Abstract
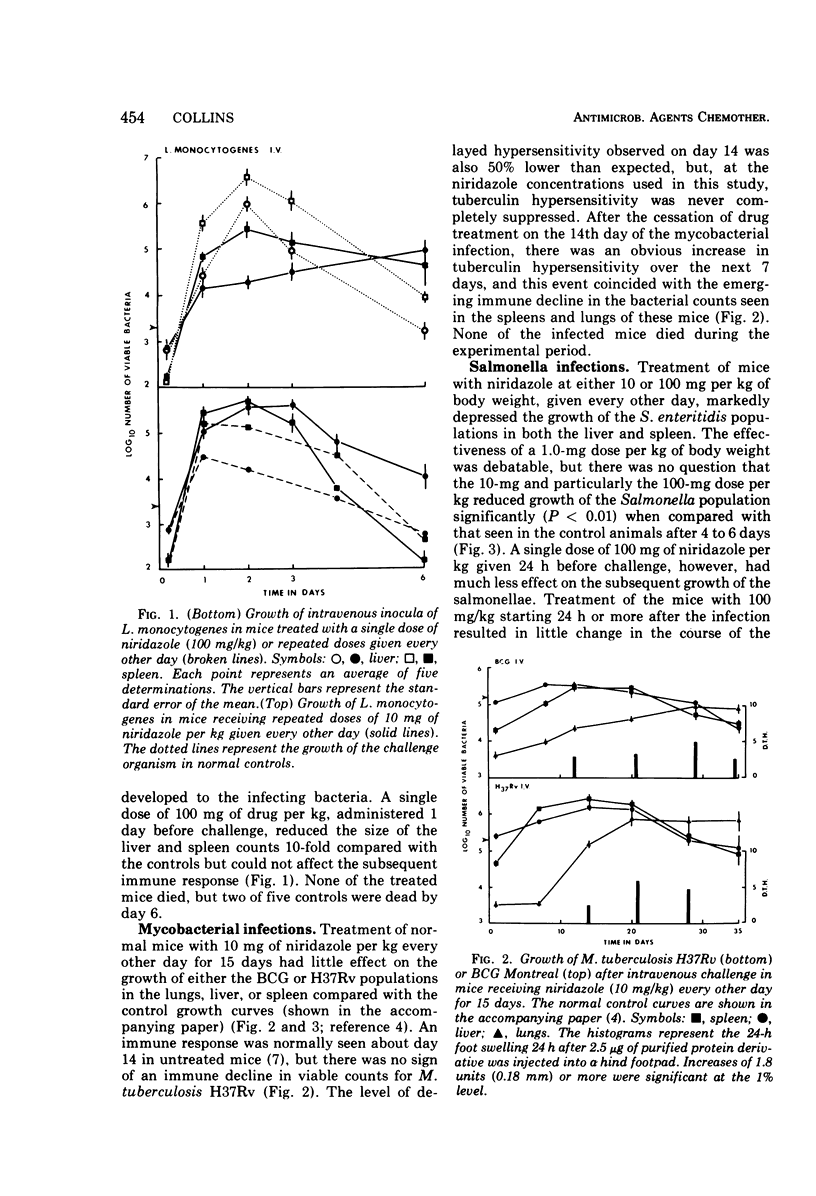
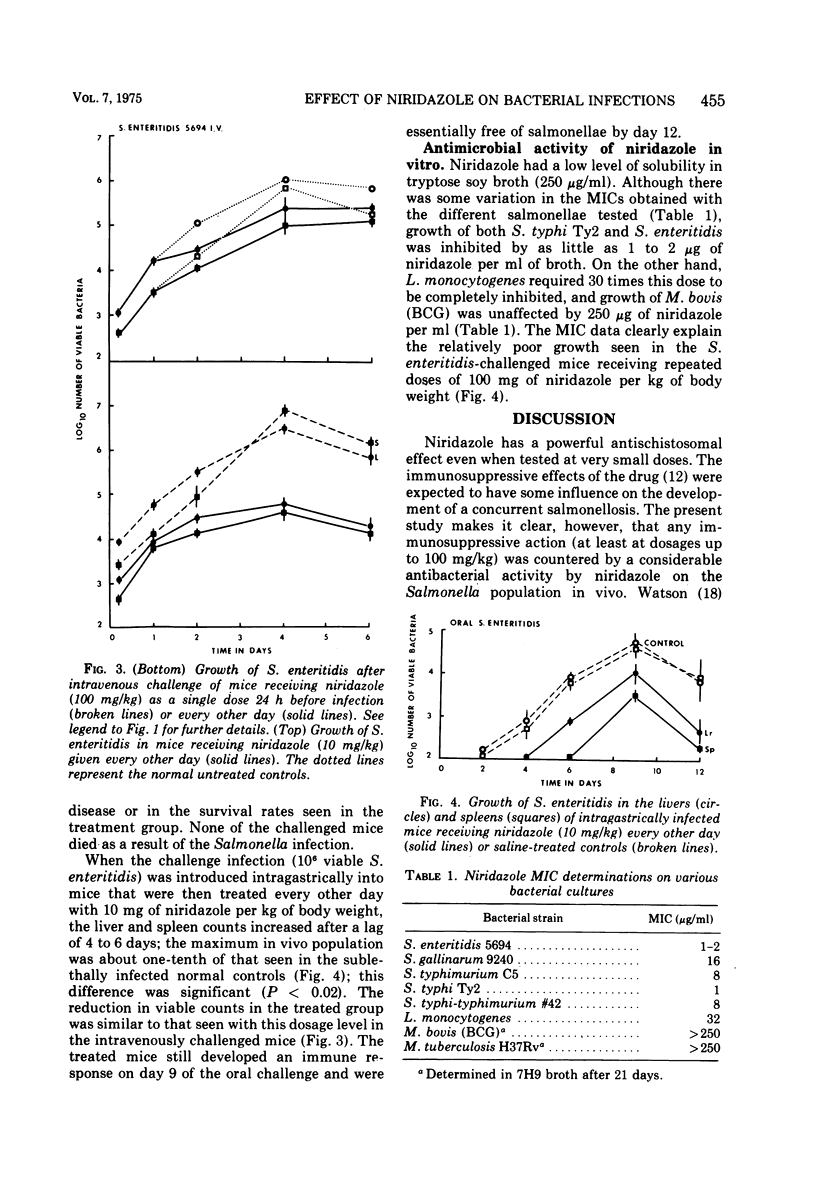
Treatment of specific-pathogen-free CD-1 mice with oral doses of 10 or 100 mg of niridazole per kg of body weight given 24 h before challenge and then every other day for up to 15 days altered the growth curves for Listeria monocytogenes, Mycobacterium bovis (BCG Montreal), M. tuberculosis H37Rv, and Salmonella enteritidis seen in the livers and spleens of the treated animals. Niridazole in an oral dosage of 10 mg/kg reduced (but did not eliminate) tuberculin hypersensitivity in the mycobacteria-infected mice. Both delayed hypersensitivity and antimycobacterial resistance quickly returned to normal levels once the drug treatment was stopped. Niridazole treatment reduced the growth of S. enteritidis in both intravenously and intragastrically challenged mice; this seemed to be due to the antibacterial action of the drug on the salmonellae both in vitro and in vivo.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdallah A., Saif M. Clinical evaluation of niridazole in Schistosoma haematobium and mansoni infections. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Oct 6;160(2):686–695. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb15886.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Carter P. B. Comparative immunogenicity of heat-killed and living oral Salmonella vaccines. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):451–458. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.451-458.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Effect of tilorone treatment on intracellular microbial infections in specific-pathogen-free mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Apr;7(4):447–452. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.4.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Mackaness G. B. Delayed hypersensitivity and arthus reactivity in relation to host resistance in salmonella-infected mice. J Immunol. 1968 Nov;101(5):830–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Mackaness G. B. The relationship of delayed hypersensitivity to acquired antituberculous immunity. I. Tuberculin sensitivity and resistance to reinfection in BCG-vaccinated mice. Cell Immunol. 1970 Sep;1(3):253–265. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Mackaness G. B. The relationship of delayed hypersensitivity to acquired antituberculous immunity. II. Effect of adjuvant on the allergenicity and immunogenicity of heat-killed tubercle bacilli. Cell Immunol. 1970 Sep;1(3):266–275. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Recall of immunity in mice vaccinated with Salmonella enteritidis or Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2014–2021. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2014-2021.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Vaccines and cell-mediated immunity. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Dec;38(4):371–402. doi: 10.1128/br.38.4.371-402.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Wayne L. G., v Montalbine The effect of cultural conditions on the distribution of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the spleens and lungs of specific pathogen-free mice. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1974 Aug;110(2):147–156. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1974.110.2.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diena B. B., Johnson E. M., Baron L. S., Wallace R., Greenberg L. Assay of typhoid vaccines with Salmonella typhosa-Salmonella typhimurium hybrids. Infect Immun. 1973 Jan;7(1):5–8. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.1.5-8.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathout S el-D, Abd el-Ghaffar Y., Awny A. Y., Hassan K. Relation between urinary schistosomiasis and chronic enteric urinary carrier state among Egyptians. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1966 Mar;15(2):156–161. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1966.15.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud A. A., Mandel A., Warren K., Webster L. T., Jr Niridazole. II. A potent long-acting suppressant of cellular hypersensitivity. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):279–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud A. A., Warren K. S. Anti-inflammatory effects of tartar emetic and niridazole: suppression of schistosome egg granuloma. J Immunol. 1974 Jan;112(1):222–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neves J., Raso P., Marinho R. P. Prolonged septicaemic salmonellosis intercurrent with Schistosomiasis mansoni (intestinal polyposis, hepatic and cardiopulmonary forms) Chagas' disease, cerebral cysticercosis, taeniasis, shigellosis, ancylostomiasis, ascariasis and chronic malnutrition. Clinopathologic discussion. J Trop Med Hyg. 1971 Jan;74(1):9–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prata A. Clinical evaluation of niridazole in Schistosoma mansoni infections. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Oct 6;160(2):660–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb15884.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. S., Domingo E. O., Cowan R. B. Granuloma formation around schistosome eggs as a manifestation of delayed hypersensitivity. Am J Pathol. 1967 Nov;51(5):735–756. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson K. C. Salmonella typhimurium infection in mice treated with niridazole. J Med Microbiol. 1970 Aug;3(3):361–365. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-3-361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



