Abstract
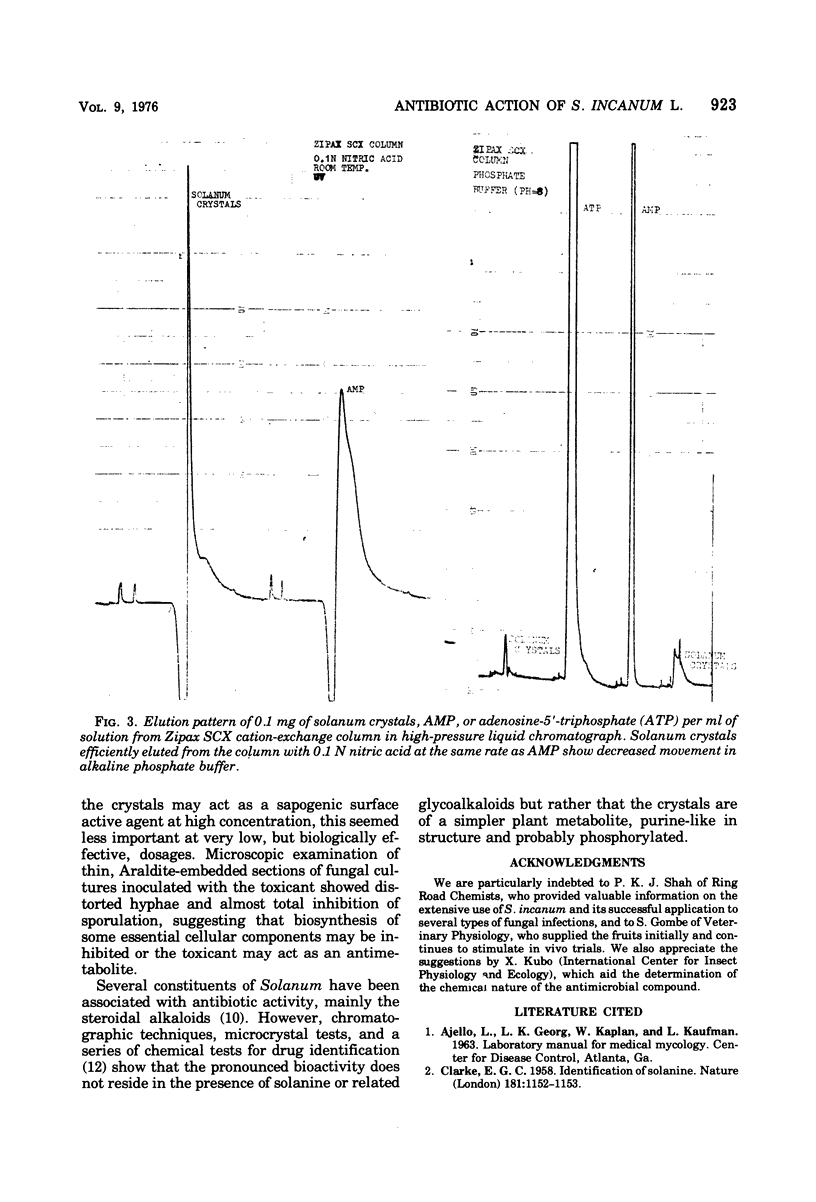
The fruits of Solanum incanum Linnaeus are extensively used in Kenya for the treatment of cutaneous mycotic infections and other pathological conditions. The therapeutic activity of the berries has been attributed to their content of solanine and related glycoalkaloids, which are saponins and cytostatic poisons. In the present study, however, a simpler more potent antimicrobial substance with a phosphorylated structure similar to the purine adenine was isolated from the berries. The crystals of this compound were effective inhibitors of the growth of gram-positive and -negative bacteria, yeasts, dermatophytes, and some pathogens of agricultural produce. High concentrations of the substance caused hemolysis of erythrocytes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CLARKE E. G. Identification of solanine. Nature. 1958 Apr 19;181(4616):1152–1153. doi: 10.1038/1811152b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupchan S. M., Barboutis S. J., Knox J. R., Cam C. A. Beta-solamarine: tumor inhibitor isolated from Solanum dulcamara. Science. 1965 Dec 31;150(3705):1827–1828. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3705.1827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKEE R. K. Factors affecting the toxicity of solanine and related alkaloids to Fusarium caeruleum. J Gen Microbiol. 1959 Jun;20(3):686–696. doi: 10.1099/00221287-20-3-686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]