Abstract
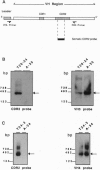
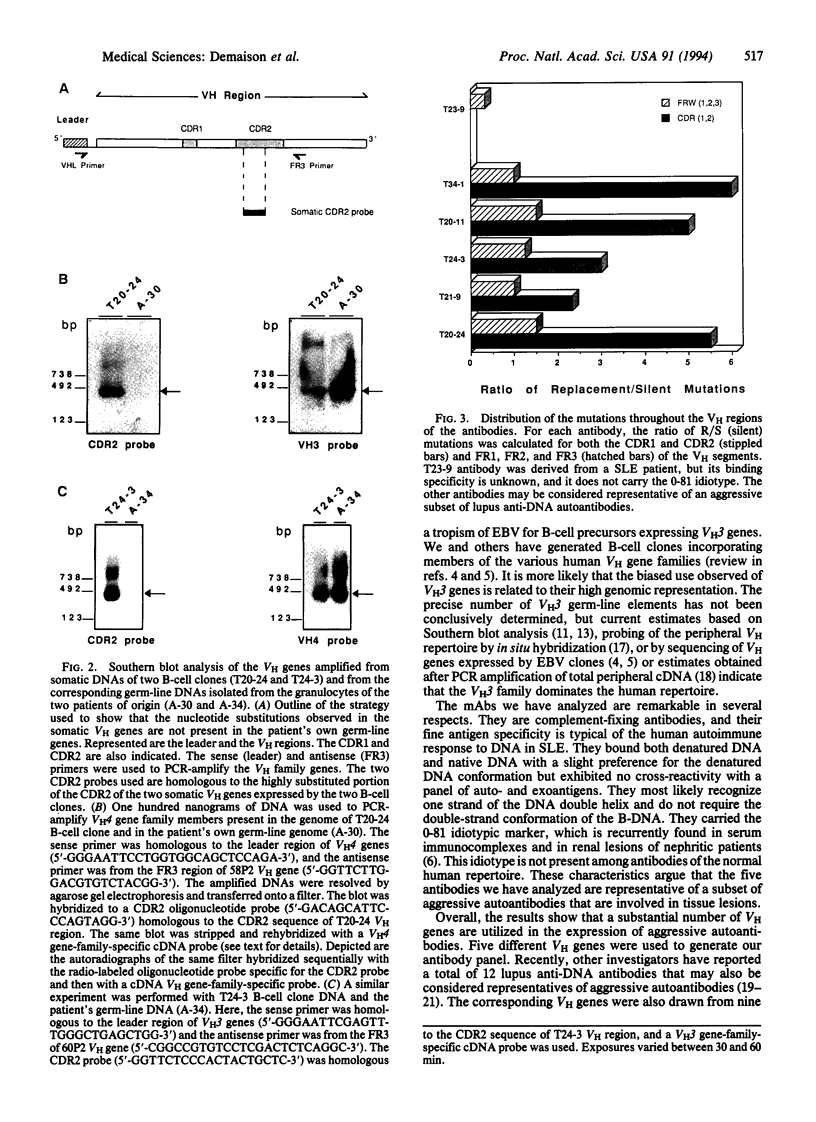
Monoclonal anti-DNA antibodies bearing a lupus nephritis-associated idiotype were derived from five patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Genes encoding their heavy (H)-chain variable (VH) regions were cloned and sequenced. When compared with their closest VH germ-line gene relatives, these sequences exhibit a number of silent (S) and replacement (R) substitutions. The ratios of R/S mutations were much higher in the complementarity-determining regions (CDRs) of the antibodies than in the framework regions. Molecular amplification of genomic VH genes and Southern hybridization with somatic CDR2-specific oligonucleotide probes showed that the configuration of the VH genes corresponding to VH sequences in the nephritogenic antibodies is not present in the patient's own germ-line DNA, implying that the B-cell clones underwent somatic mutation in vivo. These findings, together with the characteristics of the diversity and junctional gene elements utilized to form the antibody, indicate that these autoantibodies have been driven through somatic selection processes reminiscent of those that govern antibody responses triggered by exogenous stimuli.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berek C., Milstein C. The dynamic nature of the antibody repertoire. Immunol Rev. 1988 Oct;105:5–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00763.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman J. E., Mellis S. J., Pollock R., Smith C. L., Suh H., Heinke B., Kowal C., Surti U., Chess L., Cantor C. R. Content and organization of the human Ig VH locus: definition of three new VH families and linkage to the Ig CH locus. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):727–738. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02869.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond B., Scharff M. D. Somatic mutation of the T15 heavy chain gives rise to an antibody with autoantibody specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5841–5844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn B. H. Characteristics of pathogenic subpopulations of antibodies to DNA. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Jul;25(7):747–752. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. H., Matsuda F., Kinashi T., Kodaira M., Honjo T. A novel family of variable region genes of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):761–768. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90482-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy N. S., Malipiero U. V., Lebecque S. G., Gearhart P. J. Early onset of somatic mutation in immunoglobulin VH genes during the primary immune response. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):2007–2019. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manheimer-Lory A., Katz J. B., Pillinger M., Ghossein C., Smith A., Diamond B. Molecular characteristics of antibodies bearing an anti-DNA-associated idiotype. J Exp Med. 1991 Dec 1;174(6):1639–1652. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.6.1639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks J. D., Tristem M., Karpas A., Winter G. Oligonucleotide primers for polymerase chain reaction amplification of human immunoglobulin variable genes and design of family-specific oligonucleotide probes. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Apr;21(4):985–991. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthyssens G., Rabbitts T. H. Structure and multiplicity of genes for the human immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6561–6565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muryoi T., Sasaki T., Hatakeyama A., Shibata S., Suzuki M., Seino J., Yoshinaga K. Clonotypes of anti-DNA antibodies expressing specific idiotypes in immune complexes of patients with active lupus nephritis. J Immunol. 1990 May 15;144(10):3856–3861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascual V., Capra J. D. Human immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable region genes: organization, polymorphism, and expression. Adv Immunol. 1991;49:1–74. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60774-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajewsky K., Förster I., Cumano A. Evolutionary and somatic selection of the antibody repertoire in the mouse. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1088–1094. doi: 10.1126/science.3317826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanz I. Multiple mechanisms participate in the generation of diversity of human H chain CDR3 regions. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 1;147(5):1720–1729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder H. W., Jr, Hillson J. L., Perlmutter R. M. Early restriction of the human antibody repertoire. Science. 1987 Nov 6;238(4828):791–793. doi: 10.1126/science.3118465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder H. W., Jr, Wang J. Y. Preferential utilization of conserved immunoglobulin heavy chain variable gene segments during human fetal life. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6146–6150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlomchik M., Mascelli M., Shan H., Radic M. Z., Pisetsky D., Marshak-Rothstein A., Weigert M. Anti-DNA antibodies from autoimmune mice arise by clonal expansion and somatic mutation. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):265–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler T. H., Fehr H., Kalden J. R. Analysis of immunoglobulin variable region genes from human IgG anti-DNA hybridomas. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jul;22(7):1719–1728. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada M., Wasserman R., Reichard B. A., Shane S., Caton A. J., Rovera G. Preferential utilization of specific immunoglobulin heavy chain diversity and joining segments in adult human peripheral blood B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):395–407. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zouali M. Development of human antibody variable genes in systemic autoimmunity. Immunol Rev. 1992 Aug;128:73–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1992.tb00833.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zouali M., Madaio M. P., Canoso R. T., Stollar B. D. Restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of the V kappa locus in human lupus. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Sep;19(9):1757–1760. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zouali M., Stollar B. D. A rapid ELISA for measurement of antibodies to nucleic acid antigens using UV-treated polystyrene microplates. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Jun 10;90(1):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90390-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zouali M., Theze J. Probing VH gene-family utilization in human peripheral B cells by in situ hybridization. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 15;146(8):2855–2864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Es J. H., Gmelig Meyling F. H., van de Akker W. R., Aanstoot H., Derksen R. H., Logtenberg T. Somatic mutations in the variable regions of a human IgG anti-double-stranded DNA autoantibody suggest a role for antigen in the induction of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):461–470. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]