Abstract
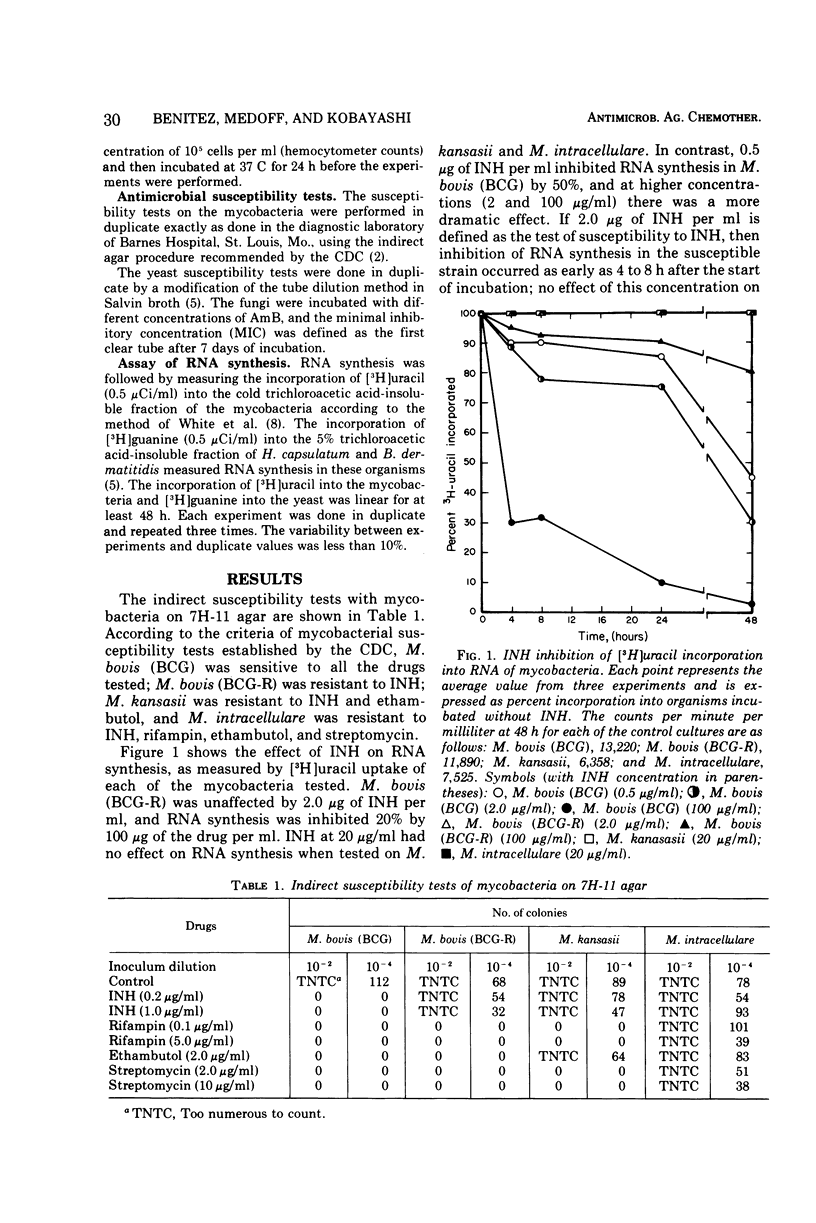
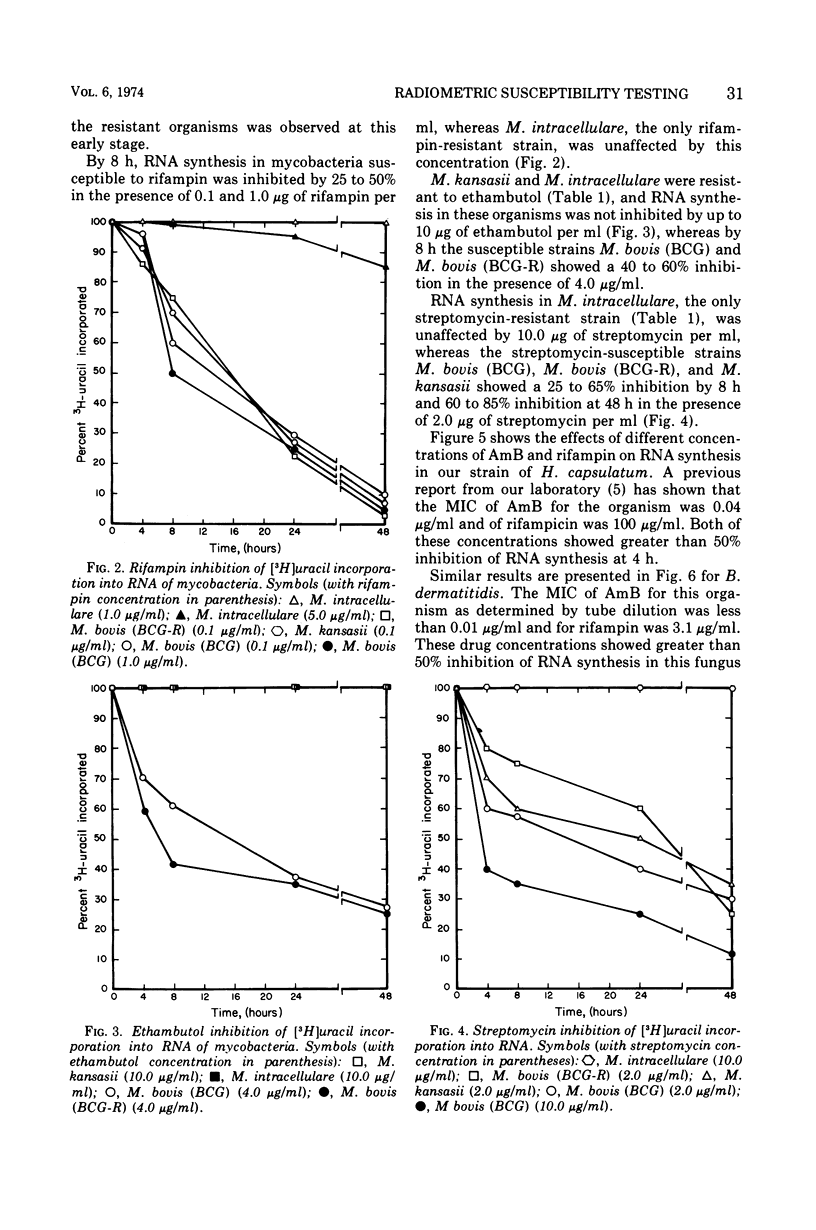
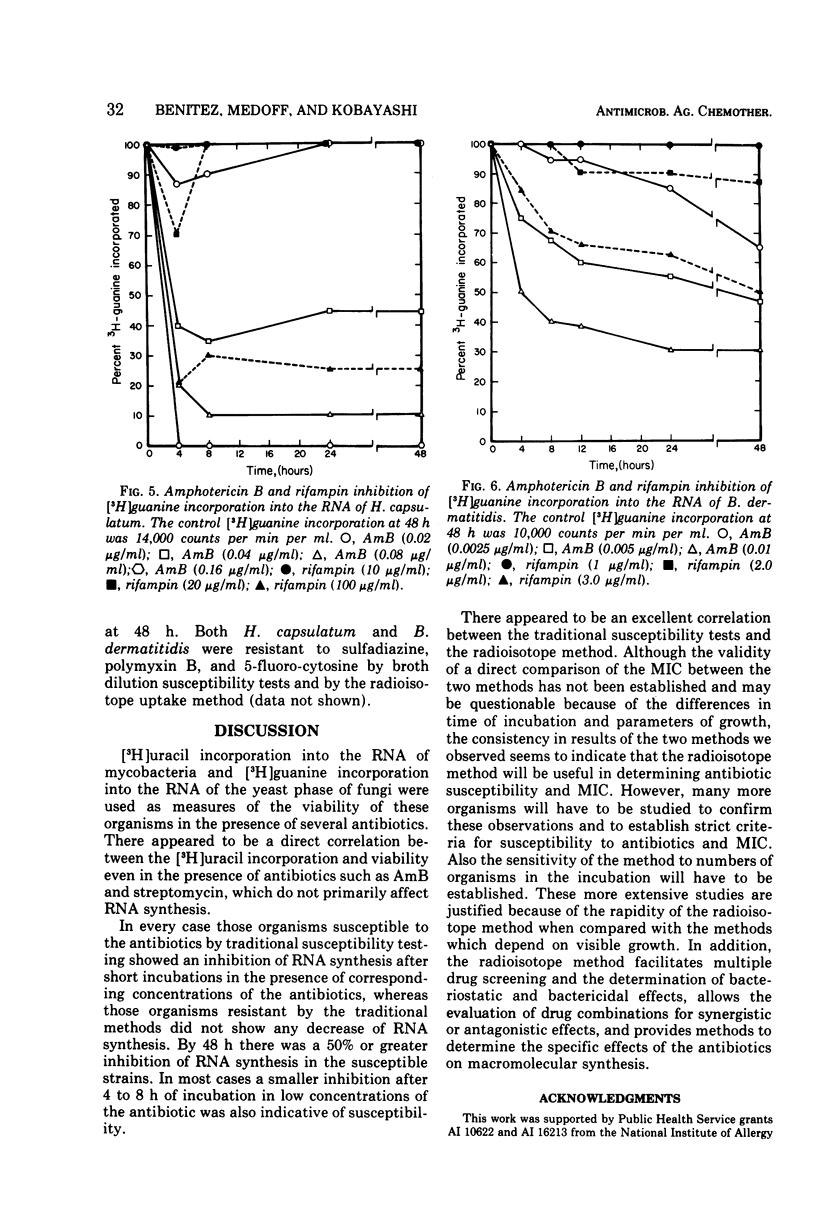
[3H]uracil incorporation into the ribonucleic acid (RNA) of mycobacteria and [3H]guanine incorporation into the RNA of fungi were used as measures of cell viability in the presence of several antimicrobial agents. There appeared to be an excellent correlation between traditional susceptibility tests, which required 1 to 4 weeks, and tests of the inhibition of incorporation of RNA precursors, which were completed in 4 to 48 h. The radiometric method may be useful in rapidly determining the susceptibility of slow-growing organisms to antimicrobial agents.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CANETTI G., FROMAN S., GROSSET J., HAUDUROY P., LANGEROVA M., MAHLER H. T., MEISSNER G., MITCHISON D. A., SULA L. MYCOBACTERIA: LABORATORY METHODS FOR TESTING DRUG SENSITIVITY AND RESISTANCE. Bull World Health Organ. 1963;29:565–578. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBlanc H. J., Jr, Charache P., Wagner H. N., Jr Automatic radiometric measurement of antibiotic effect on bacterial growth. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Nov;2(5):360–366. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.5.360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLand F. H. Metabolic inhibition as an index of bacterial susceptibility to drugs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Nov;2(5):405–412. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.5.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobbayashi G. S., Medoff G., Schlessinger D., Kwan C. N., Musser W. E. Amphotericin B potentiation of rifampicin as an antifungal agent against the yeast phase of Histoplasma capsulatum. Science. 1972 Aug 25;177(4050):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4050.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClatchy J. K., Waggoner R. F., Lester W. In vitro susceptibility of mycobacteria to rifampin. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1969 Aug;100(2):234–236. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1969.100.2.234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALVIN S. B. Growth of the yeastlike phase of Histoplasma capsulatum in a fluid medium. J Bacteriol. 1950 Feb;59(2):312–313. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.2.312-313.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. J., Lancini G. C., Silvestri L. G. Mechanism of action of rifampin on Mycobacterium smegmatis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):737–741. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.737-741.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


