Abstract
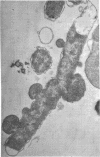
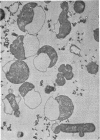
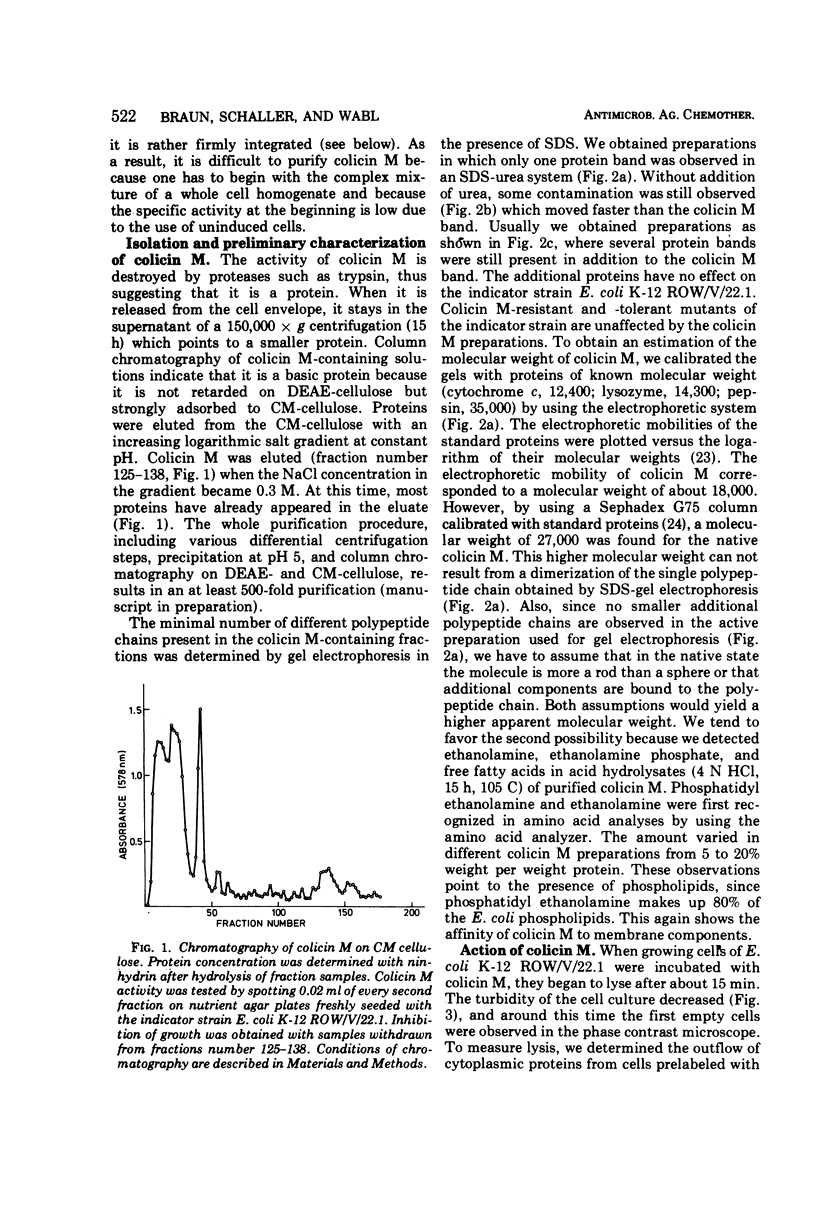
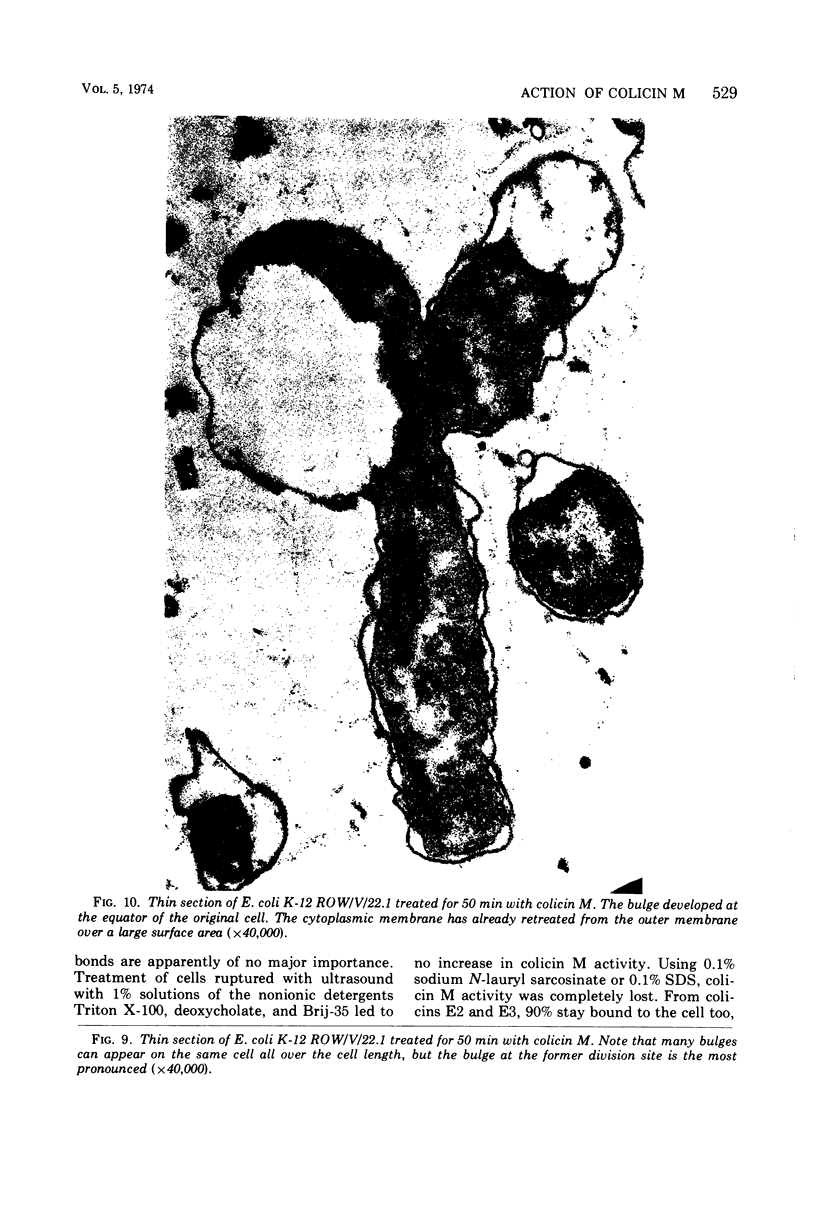
Colicin M was isolated from Escherichia coli K-12 32T 19F/T1. The purified, biologically active protein had a molecular weight of 27,000. It contained phosphatidyl ethanolamine. The molecular weight found for the polypeptide chain by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate was 18,000. Colicin M was found to be firmly integrated in the membrane of the producing strain. The action of the colicin seems to be on the membrane, since cells of the susceptible strain E. coli K-12 ROW/V/22.1 lyse rapidly. Using the phase contrast microscope, lysis was followed by decrease in turbidity of the cell culture and release of protein into the medium. Lysis started at about 15 min after addition of colicin M and was completed after 40 to 60 min. At this time, one-third of the protein had been released from the cells. The number of viable cells dropped within 10 min to 0.01%. Colicin M induced formation of spheroplasts in the presence of 16% sucrose. The electron microscope examination revealed that at first bulges in the cell envelope appear, most frequently occurring equatorially but also occurring at sites all over the cell. In the process of spheroplast formation, the cytoplasmic membrane often retreats from one-half of the outer membrane so that the cytoplasm is confined to one hemisphere. Sucrose did not prevent cells from dying unless cells were pregrown in a sucrose containing medium for several generations before colicin M was added. With cells pregrown in the presence of sucrose, the number of survivors was 100 times higher than in the absence of sucrose.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowman C. M., Sidikaro J., Nomura M. Specific inactivation of ribosomes by colicin E3 in vitro and mechanism of immunity in colicinogenic cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Dec 1;234(48):133–137. doi: 10.1038/newbio234133a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Bosch V. In vivo biosynthesis of murein-lipoprotein of the outer membrane of E. coli. FEBS Lett. 1973 Aug 15;34(2):302–306. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80817-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Bosch V. Repetitive sequences in the murein-lipoprotein of the cell wall of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):970–974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Schaller K., Wolff H. A common receptor protein for phage T5 and colicin M in the outer membrane of Escherichia coli B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 27;323(1):87–97. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90433-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Wolff H. Characterization of the receptor protein for phage T5 and colicin M in the outer membrane of E. coli B. FEBS Lett. 1973 Aug 1;34(1):77–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80707-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davie J. M., Brock T. D. Action of streptolysin S, the group D hemolysin, and phospholipase C on whole cells and spheroplasts. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):595–600. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.595-600.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDERICQ P. Recherches sur l'origine des mutants de E. coli V produisant la colicine M. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1951 Jun;145(11-12):930–933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOEBEL W. F., BARRY G. T. Colicine K. II. The preparation and properties of a substance having colicine K activity. J Exp Med. 1958 Feb 1;107(2):185–209. doi: 10.1084/jem.107.2.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschman H. R., Helinski D. R. Purification and characterization of colicin E2 and colicin E3. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 25;242(22):5360–5368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson R. E., Konisky J. Electron microscopy of colicin I-producing cells. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jan;113(1):452–460. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.1.452-460.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konisky J., Richards F. M. Characterization of colicin Ia and colicin Ib. Purification and some physical properties. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jun 10;245(11):2972–2978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunugita K., Matsuhashi M. Purification and properties of colicin K. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):1017–1019. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.1017-1019.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagel de Zwaig R., Luria S. E. Genetics and physiology of colicin-tolerant mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1112–1123. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1112-1123.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M. Colicins and related bacteriocins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1967;21:257–284. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.21.100167.001353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Witten C. Interaction of colicins with bacterial cells. 3. Colicin-tolerant mutations in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1093–1111. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1093-1111.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., KELLENBERGER E., BIRCHANDERSEN A., MAALOE O. Etude au microscope électronique de plasmas contenant de l'acide désoxyribonucliéique. I. Les nucléoides des bactéries en croissance active. Z Naturforsch B. 1958 Sep;13B(9):597–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., Tanford C. The gross conformation of protein-sodium dodecyl sulfate complexes. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):5161–5165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmis K. Purification and characterization of colicin D. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):12–20. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.12-20.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENABLE J. H., COGGESHALL R. A SIMPLIFIED LEAD CITRATE STAIN FOR USE IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1965 May;25:407–408. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]