Abstract
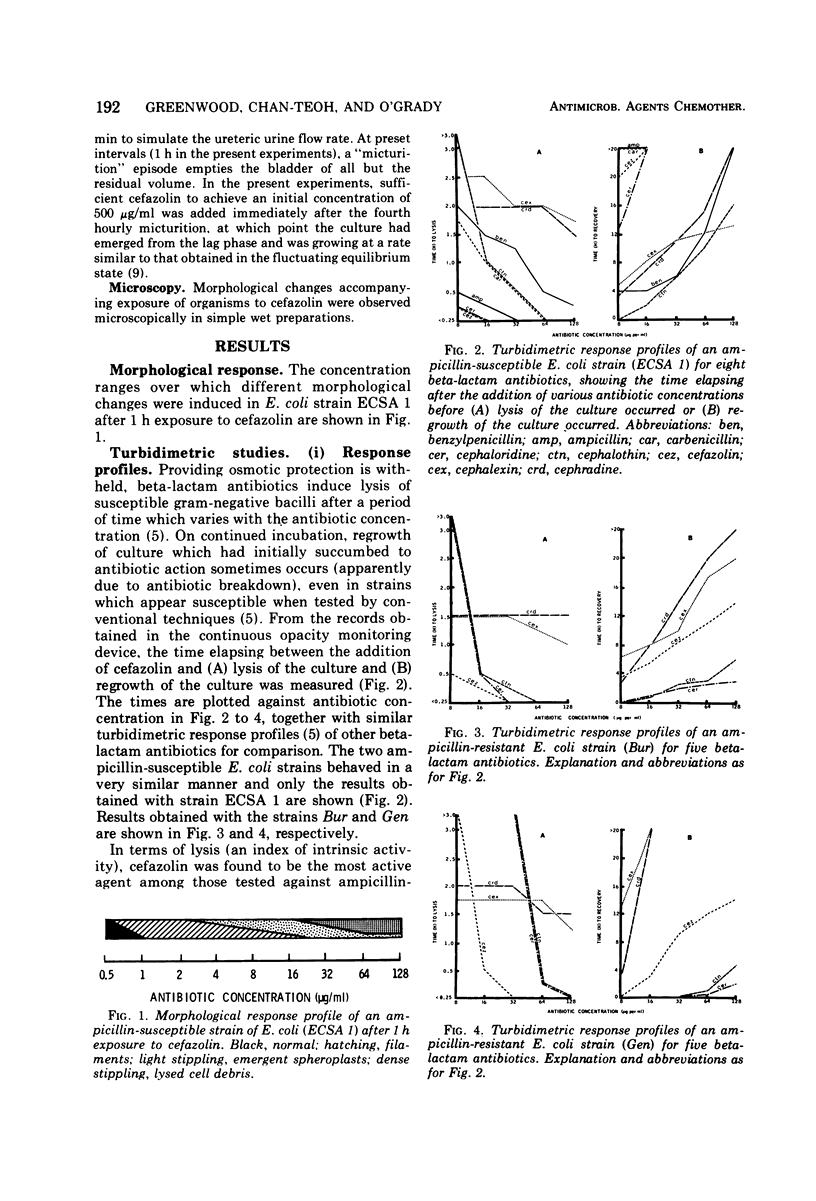
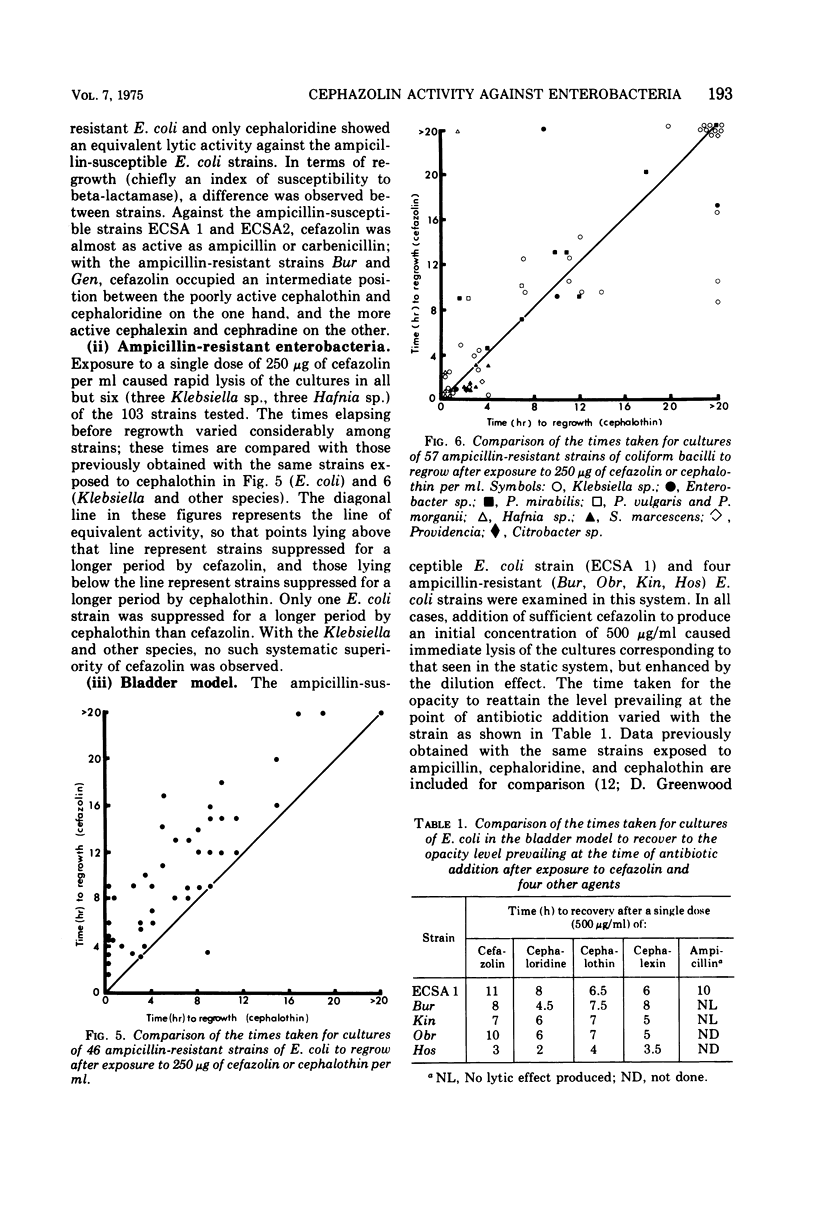
The in vitro activity of cefazolin was assessed by continuous turbidimetric monitoring of cultures of gram-negative bacilli and the results were compared with those previously obtained with other beta-lactam agents using the same strains and methods. Cefazolin was found to induce rapid lysis of ampicillin-susceptible and -resistant strains of Escherichia coli at a lower concentration than any other beta-lactam agent tested; its stability to beta-lactamase, as judged by regrowth studies, was generally considerably greater than that of other antibiotics of this group. Tested against 103 ampicillin-resistant enterobacteria, cefazolin was found to be more active than cephalothin against E. coli, but no systematic increase in susceptibility to cefazolin was seen with other species. A study of cefazolin in an in vitro model which simulates the hydrokinetic features of the urinary bladder showed it to be as active as ampicillin against ampicillin-susceptible E. coli and as active as cephalothin against ampicillin-resistant E. coli.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cox C. E. Cefazolin therapy of urinary tract infections. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(Suppl):S397–S398. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.supplement_2.s397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eykyn S. Use and control of cephalosporins. J Clin Pathol. 1971 Jul;24(5):419–429. doi: 10.1136/jcp.24.5.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold J. A., McKee J. J., Ziv D. S. Experience with cefazolin: an overall summary of pharmacologic and clinical trials in man. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(Suppl):S415–S412. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.supplement_2.s415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood D., O'Grady F. Comparison of the responses of Escherichia coli and proteus mirabilis to seven beta-lactam antibodies. J Infect Dis. 1973 Aug;128(2):211–222. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.2.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood D., O'Grady F. The comparative performance of beta-lactam antibiotics against ampicillin sensitive Escherichia coli in conditions simulating those of the infected urinary bladder. Br J Exp Pathol. 1974 Jun;55(3):245–250. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood D., O'Grady F. The effect of osmolality on the response of Escherichia coli and Proteus mirabilis to penicillins. Br J Exp Pathol. 1972 Oct;53(5):457–464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby W. M., Regamey C. Pharmacokinetics of cefazolin compared with four other cephalosporins. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(Suppl):S341–S346. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.supplement_2.s341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackintosh I. P., O'Grady F., Greenwood D., Watson B. W., Crichton T. C., Piper R., Ferrer A. A twelve channel bacterial growth monitoring system. Biomed Eng. 1973 Dec;8(12):514–passim. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Grady F., Mackintosh I. P., Greenwood D., Watson B. W. Treatment of "bacterial cystitis" in fully automatic machanical models simulating conditions of bacterial growth in the urinary bladder. Br J Exp Pathol. 1973 Jun;54(3):283–290. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steigbigel N. H., McCall C. E., Reed C. W., Finland M. Antibacterial action of "broad-spectrum" penicillins, cephalosporins and other antibiotics against Gram-negative bacilli isolated from bacteremic patients. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Sep 27;145(2):224–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb50221.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


