Abstract
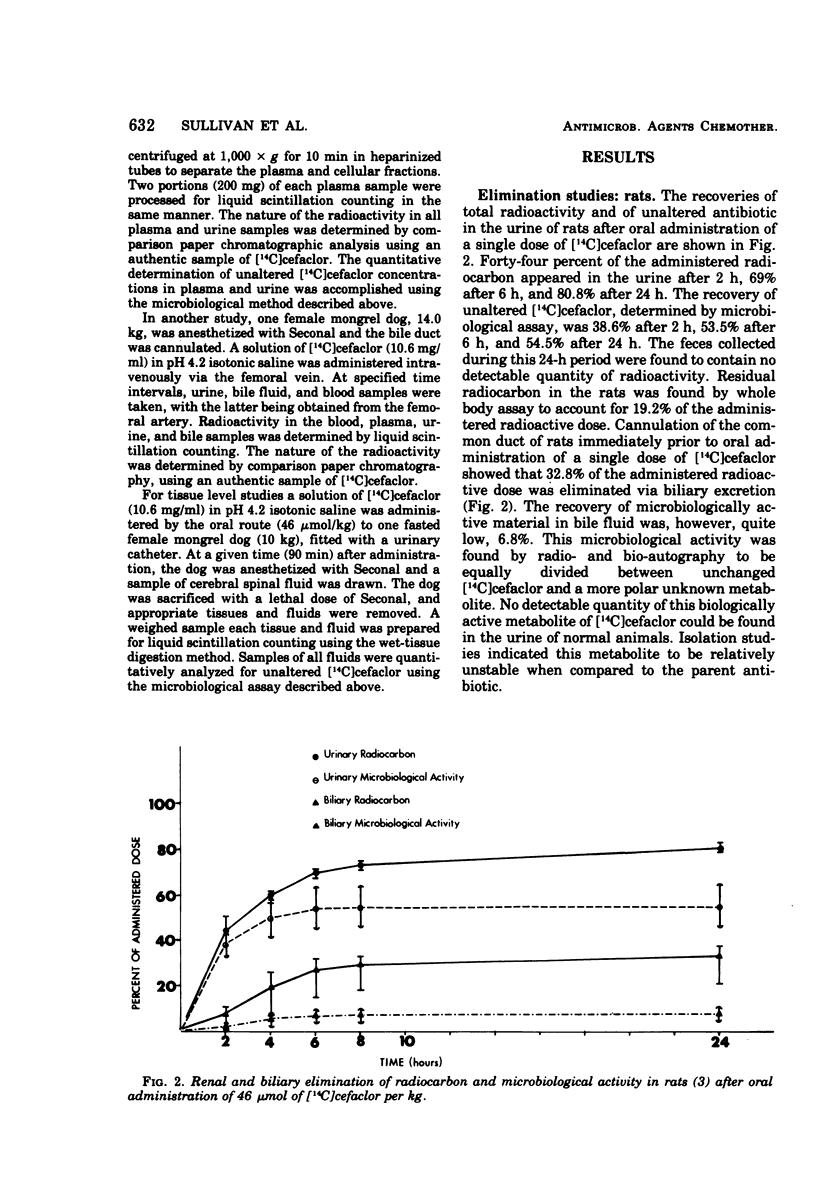
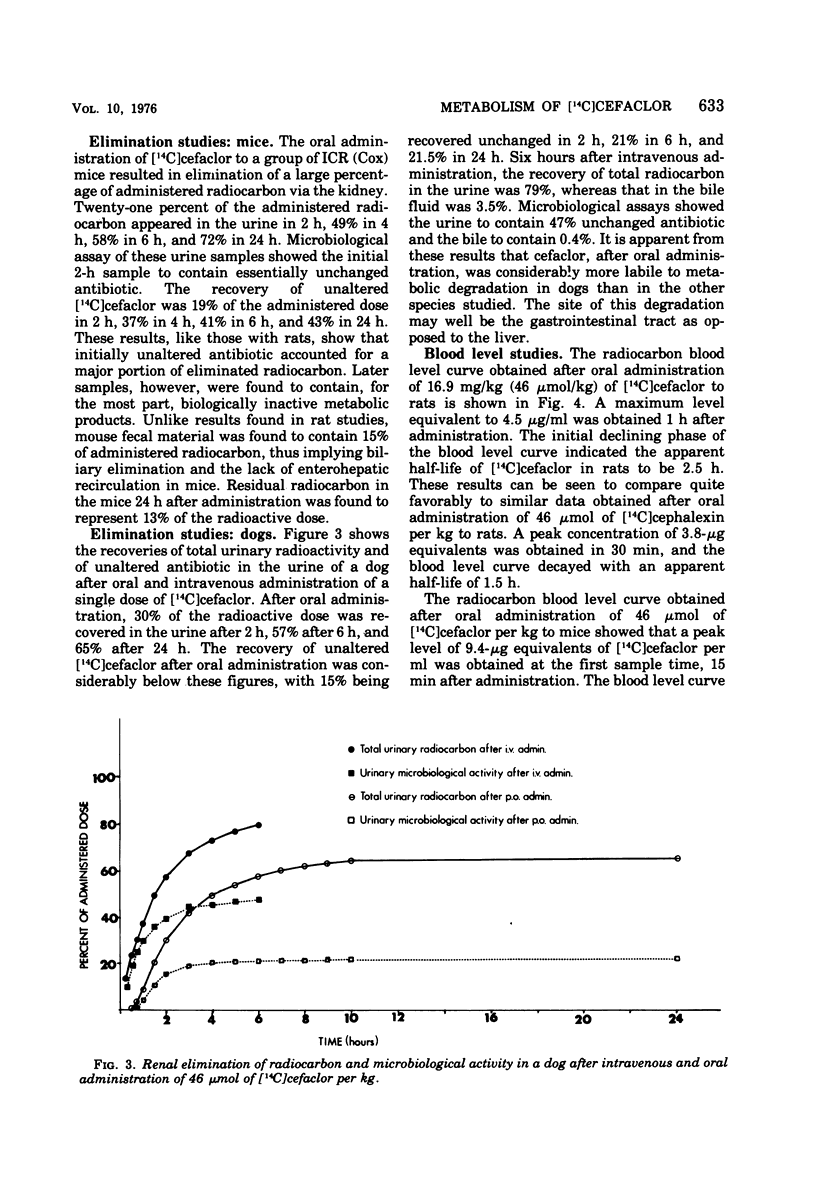
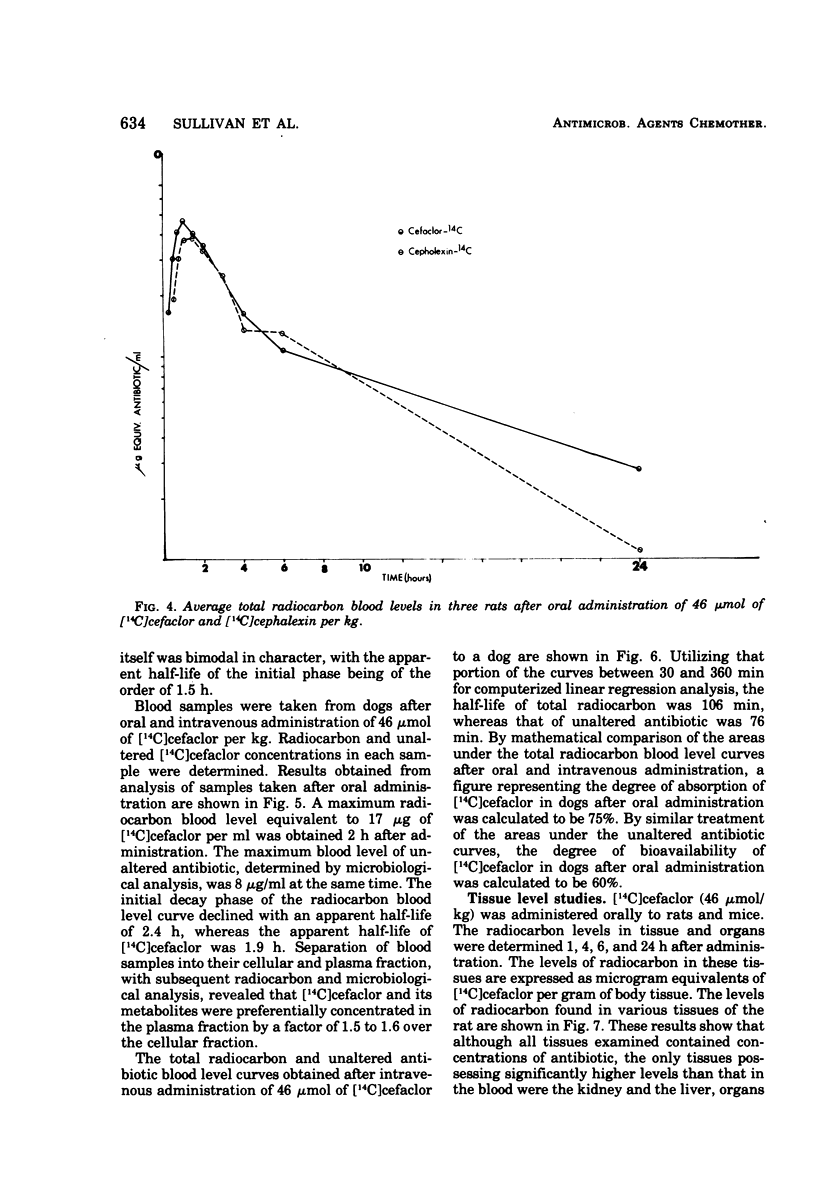
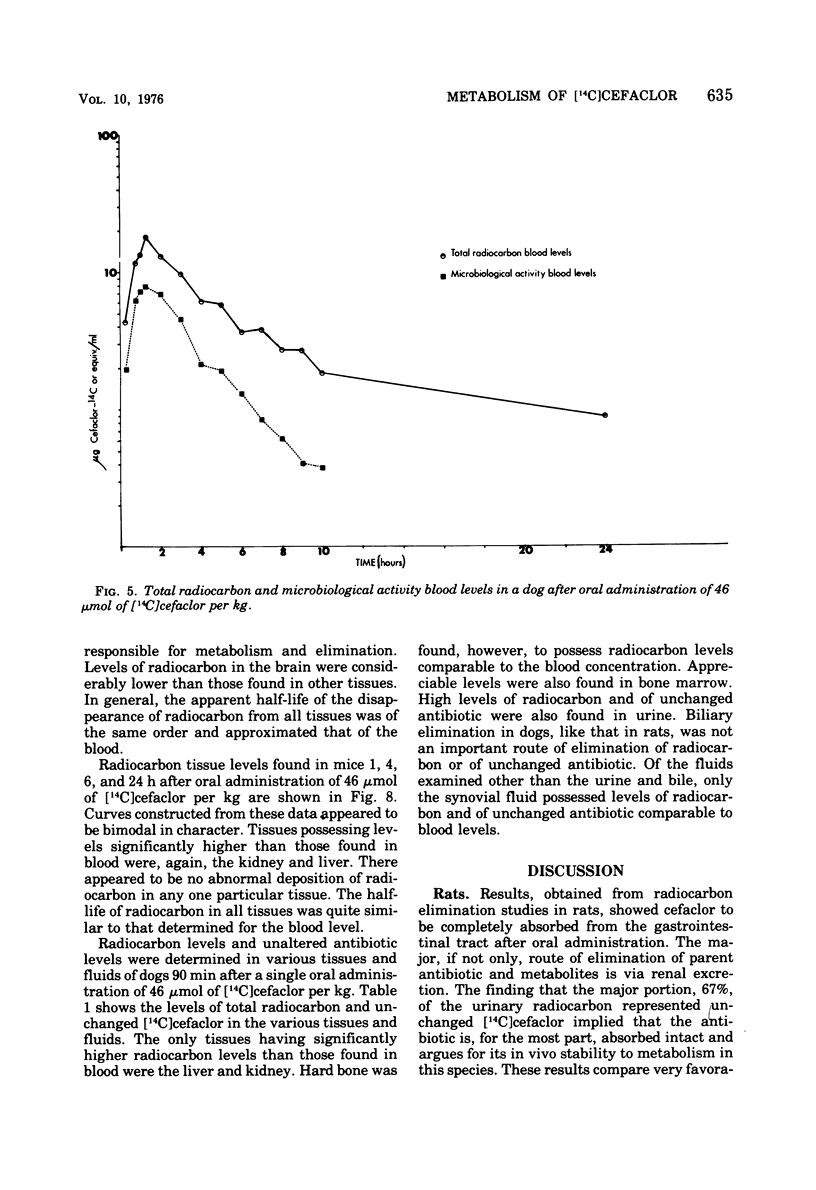
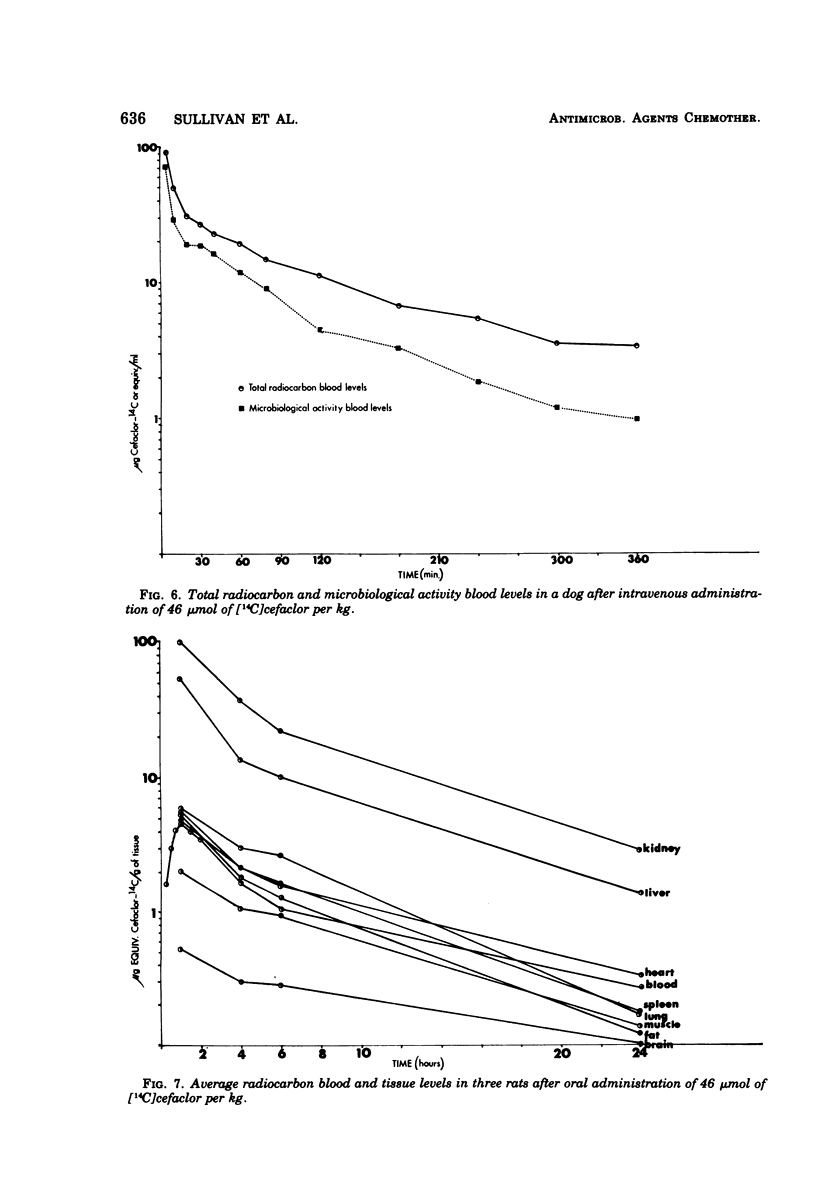
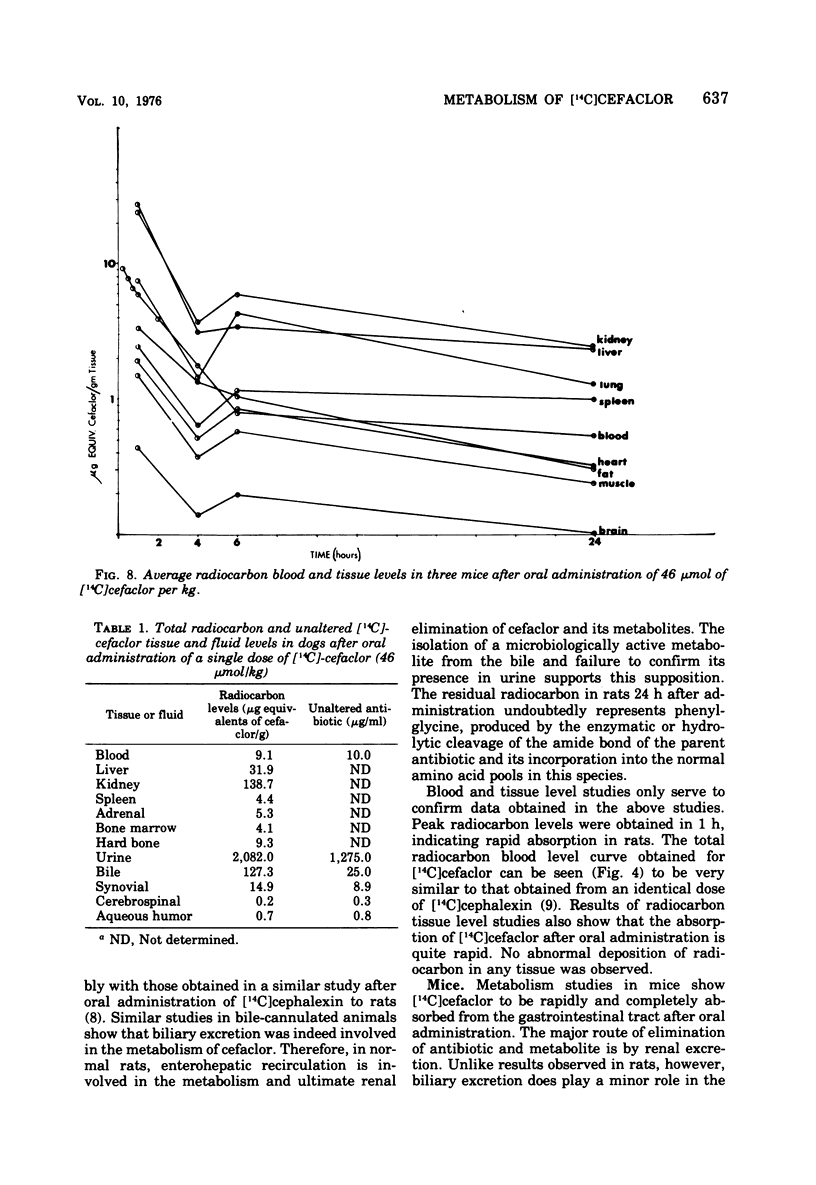
The metabolic fate of the orally effective cephalosporin antibiotic cefaclor (Lilly 99638) has been studied in rats, mice, and dogs. Cefaclor is efficiently absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract as the intact antibiotic. In rats and mice, cefaclor, for the most part, escapes metabolism in the body and is eliminated unchanged as unaltered antibiotic, primarily by renal excretion. In dogs, however, cefaclor is more labile to metabolism and only a portion of the administered antibiotic is eliminated unchanged via the kidney.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davis W. W., Stout T. R. Disc plate method of microbiological antibiotic assay. I. Factors influencing variability and error. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Oct;22(4):659–665. doi: 10.1128/am.22.4.659-665.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. W., Stout T. R. Disc plate method of microbiological antibiotic assay. II. Novel procedure offering improved accuracy. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Oct;22(4):666–670. doi: 10.1128/am.22.4.666-670.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan C. W., Simon R. L., Van Heyningen E. M. Chemistry of cephalosporin antibiotics. 13. Desacetoxycephalosporins. The synthesis of cephalexin and some analogs. J Med Chem. 1969 Mar;12(2):310–313. doi: 10.1021/jm00302a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan H. R., Billings R. E., McMahon R. E. Metabolism of D-cephaloglycin-14C and L-cephaloglycin-14C in the rat. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1969 Jan;22(1):27–33. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.22.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan H. R., Billings R. E., McMahon R. E. Metabolism of cephalexin-14C in mice and in rats. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1969 May;22(5):195–200. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.22.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan H. R., McMahon R. E. Metabolism of oral cephalothin and related cephalosporins in the rat. Biochem J. 1967 Mar;102(3):976–982. doi: 10.1042/bj1020976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


