Abstract
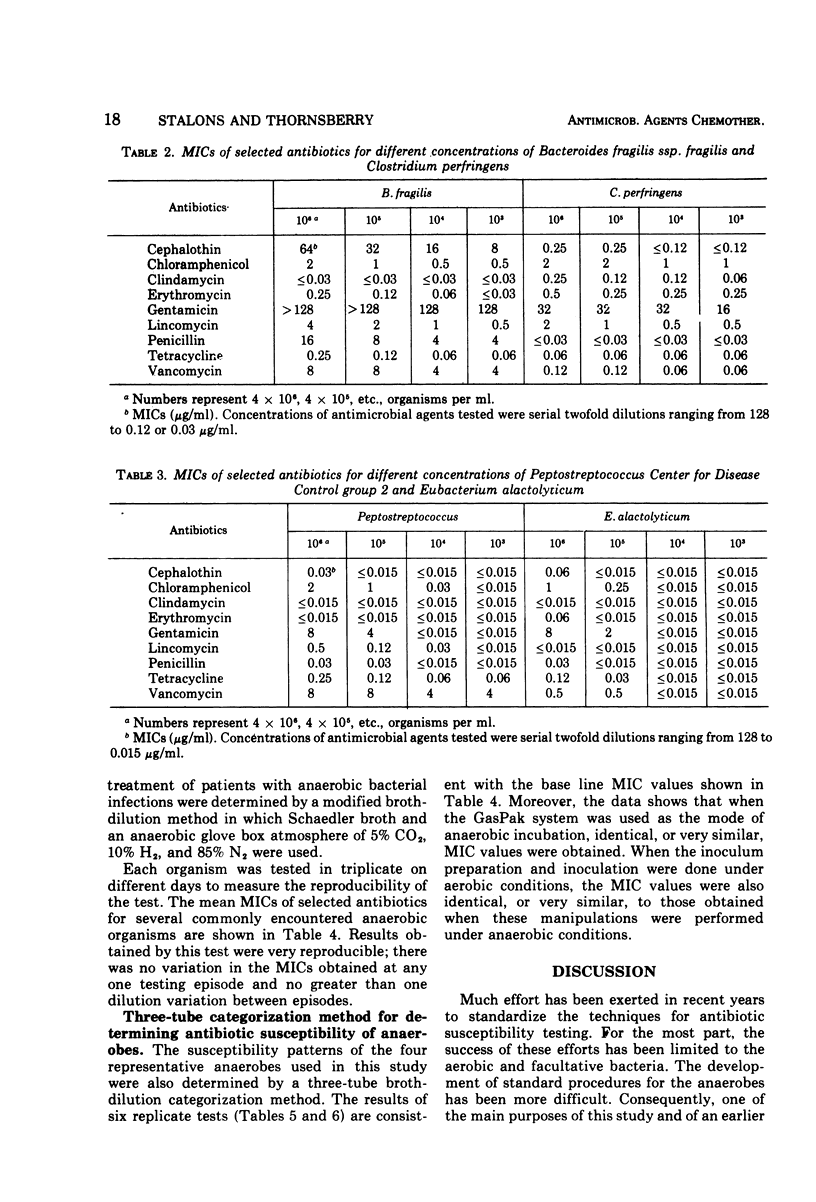
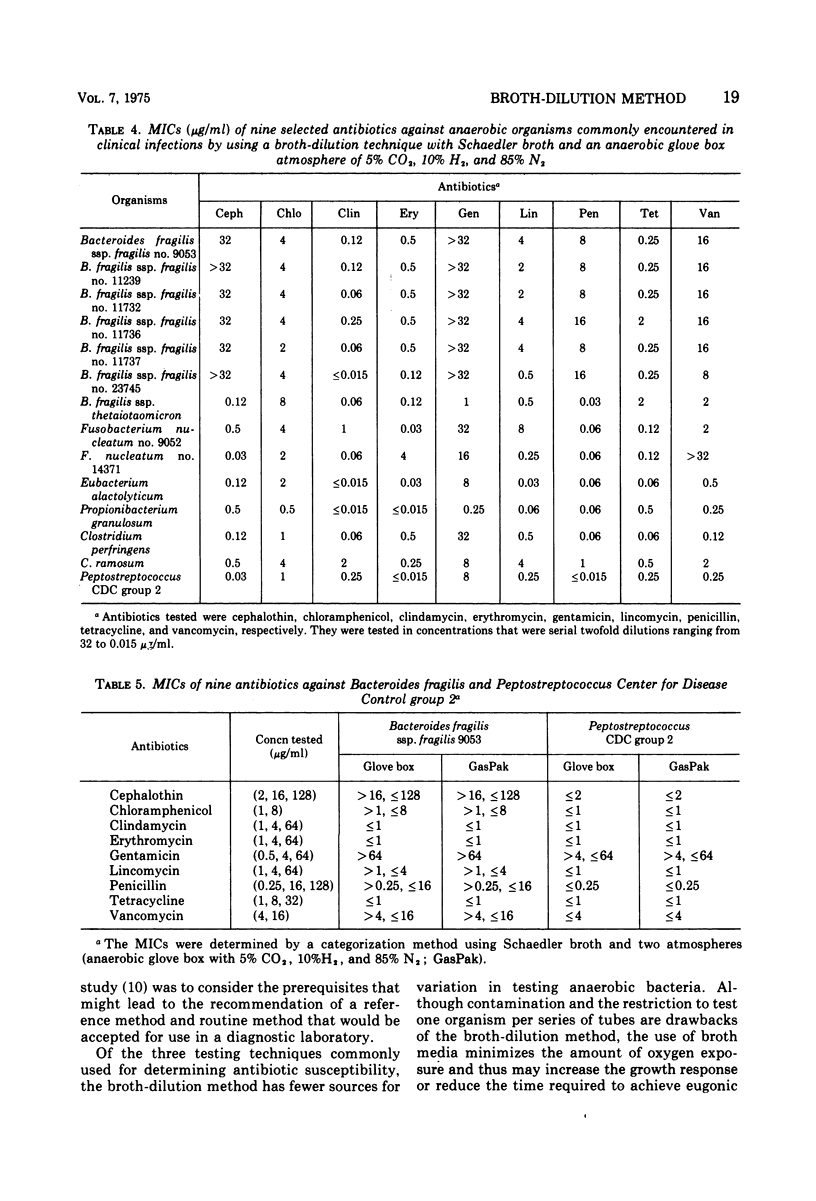
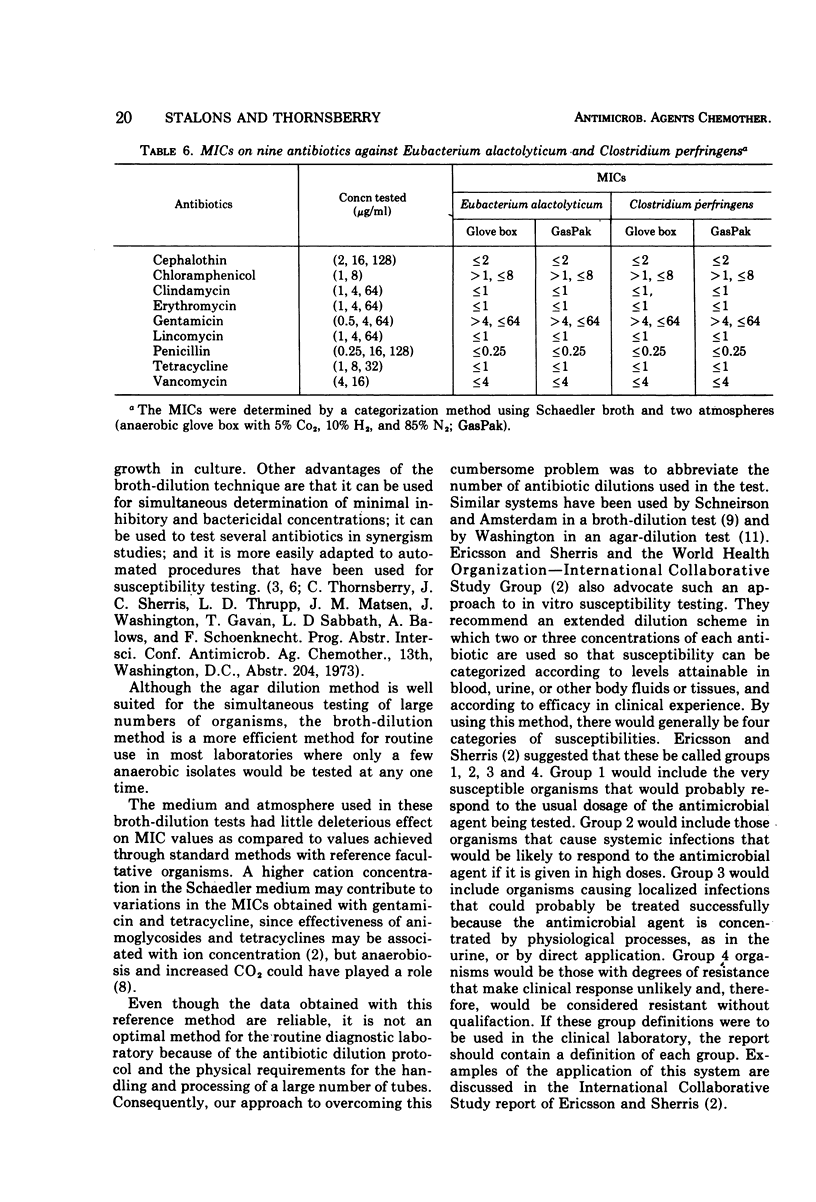
A broth-dilution method for performing antimicrobial susceptibility tests on anaerobic bacteria has been proposed. The medium used in the test was Schaedler broth, with incubation in a glove box with an atmosphere of 5% CO2, 10% H2, and 85% N2, or in the GasPak system. Minimal inhibitory concentrations for selected antibiotics were determined, under these conditions, by using a conventional twofold dilution scheme for the antibiotics and a “categorization three-tube method” in which two or three clinically significant concentrations of each antibiotic were used. Minimal inhibitory concentrations obtained by both methods were very similar. The categorization method could be used routinely to test the antimicrobial susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ericsson H. M., Sherris J. C. Antibiotic sensitivity testing. Report of an international collaborative study. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;217(Suppl):1+–1+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBONS R. J., MACDONALD J. B. Hemin and vitamin K compounds as required factors for the cultivation of certain strains of Bacteroides melaninogenicus. J Bacteriol. 1960 Aug;80:164–170. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.2.164-170.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg H. D., Reichler A., Wiseman D. Prototype of a fully automated device for determination of bacterial antibiotic susceptibility in the clinical laboratory. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Dec;22(6):980–986. doi: 10.1128/am.22.6.980-986.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt J. E., Schoenknecht F. Effect of several components of anaerobic incubation on antibiotic susceptibility test results. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 May;1(5):433–440. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.5.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHNEIERSON S. S., AMSTERDAM D. A simplified tube procedure for the routine determination of bacterial sensitivity to antibiotics. Am J Clin Pathol. 1959 Jan;31(1):81–86. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/31.1_ts.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalons D. R., Thornsberry C., Dowell V. R., Jr Effect of culture medium and carbon dioxide concentration on growth of anaerobic bacteria commonly encountered in clinical specimens. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jun;27(6):1098–1104. doi: 10.1128/am.27.6.1098-1104.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins T. D., Thiel T. Modified broth-disk method for testing the antibiotic susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Mar;3(3):350–356. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.3.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


