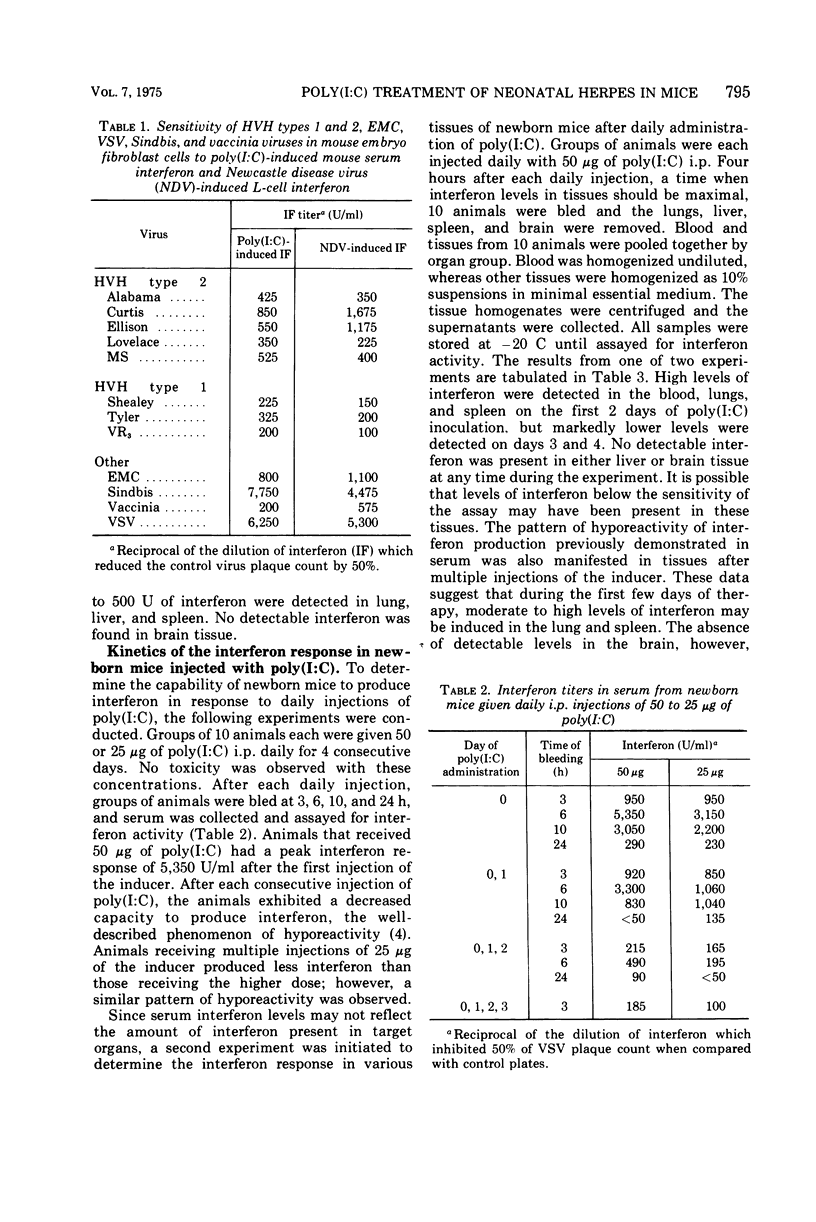
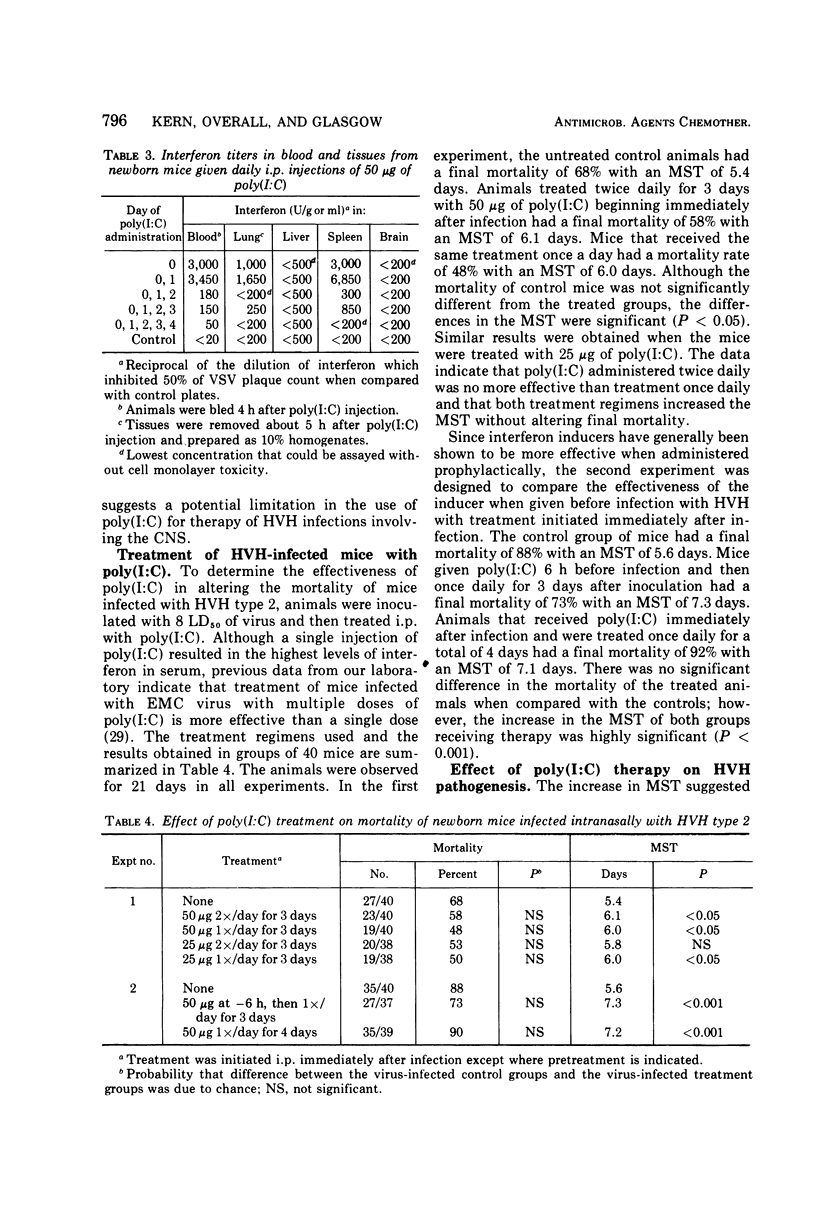
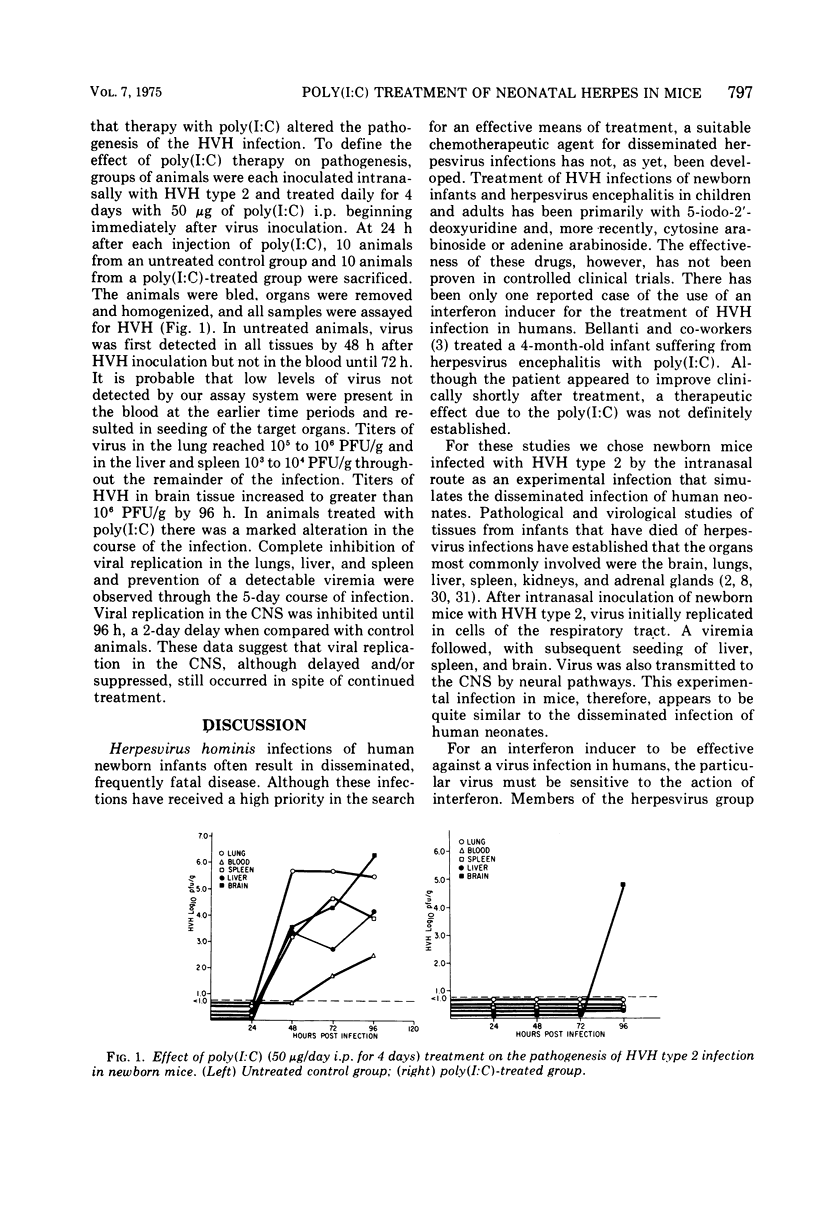
Abstract
Intranasal inoculation of newborn mice with Herpesvirus hominis (HVH) type 2 provides a model for disseminated herpesvirus infections of human newborn infants. Treatment of this experimental infection with polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid [poly(I:C)] significantly increased the mean survival time and markedly altered the pathogenesis of the infection. No significant protection against final mortality was observed. Poly(I:C) therapy completely inhibited detectable viral replication in all target organs tested except the brain. In the brain there was a 2-day delay in the onset of viral replication in treated animals, which correlated with the 1- to 2-day increase in mean survival time. In general, the control of HVH replication occurred in those target organs in which poly(I:C)-induced interferon was detectable. The failure of poly(I:C) to alter the final mortality of newborn mice infected with HVH appears to be primarily due to the lack of sufficient levels of interferon induced in brain tissue and the failure to prevent viral replication in this critical target organ.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen L. B., Cochran K. W. Target-organ treatment of neurotropic virus disease with interferon inducers. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):819–823. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.819-823.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker W. B., Kipps A., McKenzie D. Disseminated herpes simplex virus infection. Its pathogenesis based on virological and pathological studies in 33 cases. Am J Dis Child. 1968 Jan;115(1):1–8. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1968.02100010003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellanti J. A., Catalano L. W., Jr, Chambers R. W. Herpes simplex encephalitis: virologic and serologic study of a patient treated with an interferon inducer. J Pediatr. 1971 Jan;78(1):136–145. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80281-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckler C. E., DuBuy H. G., Johnson M. L., Baron S. Kinetics of serum interferon response in mice after single and multiple injections of polyI-poly C. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Feb;136(2):394–398. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CANTELL K., TOMMILA V. Effect of interferon on experimental vaccinia and herpes-simplex virus infections in rabbits' eyes. Lancet. 1960 Sep 24;2(7152):682–684. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(60)91751-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catalano L. W., Jr, Baron S. Protection against herpes virus and encephalomyocarditis virus encephalitis with a double-stranded RNA inducer of interferon. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Feb;133(2):684–687. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catalano L. W., Jr, London W. T., Rice J. M., Sever J. L. Prophylactic and therapeutic use of poly(I)-poly(C) (poly-D-lysine) against herpesvirus encephalitis in mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 May;140(1):66–71. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catalano L. W., Jr, Safley G. H., Museles M., Jarzynski D. J. Disseminated herpesvirus infection in a newborn infant. Virologic, serologic, coagulation, and interferon studies. J Pediatr. 1971 Sep;79(3):393–400. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80146-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala F., Baron S. Interferon in rabbit brain, cerebrospinal fluid and serum following administration of polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid. J Immunol. 1970 Jun;104(6):1355–1358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Merigan T. C. Current concepts of interferon and interferon induction. Annu Rev Med. 1970;21:17–46. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.21.020170.000313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finter N. B. Exogenous interferon in animals and its clinical implications. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Jul;126(1):147–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasgow L. A., Hanshaw J. B., Merigan T. C., Petralli J. K. Interferon and cytomegalovirus in vivo and in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Jul;125(3):843–849. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Bourali C., Thomas M. T., Falcoff E. Effect of repeated inoculation of interferon preparations on infection of mice with encephalomyocarditis virus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Feb;127(2):491–496. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEINEBERG H., GOLD E., ROBBINS F. C. DIFFERENCES IN INTERFERON CONTENT IN TISSUES OF MICE OF VARIOUS AGES INFECTED WITH COXSACKIE B1 VIRUS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Apr;115:947–953. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-29086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton L. D., Babcock V. I., Southam C. M. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus by synthetic double-stranded RNA (polyriboadenylic and polyribouridylic acids and polyriboinosinic and polyribocytidylic acids). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Nov;64(3):878–883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.3.878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilleman M. R. Double-stranded RNAs (poly I:C) in the prevention of viral infections. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Jul;126(1):109–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilleman M. R. Prospects for the use of double-stranded ribonucleic acid (poly I:C) inducers in man. J Infect Dis. 1970 Feb;121(2):196–211. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.2.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES B. R., GALBRAITH J. E., AL-HUSSAINI M. K. Vaccinial keratitis treated with interferon. Lancet. 1962 Apr 28;1(7235):875–879. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(62)91908-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern E. R., Overall J. C., Jr, Glasgow L. A. Herpesvirus hominis infection in newborn mice. I. An experimental model and therapy with iododeoxyuridine. J Infect Dis. 1973 Sep;128(3):290–299. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.3.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morahan P. S., Grossberg S. E. Age-related cellular resistance of the chicken embryo to viral infections. I. Interferon and natural resistance to myxoviruses and vesicular stomatitis virus. J Infect Dis. 1970 Jun;121(6):615–623. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.6.615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahmias A. J., Alford C. A., Korones S. B. Infection of the newborn with herpesvirus hominis. Adv Pediatr. 1970;17:185–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh J. O. Sensitivity of Types 1 and 2 Herpesvirus hominis to an Interferon Inducer, Poly I:C. Infect Immun. 1971 Jun;3(6):847–848. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.6.847-848.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. E., Medearis D. N., Jr Suppression of interferon and antibody and multiplication of Newcastle disease virus in cytomegalovirus infected mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Feb;124(2):347–353. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park J. H., Baron S. Herpetic keratoconjunctivitis: therapy with synthetic double-stranded RNA. Science. 1968 Nov 15;162(3855):811–813. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3855.811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringfellow D. A., Glasgow L. A. Hyporeactivity of infection: potential limitation to therapeutic use of interferon-inducing agents. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):743–747. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.743-747.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringfellow D. A., Glasgow L. A. Tilorone hydrochloride: an oral interferon-inducing agent. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Aug;2(2):73–78. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.2.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringfellow D. A., Overall J. C., Jr, Glasgow L. A. Interferon inducers in therapy of infection with encephalomyocarditis virus in mice. II. Effect of multiple doses of polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid on viral pathogenesis. J Infect Dis. 1974 Nov;130(5):481–488. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.5.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHEELER C. E., Jr, HUFFINES W. D. PRIMARY DISSEMINATED HERPES SIMPLEX OF THE NEWBORN. JAMA. 1965 Feb 8;191:455–460. doi: 10.1001/jama.1965.03080060029005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE J. G. Fulminating infection with herpes-simplex virus in premature and newborn infants. N Engl J Med. 1963 Aug 29;269:455–460. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196308292690906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


