Abstract
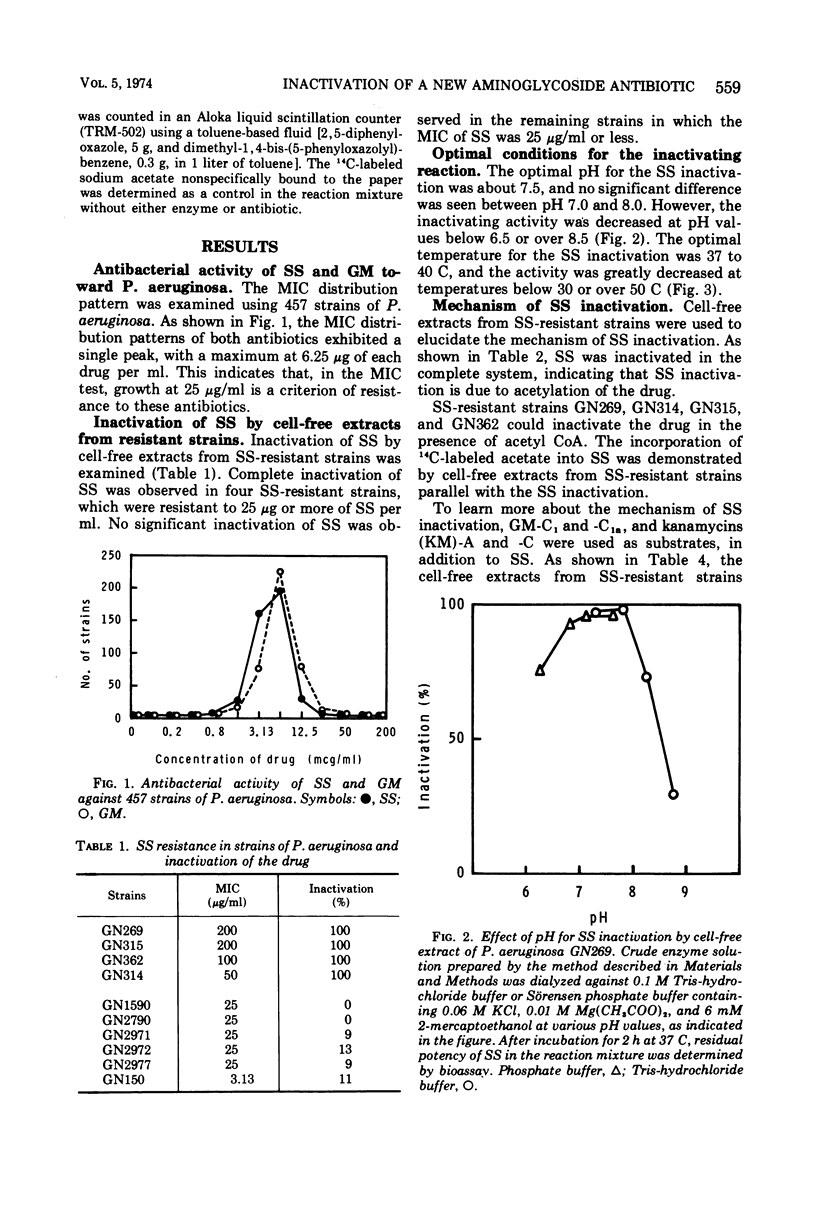
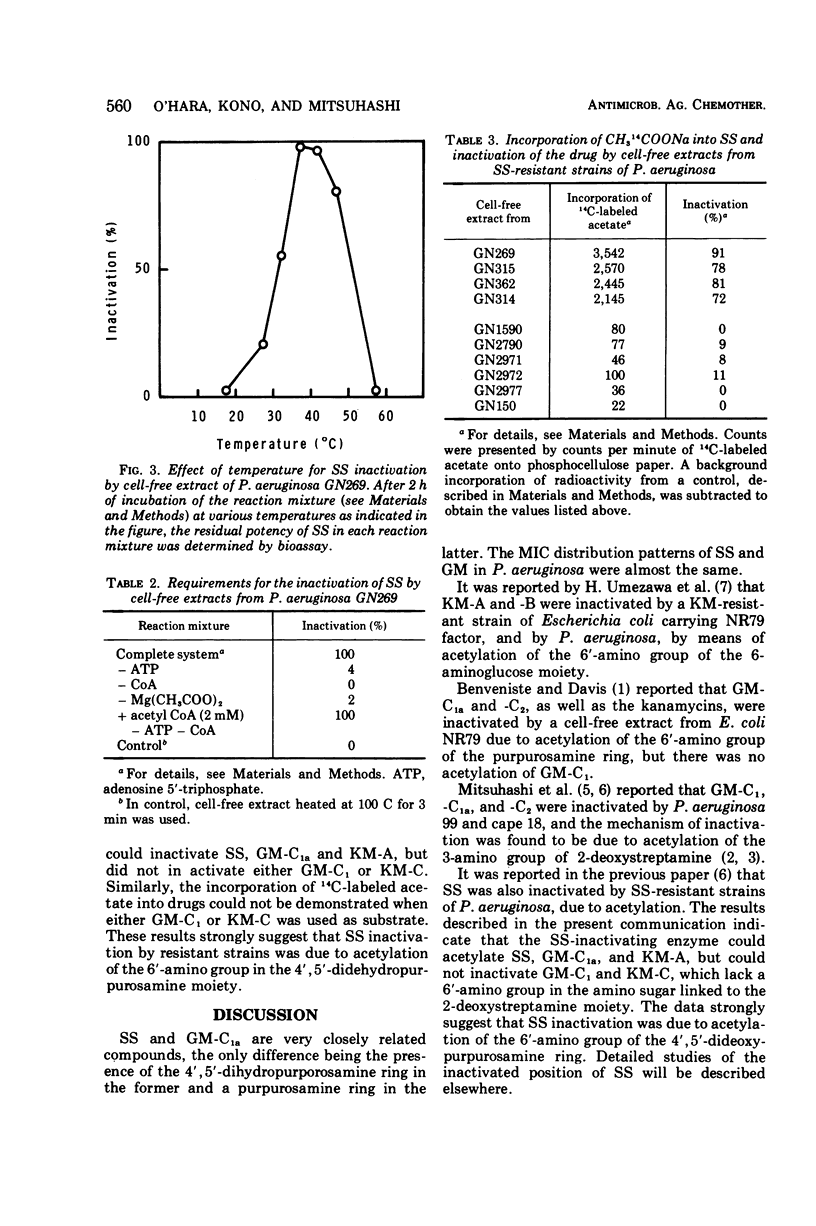
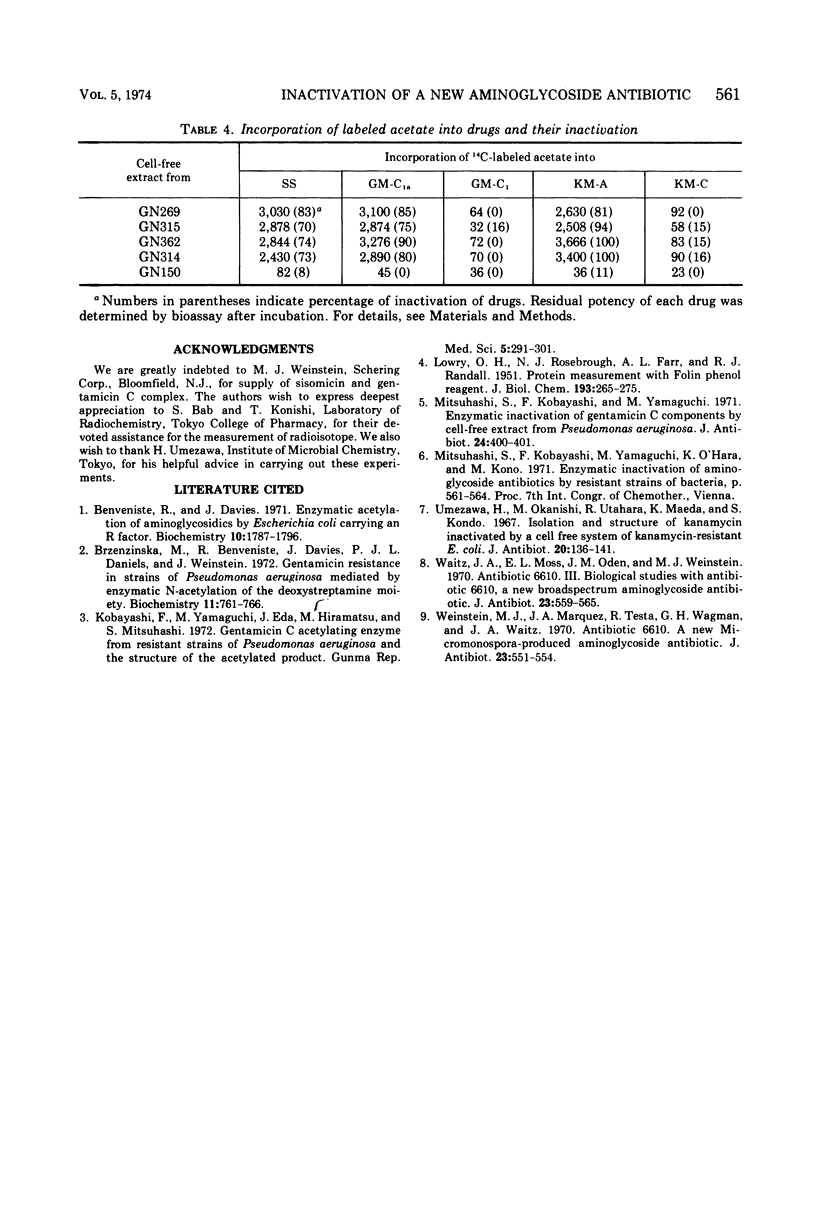
The antibacterial activity of sisomicin (SS), a new aminoglycoside antibiotic active toward clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, was determined and compared with that of the gentamicin C complex. Both drugs were effective against these strains and showed almost the same antibacterial activity. A few strains were found to be resistant to SS. The antibiotic was inactivated by a cell-free extract from the SS-resistant strains due to acetylation of the drug. Comparative studies of the inactivation of the drugs which lack a 6′-amino group in the amino sugar linked to 2-deoxystreptamine strongly suggested that SS inactivation was due to acetylation of the 6′-amino group of the 4′,5′-didehydropurpurosamine moiety.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benveniste R., Davies J. Enzymatic acetylation of aminoglycoside antibiotics by Escherichia coli carrying an R factor. Biochemistry. 1971 May 11;10(10):1787–1796. doi: 10.1021/bi00786a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzezinska M., Benveniste R., Davies J., Daniels P. J., Weinstein J. Gentamicin resistance in strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa mediated by enzymatic N-acetylation of the deoxystreptamine moiety. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 29;11(5):761–765. doi: 10.1021/bi00755a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuhashi S., Kobayashi F., Yamaguchi M. Enzymatic inactivation of gentamicin C components by cell-free extract from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Jun;24(6):400–401. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Okanishi M., Utahara R., Maeda K., Kondo S. Isolation and structure of kanamycin inactivated by a cell free system of kanamycin-resistant E. coli. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1967 Jul;20(3):136–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waitz J. A., Moss E. L., Jr, Oden E. M., Weinstein M. J. Antibiotic 6640. 3. Biological studies with antibiotic 6640, a new broad-spectrum aminoglycoside antibiotic. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1970 Nov;23(11):559–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein M. J., Marquez J. A., Testa R. T., Wagman G. H., Oden E. M., Waitz J. A. Antibiotic 6640, a new Micromonospora-produced aminoglycoside antibiotic. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1970 Nov;23(11):551–554. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.23.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


