Abstract
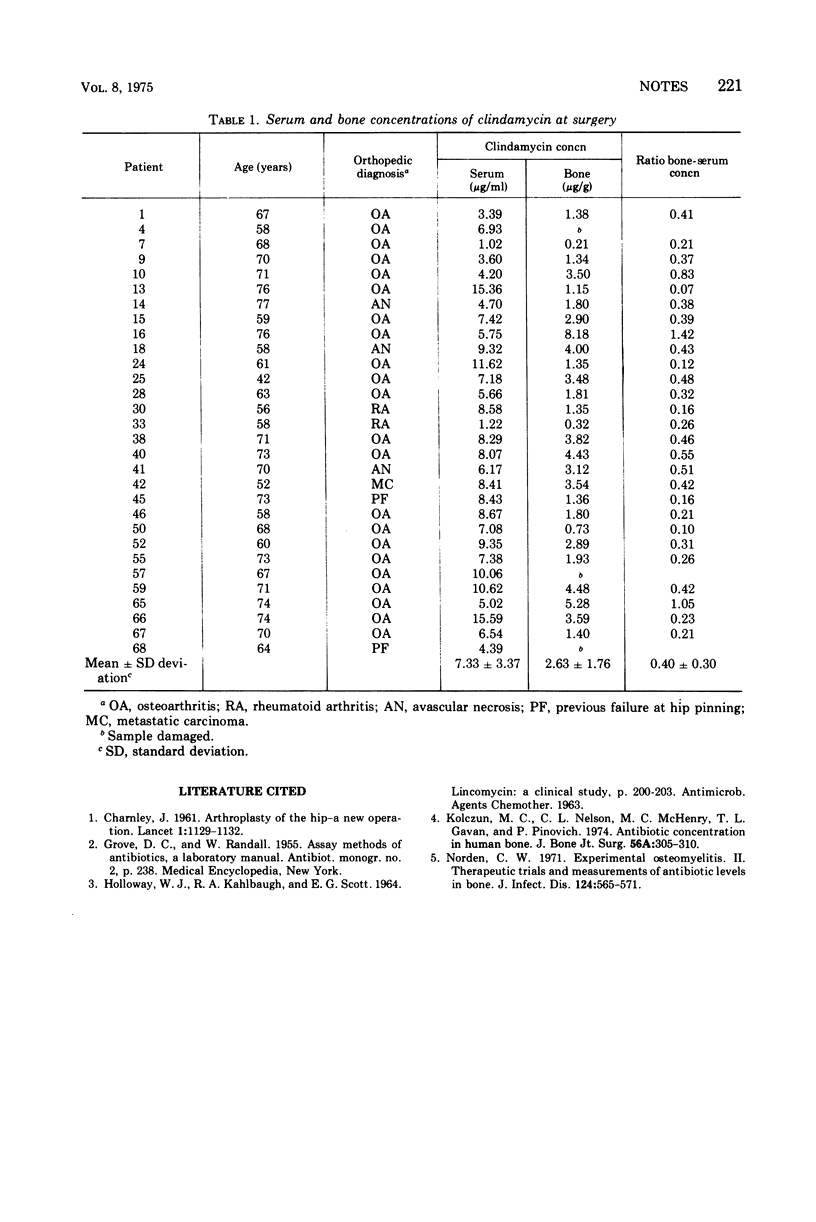
Thirty patients undergoing total hip replacement received clindamycin beginning the day before surgery. Mean clindamycin concentrations during surgery were 7.33 ± 3.37 μg/ml in serum and 2.63 ± 1.76 μg/g in bone; mean ratio of bone-serum concentration was 0.40 ± 0.30.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Charnley J. Arthroplasty of the hip. A new operation. Lancet. 1961 May 27;1(7187):1129–1132. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)92063-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolczun M. C., Nelson C. L., McHenry M. C., Gavan T. L., Pinovich P. Antibiotic concentrations in human bone. A preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974 Mar;56(2):305–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden C. W. Experimental osteomyelitis. II. Therapeutic trials and measurement of antibiotic levels in bone. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124(6):565–571. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.6.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


