Abstract
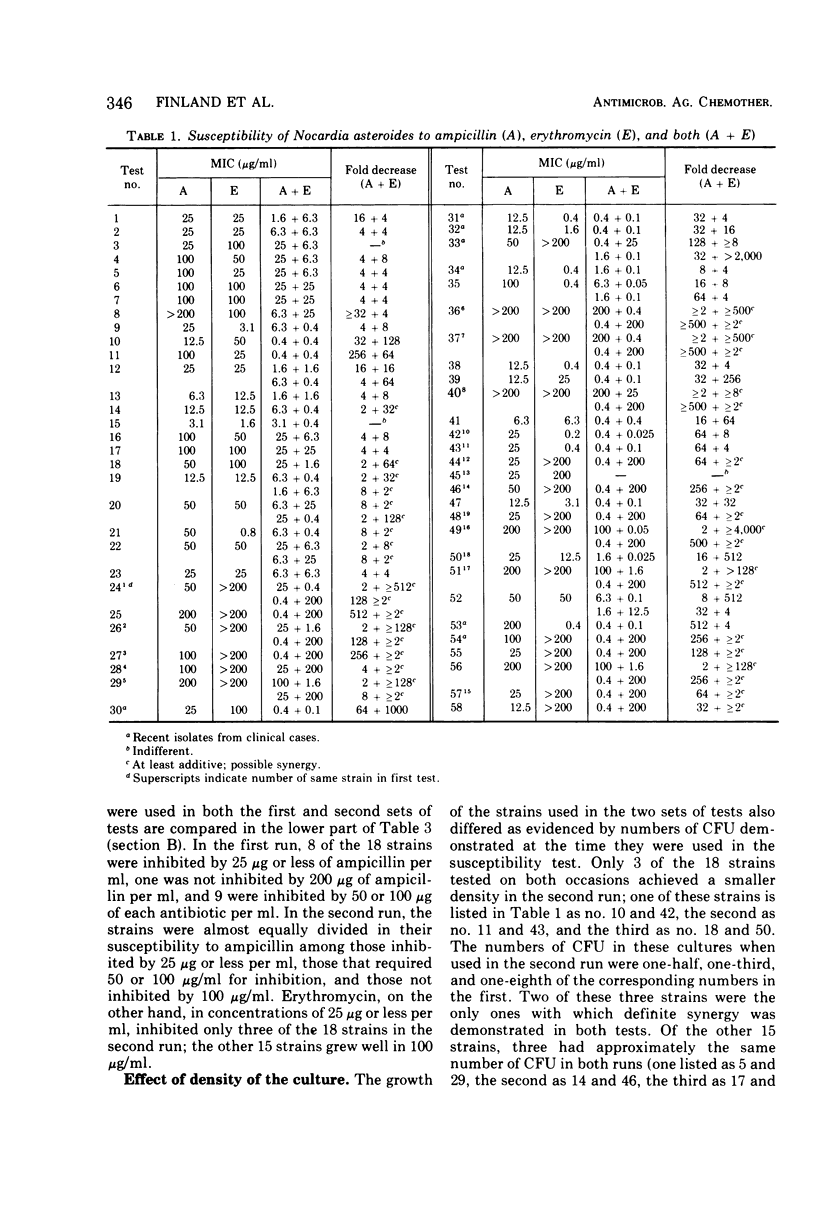
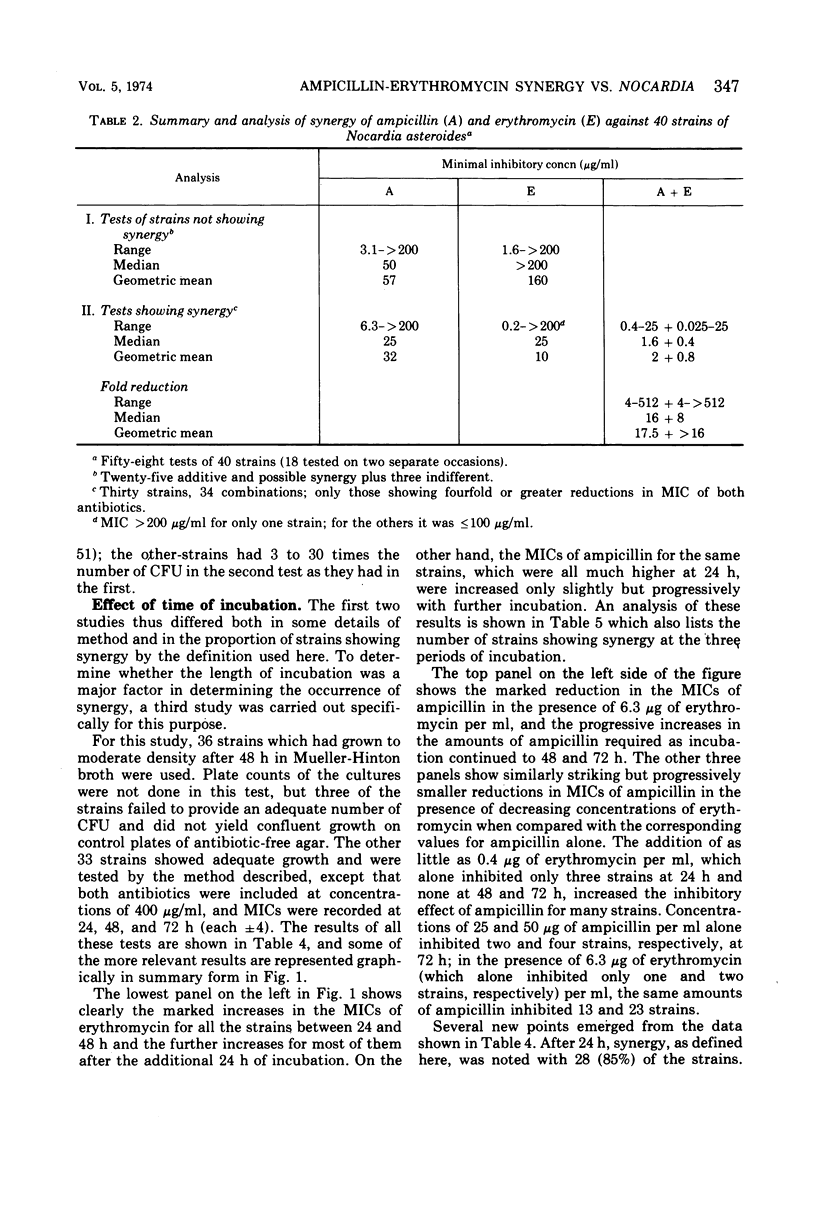
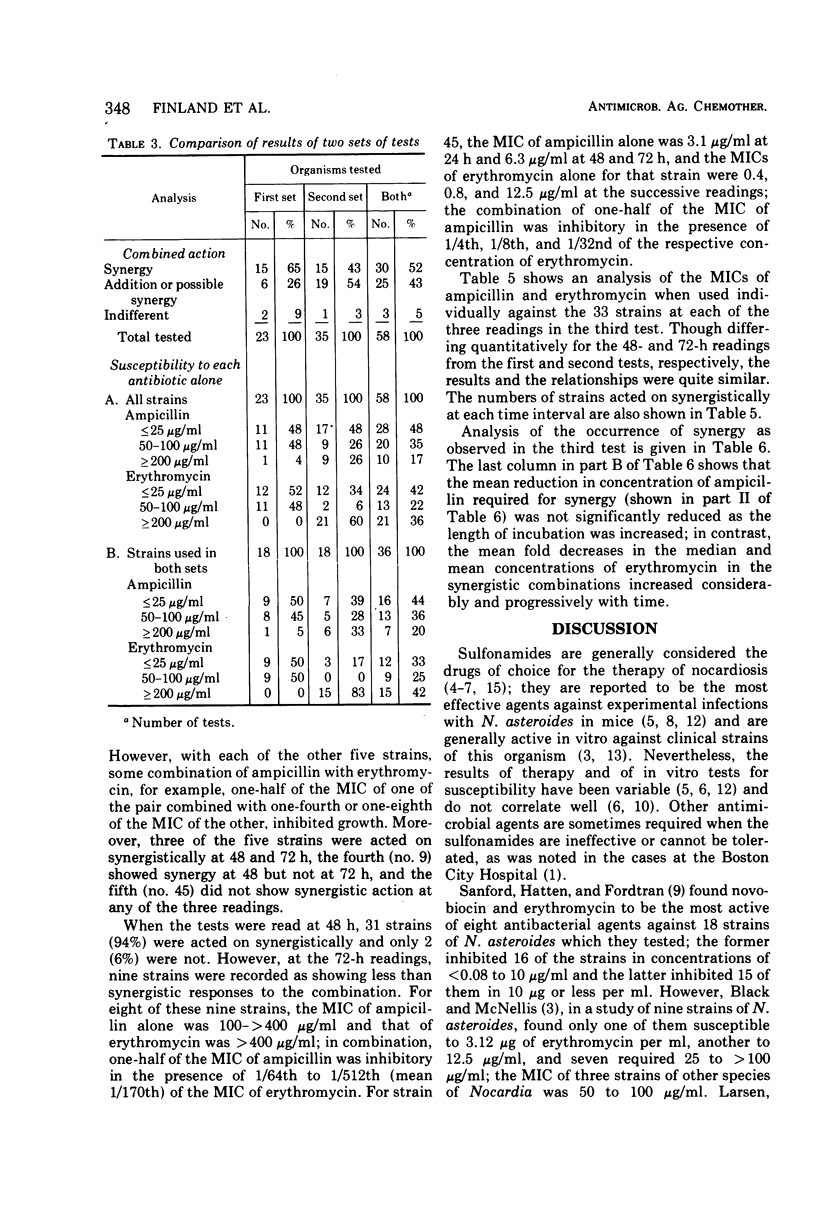
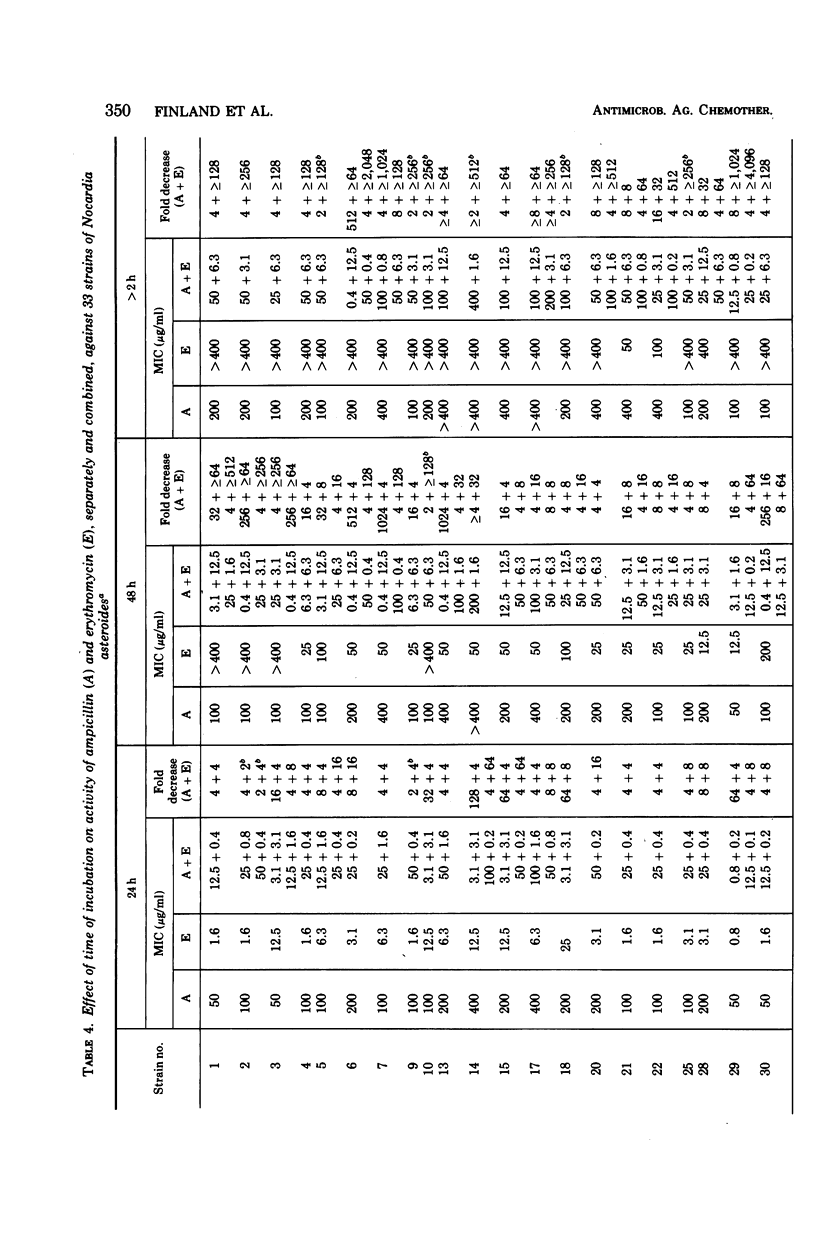
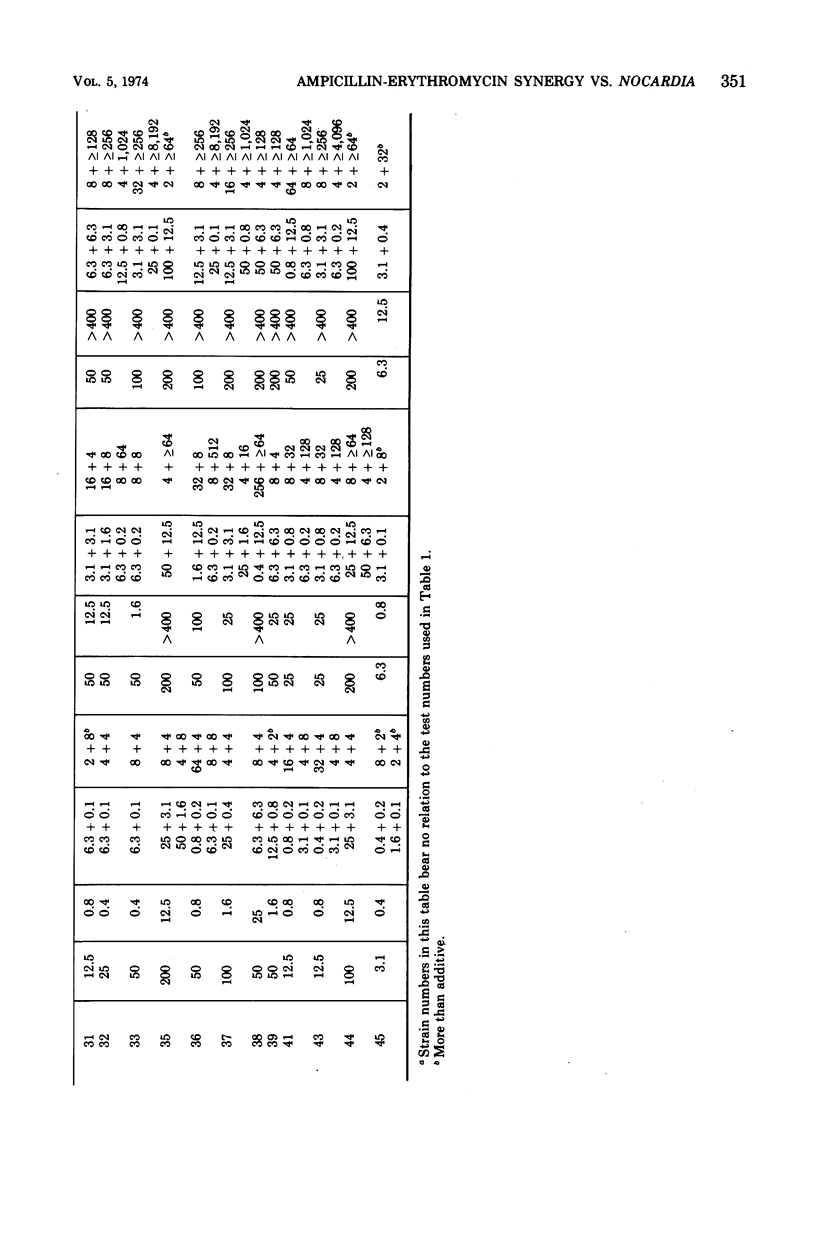
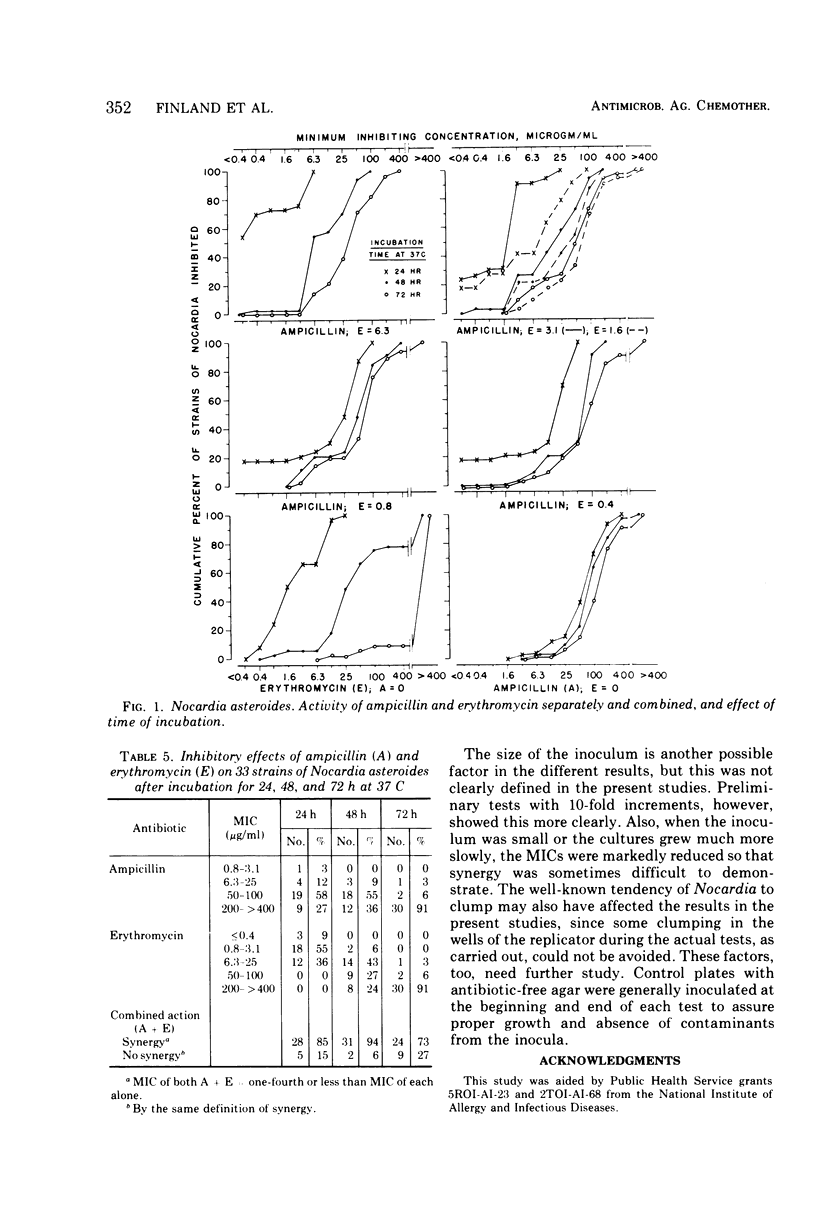
Ampicillin and erythromycin were shown to act synergistically in vitro against the majority of strains of Nocardia asteroides tested. With these strains, the minimal inhibiting concentration (MIC) of each drug when combined was reduced 4- to more than 512-fold as compared with the MIC of each antibiotic acting individually against the same strains. The combined action against other strains was at least additive, and occasionally indifferent, but antagonism was not observed. The duration of incubation greatly influenced the MIC of erythromycin but had less effect on the action of ampicillin. Synergistic action was still demonstrable, although less frequently, when the period of incubation was increased from 48 to 72 h.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach M. C., Monaco A. P., Finland M. Pulmonary nocardiosis. Therapy with minocycline and with erythromycin plus ampicillin. JAMA. 1973 Jun 4;224(10):1378–1381. doi: 10.1001/jama.224.10.1378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach M. C., Sabath L. D., Finland M. Susceptibility of Nocardia asteroides to 45 antimicrobial agents in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Jan;3(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HATHAWAY B. M., MASON K. N. Nocardiosis. Study of fourteen cases. Am J Med. 1962 Jun;32:903–909. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(62)90036-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARSEN M. C., DIAMOND H. D., COLLINS H. S. Nocardia asteroides infection; a report of seven cases. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1959 May;103(5):712–725. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1959.00270050034007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY J. F., FINEGOLD S. M., FROMAN S., WILL D. W. The changing spectrum of nocardiosis. A review and presentation of nine cases. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1961 Mar;83:315–330. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1961.83.3.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orfanakis M. G., Wilcox H. G., Smith C. B. In vitro studies of the combined effect of ampicillin and sulfonamides on Nocardia asteroides and results of therapy in four patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Mar;1(3):215–220. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.3.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUNYON E. H. Nocardia asteroides; studies of its pathogenicity and drug sensitivities. J Lab Clin Med. 1951 May;37(5):713–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANFORD J. P., HATTEN B. E., FORDTRAN J. S. Effectiveness of novobiocin and cycloserine on Nocardia asteroides; preliminary evaluation in vitro and in vivo. Antibiot Annu. 1957;5:22–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEABURY J. H., DASCOMB H. E. RESULTS OF THE TREATMENT OF SYSTEMIC MYCOSES. JAMA. 1964 May 11;188:509–513. doi: 10.1001/jama.1964.03060320031007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRAUSS R. E., KLIGMAN A. M., PILLSBURY D. M. The chemotherapy of actinomycosis and nocardiosis. Am Rev Tuberc. 1951 Apr;63(4):441–448. doi: 10.1164/art.1951.63.4.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Armstrong D., Blevins A., Lieberman P. Nocardia asteroides infection complicating neoplastic disease. Am J Med. 1971 Mar;50(3):356–367. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(71)90224-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


