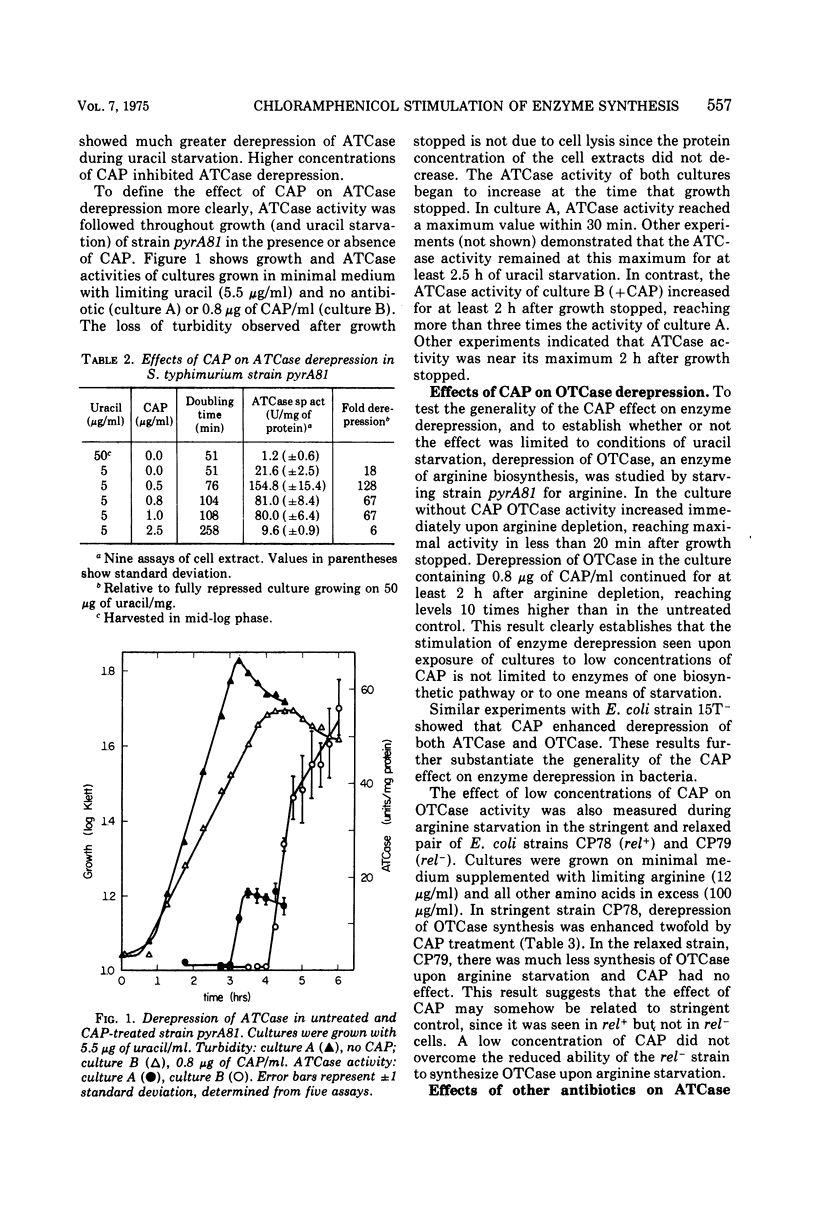
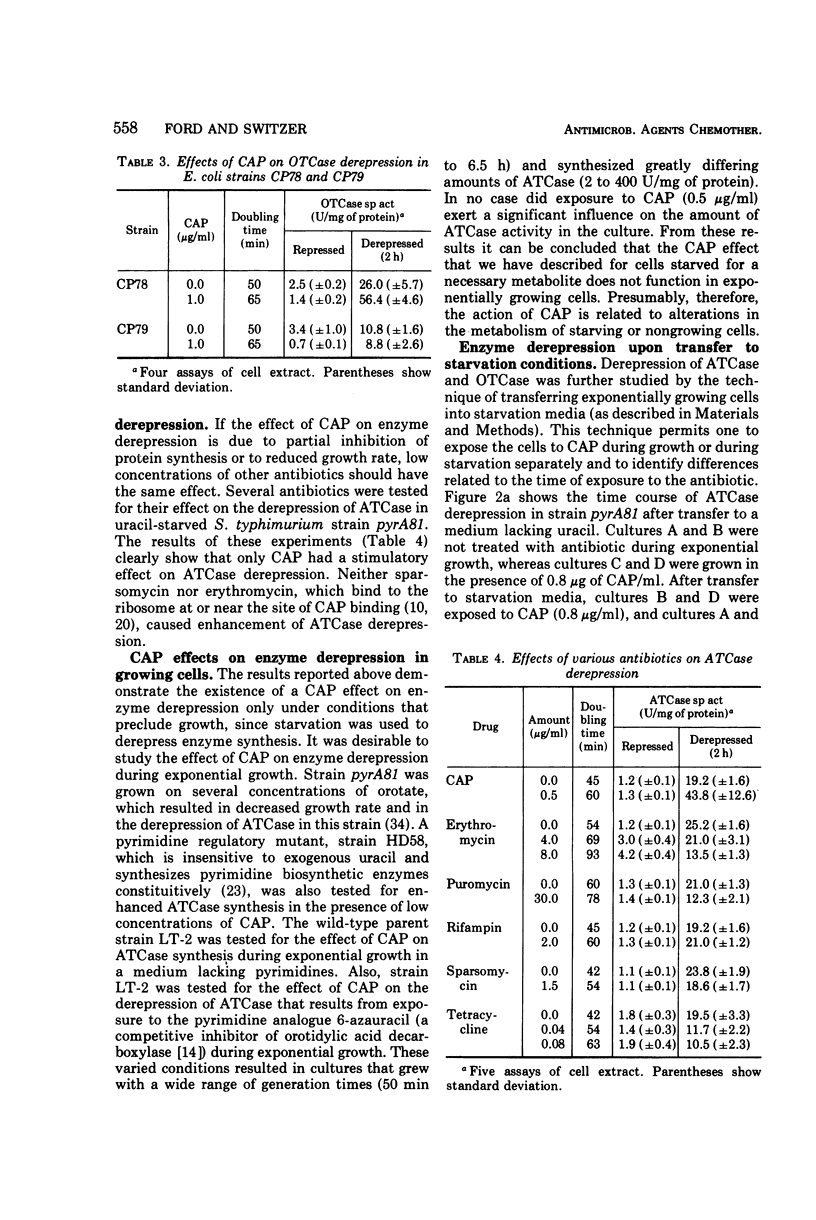
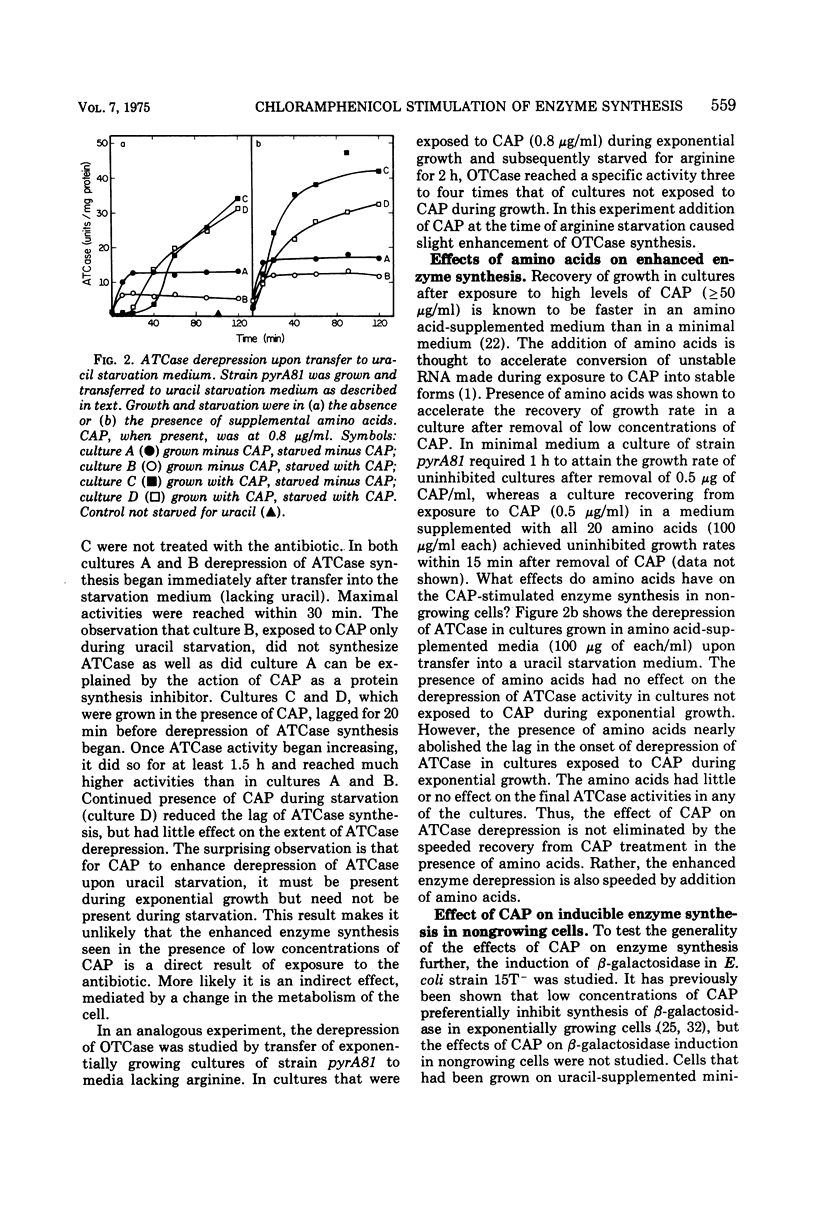
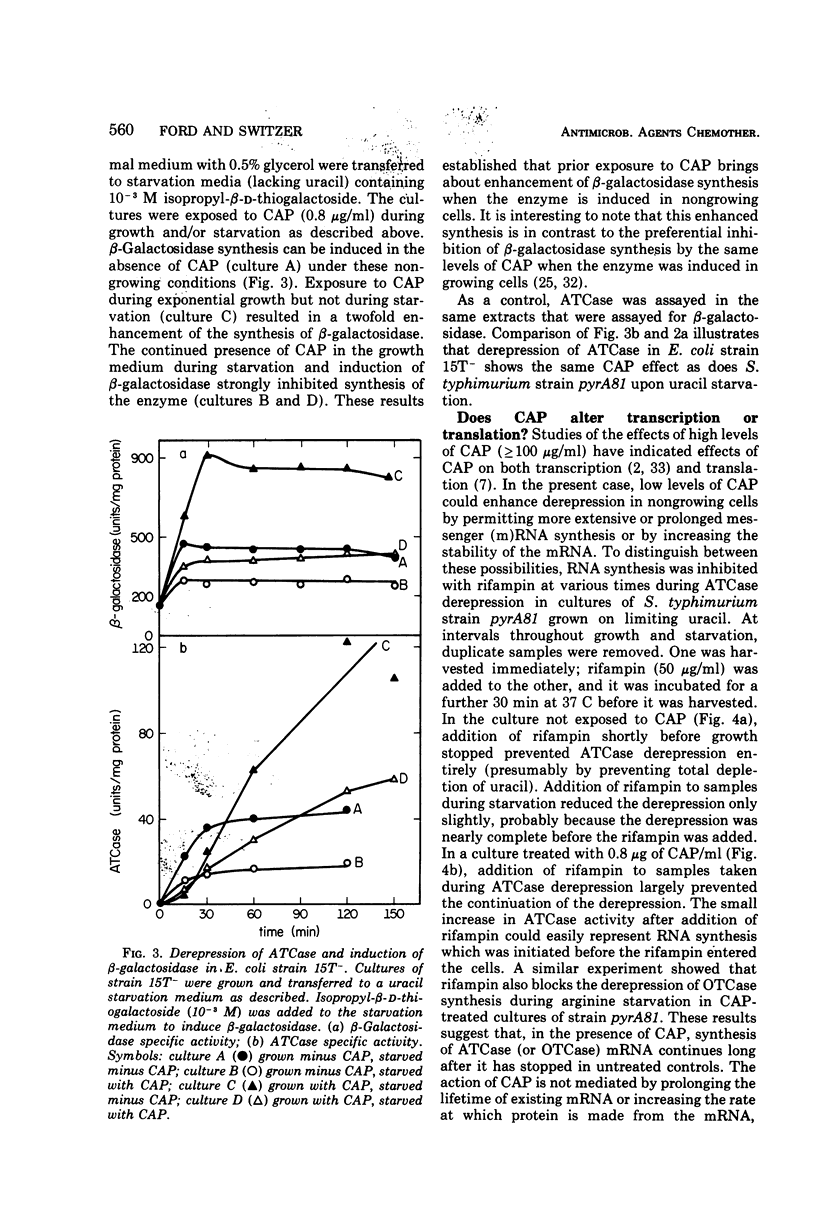
Abstract
Culturing of Salmonella typhimurium or Escherichia coli cells in the presence of low concentrations (≤1 μg/ml) of chloramphenicol (CAP) permitted exponential growth, but at doubling times up to twice those of controls. When such cultures were subsequently starved for uracil or arginine, derepression of aspartate transcarbamylase (ATCase) or ornithine transcarbamylase, respectively, was enhanced three- to 10-fold as compared to cultures not exposed to CAP. Enhancement of β-galactosidase synthesis by prior exposure to CAP was also observed in uracil-starved E. coli cultures. Stimulation of enzyme synthesis appeared to be a specific effect of CAP; low levels of erythromycin, puromycin, sparsomycin, tetracycline, and rifampin did not show such effects. Derepression of ATCase synthesis in exponentially growing cells in the presence of CAP did not result in stimulation of enzyme synthesis by CAP. A prior history of growth of a culture in the presence of CAP was shown to be necessary for enhancement of enzyme synthesis by CAP; furthermore, continued presence of CAP in the medium during starvation was not necessary for enhanced enzyme synthesis and inhibited it in some instances. Enhanced enzyme synthesis in starving, CAP-treated cultures could be blocked by rifampin, which suggested that CAP treatment allows prolonged or more extensive messenger ribonucleic acid synthesis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARONSON A. I., SPIEGELMAN S. On the nature of the ribonucleic acid synthesized in the presence of chloramphenicol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Oct 14;53:84–95. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90796-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artman M., Ennis H. L. Dissociation of Lac messenger ribonucleic acid transcription from translation during recovery from inhibition of protein synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):652–660. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.652-660.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagnara A. S., Finch L. R. Ribonucleoside triphosphate accumulation on amino acid starvation of "stringent" Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Oct 10;33(1):15–21. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90247-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz D., Hushon J. M., Whitfield H. J., Jr, Roth J., Ames B. N. Procedure for identifying nonsense mutations. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jul;96(1):215–220. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.1.215-220.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashel M., Gallant J. Control of RNA synthesis in Escherichia coli. I. Amino acid dependence of the synthesis of the substrates of RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 14;34(2):317–330. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90256-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis P. P., Herman R. K. Pyrimidine pools and macromolecular composition of pyrimidine-limited Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Apr;102(1):118–123. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.1.118-123.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dütting D., Hübner L. The effect of antibiotics on the in vivo synthesis of messenger ribonucleic acid from the lactose operon of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;116(3):277–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00269771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlin G., Maaloe O. Synthesis and breakdown of messenger RNA without protein synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1966 Feb;15(2):428–434. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlin G., Neuhard J. Regulation of nucleoside triphosphate pools in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1967 Mar 14;24(2):225–230. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90328-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Munoz R., Monro R. E., Torres-Pinedo R., Vazquez D. Substrate- and antibiotic-binding sites at the peptidyl-transferase centre of Escherichia coli ribosomes. Studies on the chloramphenicol. lincomycin and erythromycin sites. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Nov 11;23(1):185–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiil N., Friesen J. D. Isolation of "relaxed" mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):729–731. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.729-731.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford S. R., Switzer R. L. Stimulation of enzyme synthesis by sublethal concentrations of chloramphenicol is not mediated by ribonucleotide pools. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 May;7(5):564–570. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.5.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAHN F. E., SCHAECHTER M., CEGLOWSKI W. S., HOPPS H. E., CIAK J. Interrelations between nucleic acid and protein biosynthesis. I. Synthesis and fate of bacterial nucleic acids during exposure to, and recovery from the action of chloramphenicol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Dec;26(3):469–476. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90092-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANDSCHUMACHER R. E. Orotidylic acid decarboxylase: inhibition studies with azauridine 5'-phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1960 Oct;235:2917–2919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irr J., Gallant J. The control of ribonucleic acid synthesis in Escherichia coli. II. Stringent control of energy metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1969 Apr 25;244(8):2233–2239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KURLAND C. G., MAALOE O. Regulation of ribosomal and transfer RNA synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1962 Mar;4:193–210. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midgley J. E., Gray W. J. The control of ribonucleic acid synthesis in bacteria. The synthesis and stability of ribonucleic acid in chloramphenicol-inhibited cultures of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1971 Apr;122(2):149–159. doi: 10.1042/bj1220149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monro R. E., Staehelin T., Celma M. L., Vazquez D. The peptidyl transferase activity of ribosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:357–368. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKADA D., MAGASANIK B. THE ROLES OF INDUCER AND CATABOLITE REPRESSOR IN THE SYNTHESIS OF BETA-GALACTOSIDASE BY ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Mol Biol. 1964 Jan;8:105–127. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80153-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEIDHARDT F. C., GROS F. Metabolic instability of the ribonucleic acid synthesized by Escherichia coli in the presence of chloromycetin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Sep;25(3):513–520. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90521-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donovan G. A., Gerhart J. C. Isolation and partial characterization of regulatory mutants of the pyrimidine pathway in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1972 Mar;109(3):1085–1096. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.3.1085-1096.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa S. Ribosome formation and structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1968;37:109–130. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.37.070168.000545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAIGEN K. CHANGES IN THE INDUCIBILITY OF GALACTOKINASE AND BETA-GALACTOSIDASE DURING INHIBITION OF GROWTH IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Oct 1;77:318–328. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90502-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine M. J. Regulation of intracellular proteolysis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):107–116. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.107-116.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott L. M., Jones M. E. Modified methods for the determination of carbamyl aspartate. Anal Biochem. 1969 Dec;32(3):408–419. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(69)80008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SYPHERD P. S., DEMOSS J. A. THE STIMULATION BY CHLORAMPHENICOL OF "REPRESSOR" FORMATION IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Dec 20;76:589–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SYPHERD P. S., STRAUSS N. THE ROLE OF RNA IN REPRESSION OF ENZYME SYNTHESIS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Dec;50:1059–1066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.6.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman A. J., Gilvarg C. Protein turnover in amino acid-starved strains of Escherichia coli K-12 differing in their ribonucleic acid control. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6304–6306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sypherd P. S., Strauss N. CHLORAMPHENICOL-PROMOTED REPRESSION OF beta-GALACTOSIDASE SYNTHESIS IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Mar;49(3):400–407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.3.400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E., Perlman R. L., Pastan I. Regulation of lac transcription in antibiotic-treated E. coli. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 10;230(10):41–44. doi: 10.1038/newbio230041a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. N., Olszowy J., Switzer R. L. Regulation and mechanism of phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase: repression by end products. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):122–131. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.122-131.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YATES R. A., PARDEE A. B. Control by uracil of formation of enzymes required for orotate synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1957 Aug;227(2):677–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan Y., Demerec M. Genetic analysis of pyrimidine mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. Genetics. 1965 Sep;52(3):643–651. doi: 10.1093/genetics/52.3.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


