Abstract
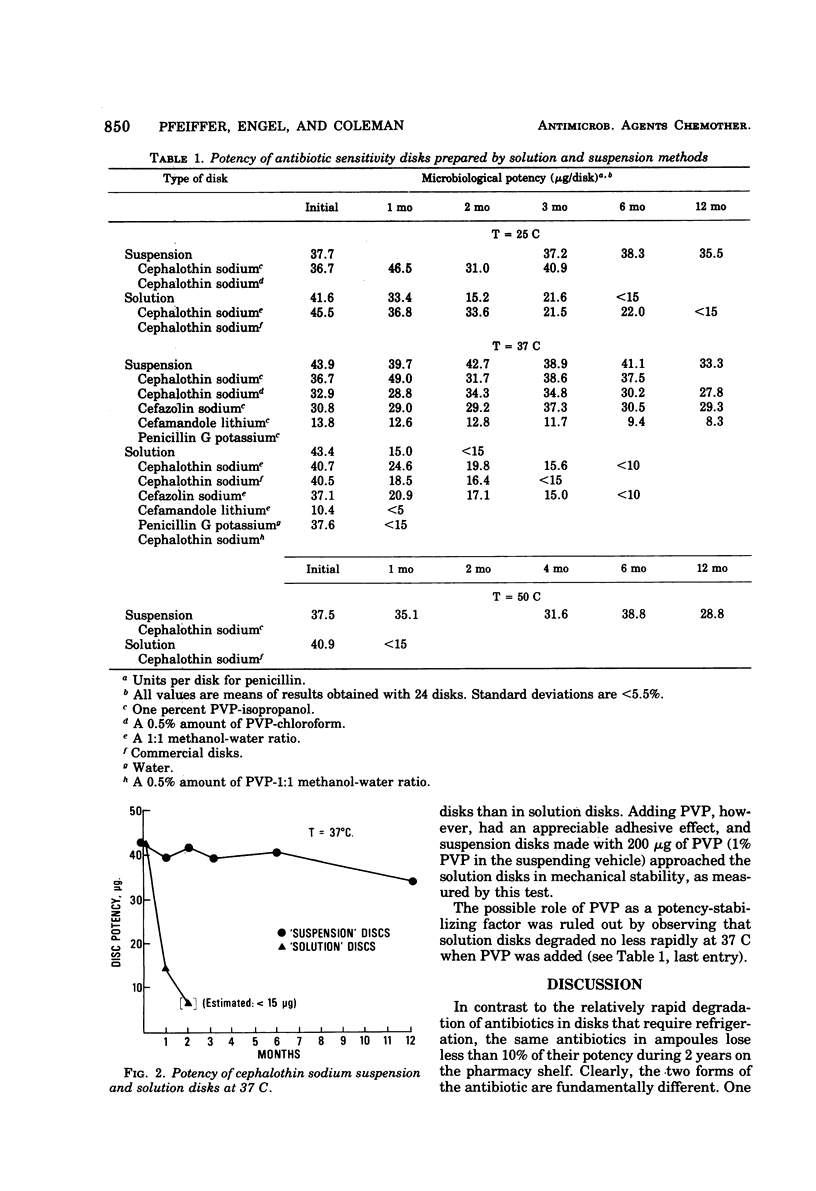
Two methods of preparing sensitivity disks were compared for their effect on disk stability at 25 and 37 C. One method consisted of applying a solution of the antibiotic to blank disks by the conventional procedure; the second method consisted of applying the antibiotic to the disks as a suspension of crystals. Of the four β-lactam antibiotics that were studied, disks made with suspended crystals were substantially more stable than corresponding disks made by the conventional method. The increased stability is related to the greater chemical stability of the antibiotics in the crystalline versus the amorphous state.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Mathews A. G., Schram C. J., Minty D. Crystallization of penicillin in the solid phase. Nature. 1966 Aug 27;211(5052):959–959. doi: 10.1038/211959a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick W. E., Preston D. A. Biological properties of three 3-heterocyclic-thiomethyl cephalosporin antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Mar;1(3):221–234. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.3.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]