. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(89)90029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glimåker M., Kragsbjerg P., Forsgren M., Olcén P. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF alpha) in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with meningitis of different etiologies: high levels of TNF alpha indicate bacterial meningitis. J Infect Dis. 1993 Apr;167(4):882–889. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.4.882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofman F. M., von Hanwehr R. I., Dinarello C. A., Mizel S. B., Hinton D., Merrill J. E. Immunoregulatory molecules and IL 2 receptors identified in multiple sclerosis brain. J Immunol. 1986 May 1;136(9):3239–3245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman A. P., Pitha P. M., Shin H. S., Shin M. L. Production of tumor necrosis factor and other cytokines by astrocytes stimulated with lipopolysaccharide or a neurotropic virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6348–6352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Cortés L. F., Cruz-Ruiz M., Gómez-Mateos J., Jiménez-Hernández D., Palomino J., Jiménez E. Measurement of levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 beta in the CSF of patients with meningitis of different etiologies: utility in the differential diagnosis. Clin Infect Dis. 1993 Apr;16(4):534–539. doi: 10.1093/clind/16.4.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Male D., Pryce G., Rahman J. Comparison of the immunological properties of rat cerebral and aortic endothelium. J Neuroimmunol. 1990 Dec;30(2-3):161–168. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(90)90100-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matyszak M. K., Lawson L. J., Perry V. H., Gordon S. Stromal macrophages of the choroid plexus situated at an interface between the brain and peripheral immune system constitutively express major histocompatibility class II antigens. J Neuroimmunol. 1992 Oct;40(2-3):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(92)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister C. K., O'Donoghue J. M., Beaty H. N. Experimental pneumococcal meningitis. II. Characterization and quantitation of the inflammatory process. J Infect Dis. 1975 Oct;132(4):355–360. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.4.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meager A., Leung H., Woolley J. Assays for tumour necrosis factor and related cytokines. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Jan 6;116(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90306-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morganti-Kossmann M. C., Kossmann T., Wahl S. M. Cytokines and neuropathology. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Jul;13(7):286–291. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90087-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathanson J. A., Chun L. L. Immunological function of the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1684–1688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathavitharana K. A., Tarlow M. J. Current trends in the management of bacterial meningitis. Br J Hosp Med. 1993 Oct 6;50(7):403–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohga S., Aoki T., Okada K., Akeda H., Fujioka K., Ohshima A., Mori T., Minamishima I., Ueda K. Cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of interleukin-1 beta, tumour necrosis factor-alpha, and interferon gamma in bacterial meningitis. Arch Dis Child. 1994 Feb;70(2):123–125. doi: 10.1136/adc.70.2.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry V. H., Andersson P. B. The inflammatory response in the CNS. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1992 Oct;18(5):454–459. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1992.tb00811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry V. H., Gordon S. Macrophages and microglia in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Jun;11(6):273–277. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90110-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry V. H., Gordon S. Macrophages and the nervous system. Int Rev Cytol. 1991;125:203–244. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61220-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pich E. M., Koob G. F., Heilig M., Menzaghi F., Vale W., Weiss F. Corticotropin-releasing factor release from the mediobasal hypothalamus of the rat as measured by microdialysis. Neuroscience. 1993 Aug;55(3):695–707. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90435-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Righi M., Mori L., De Libero G., Sironi M., Biondi A., Mantovani A., Donini S. D., Ricciardi-Castagnoli P. Monokine production by microglial cell clones. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Aug;19(8):1443–1448. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruzicka V., März W., Russ A., Gross W. Immuno-PCR with a commercially available avidin system. Science. 1993 Apr 30;260(5108):698–699. doi: 10.1126/science.8480182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano T., Smith C. L., Cantor C. R. Immuno-PCR: very sensitive antigen detection by means of specific antibody-DNA conjugates. Science. 1992 Oct 2;258(5079):120–122. doi: 10.1126/science.1439758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saukkonen K., Sande S., Cioffe C., Wolpe S., Sherry B., Cerami A., Tuomanen E. The role of cytokines in the generation of inflammation and tissue damage in experimental gram-positive meningitis. J Exp Med. 1990 Feb 1;171(2):439–448. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.2.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saukkonen K., Sande S., Cioffe C., Wolpe S., Sherry B., Cerami A., Tuomanen E. The role of cytokines in the generation of inflammation and tissue damage in experimental gram-positive meningitis. J Exp Med. 1990 Feb 1;171(2):439–448. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.2.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada M., Kondo N., Suzumura A., Marunouchi T. Production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha by microglia and astrocytes in culture. Brain Res. 1989 Jul 10;491(2):394–397. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90078-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaad U. B., Lips U., Gnehm H. E., Blumberg A., Heinzer I., Wedgwood J. Dexamethasone therapy for bacterial meningitis in children. Swiss Meningitis Study Group. Lancet. 1993 Aug 21;342(8869):457–461. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91592-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoendorf K. C., Adams W. G., Kiely J. L., Wenger J. D. National trends in Haemophilus influenzae meningitis mortality and hospitalization among children, 1980 through 1991. Pediatrics. 1994 Apr;93(4):663–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarlow M. J., Jenkins R., Comis S. D., Osborne M. P., Stephens S., Stanley P., Crocker J. Ependymal cells of the choroid plexus express tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1993 Aug;19(4):324–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1993.tb00447.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Weemen B. K., Schuurs A. H.W.M. Immunoassay using antigen-enzyme conjugates. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jun 24;15(3):232–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80319-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenger J. D. Impact of Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccines on the epidemiology of bacterial meningitis. Infect Agents Dis. 1993 Oct;2(5):324–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodroofe M. N., Sarna G. S., Wadhwa M., Hayes G. M., Loughlin A. J., Tinker A., Cuzner M. L. Detection of interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 in adult rat brain, following mechanical injury, by in vivo microdialysis: evidence of a role for microglia in cytokine production. J Neuroimmunol. 1991 Sep;33(3):227–236. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90110-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou H., Fisher R. J., Papas T. S. Universal immuno-PCR for ultra-sensitive target protein detection. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Dec 25;21(25):6038–6039. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.25.6038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]