Abstract
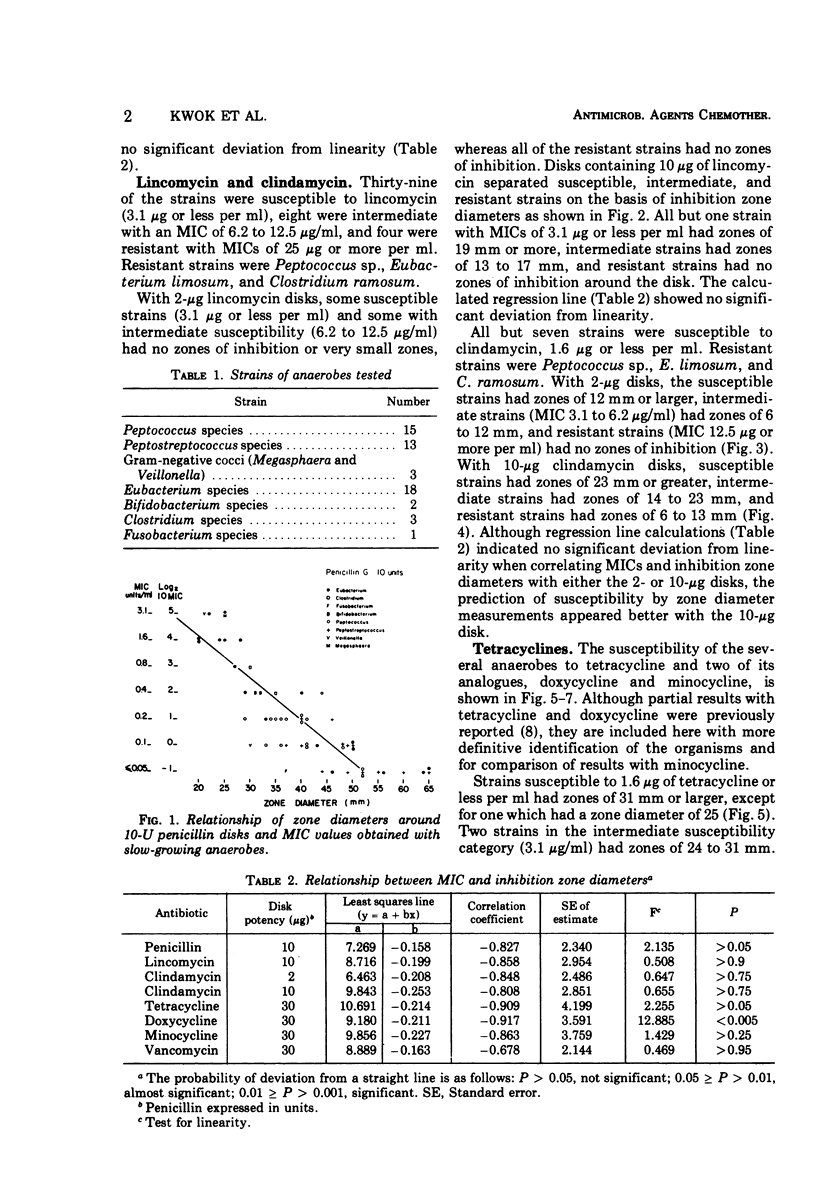
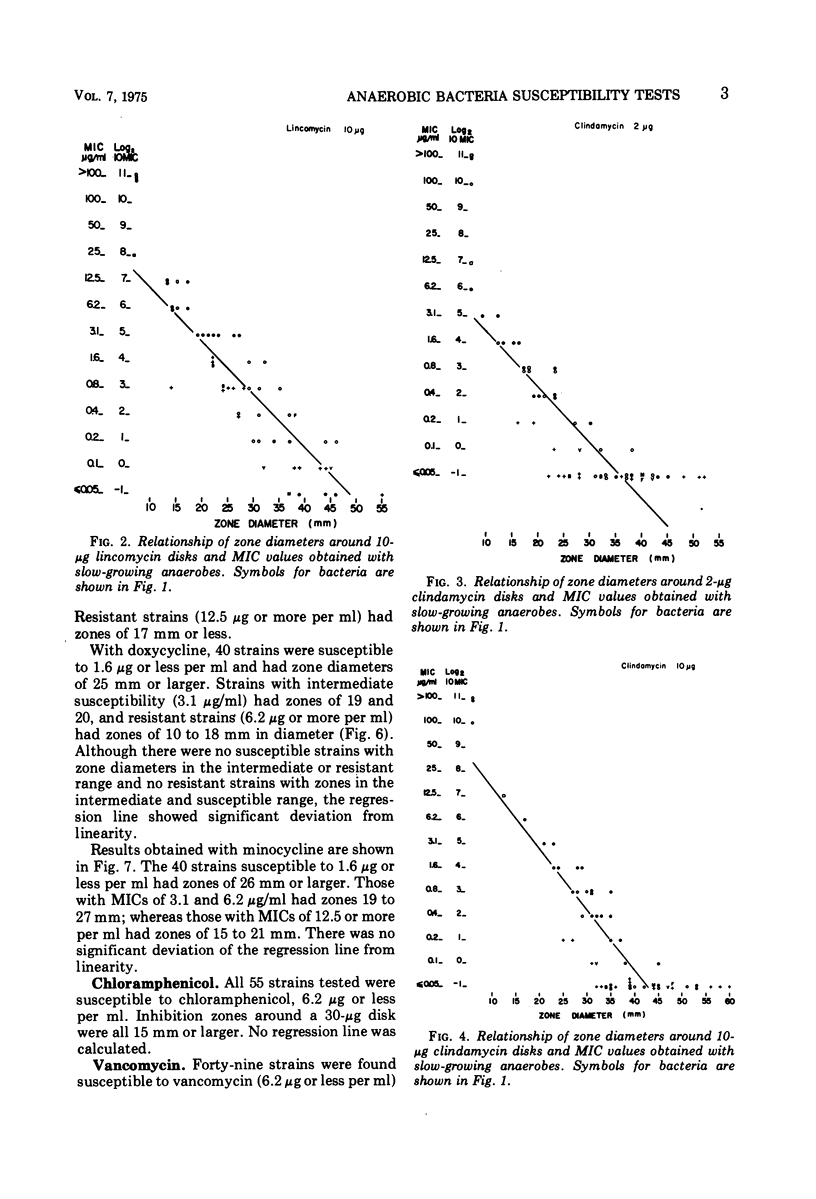
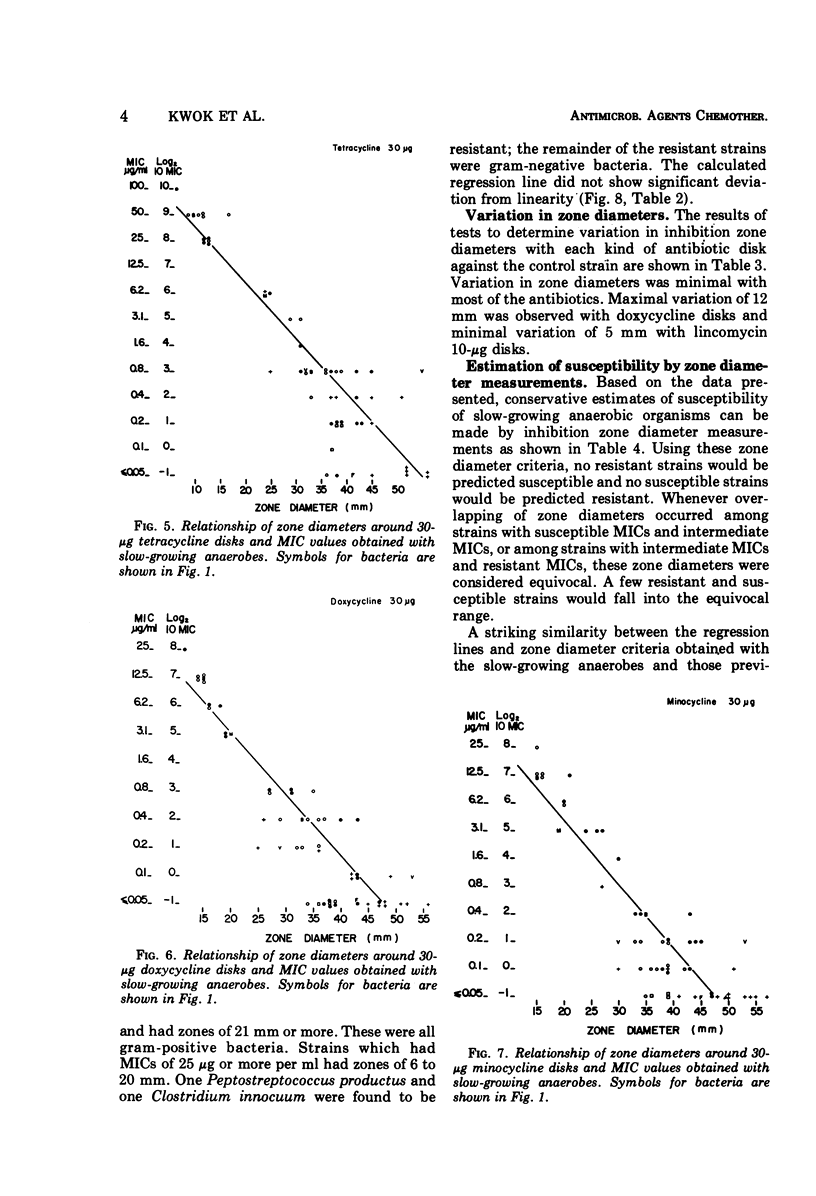
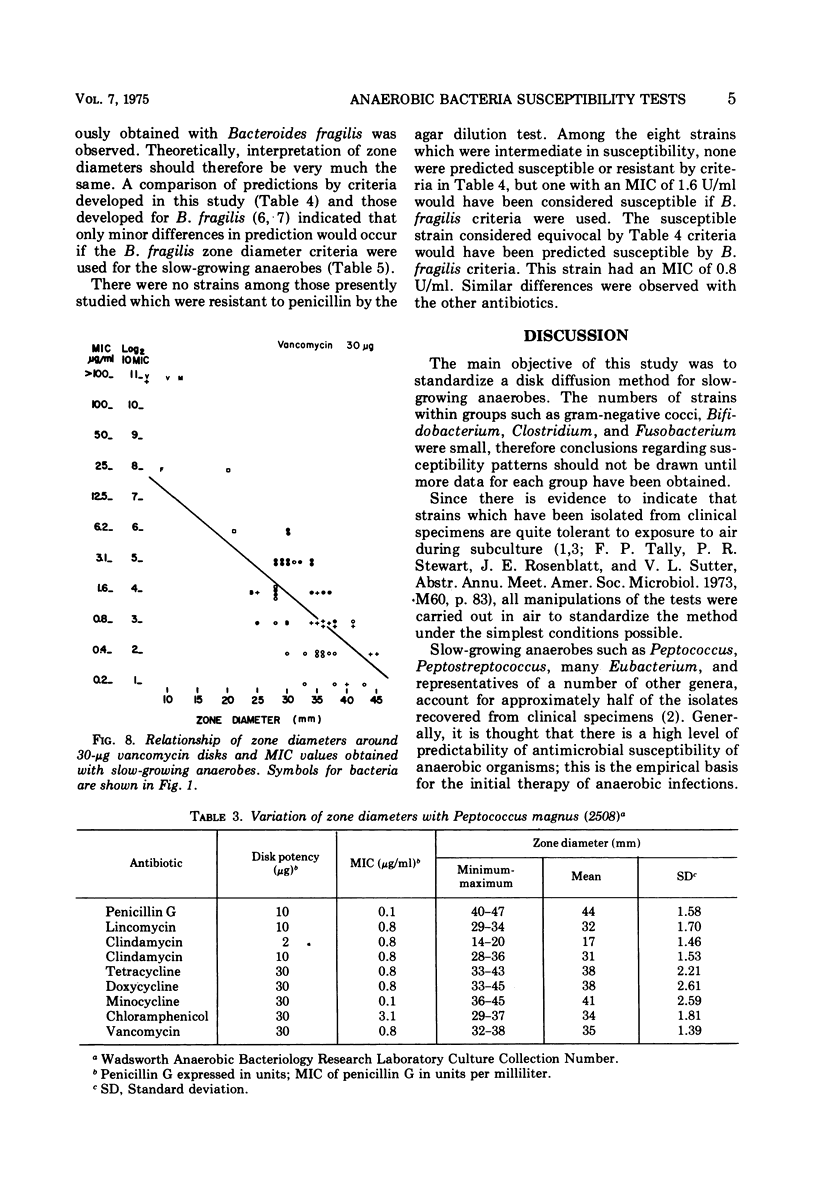
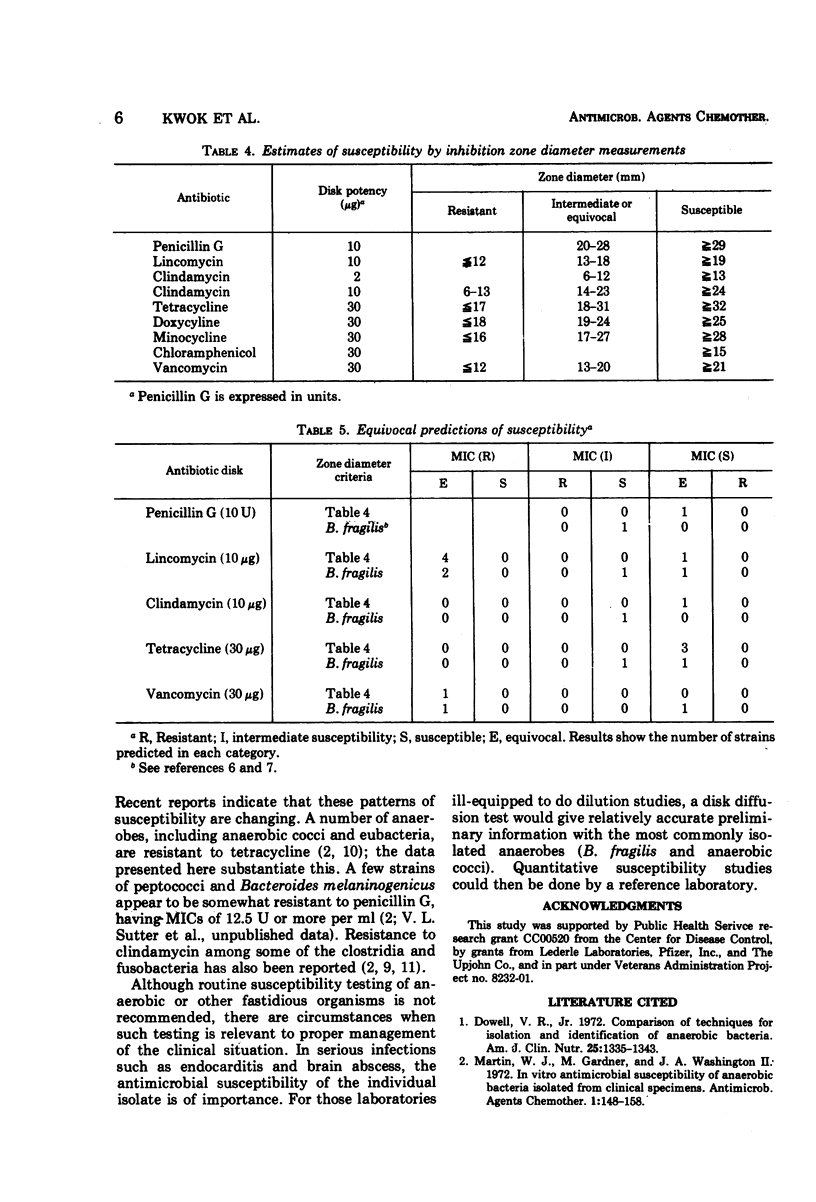
The susceptibility of 55 strains of slow-growing anaerobes to eight clinically useful or potentially useful antibiotics was determined by agar dilution and disk diffusion tests. Strains of the genera Peptococcus, Peptostreptococcus, Megasphaera, Veillonella, Eubacterium, Bifidobacterium, Clostridium, and Fusobacterium were included. All strains were susceptible to chloramphenicol, but varied in their susceptibility to penicillin, lincomycin, clindamycin, tetracyclines, and vancomycin. Correlation between minimal inhibitory concentration and inhibition zone diameters was generally good. Prediction of susceptibility based on zone diameter measurements appeared satisfactory. Although routine susceptibility testing of anaerobic bacteria is not recommended, there are circumstances where such testing is relevant to the clinical situation. For those laboratories ill-equipped to do dilution tests, a disk diffusion test would give relatively accurate preliminary information. Quantitative susceptibility tests could then be done by a reference laboratory.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dowell V. R., Jr Comparison of techniques for isolation and identification of anaerobic bacteria. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1335–1343. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. J., Gardner M., Washington J. A., 2nd In vitro antimicrobial susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria isolated from clinical specimens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Feb;1(2):148–158. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.2.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt J. E., Fallon A., Finegold S. M. Comparison of methods for isolation of anaerobic bacteria from clinical specimens. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Jan;25(1):77–85. doi: 10.1128/am.25.1.77-85.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapico F. L., Kwok Y. Y., Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Standardized antimicrobial disc susceptibility testing of anaerobic bacteria: in vitro susceptibility of Clostridium perfringens to nine antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Oct;2(4):320–325. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.4.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Kwok Y. Y., Finegold S. M. Standardized antimicrobial disc susceptibility testing of anaerobic bacteria. I. Susceptibility of Bacteroides fragilis to tetracycline. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Feb;23(2):268–275. doi: 10.1128/am.23.2.268-275.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Kwok Y., Finegold S. M. Susceptibility of Bacteroides fragilis to six antibiotics determined by standardized antimicrobial disc susceptibility testing. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Feb;3(2):188–193. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.2.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Armfield A. Y., Dowell V. R., Jr, Kwok Y. Y., Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Susceptibility of Clostridium ramosum to antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jun;5(6):589–593. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.6.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikins T. D., Holdeman L. V., Abramson I. J., Moore W. E. Standardized single-disc method for antibiotic susceptibility testing of anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Jun;1(6):451–459. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.6.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins T. D., Thiel T. Resistance of some species of Clostridium to clindamycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Jan;3(1):136–137. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.1.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



