Abstract
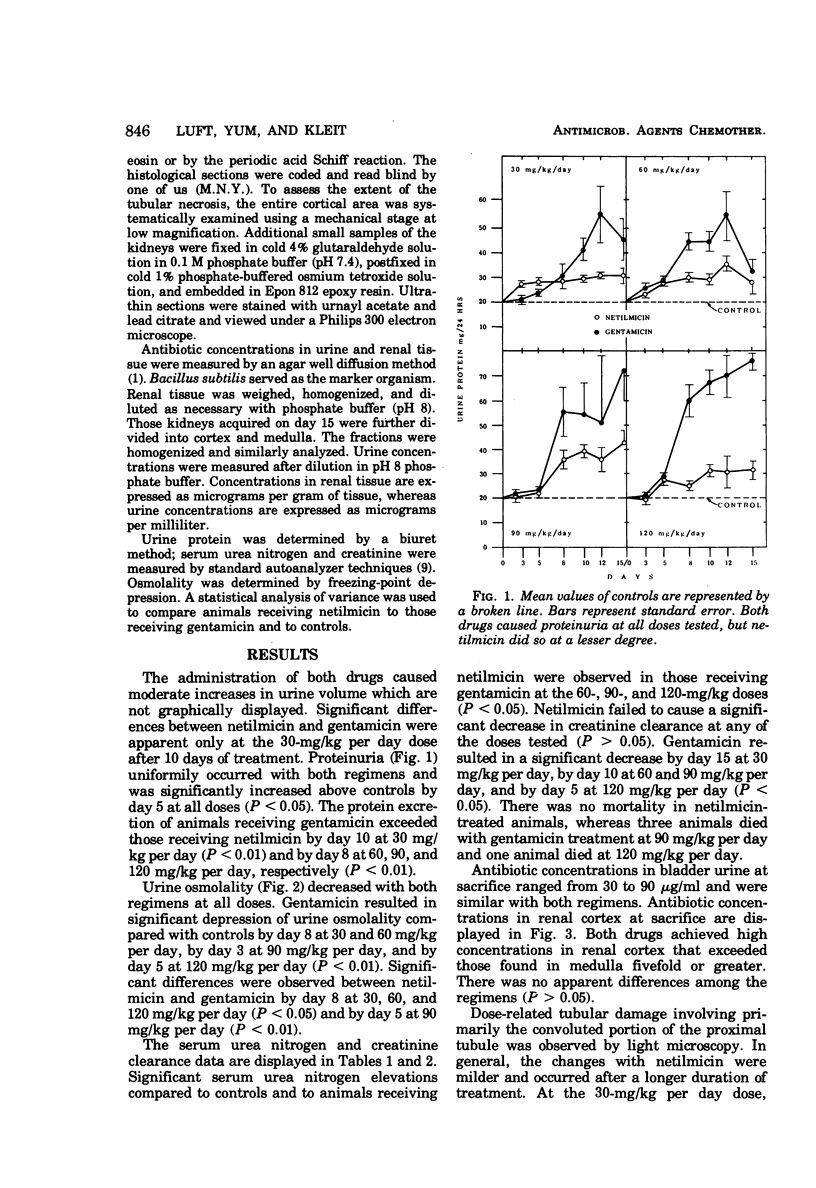
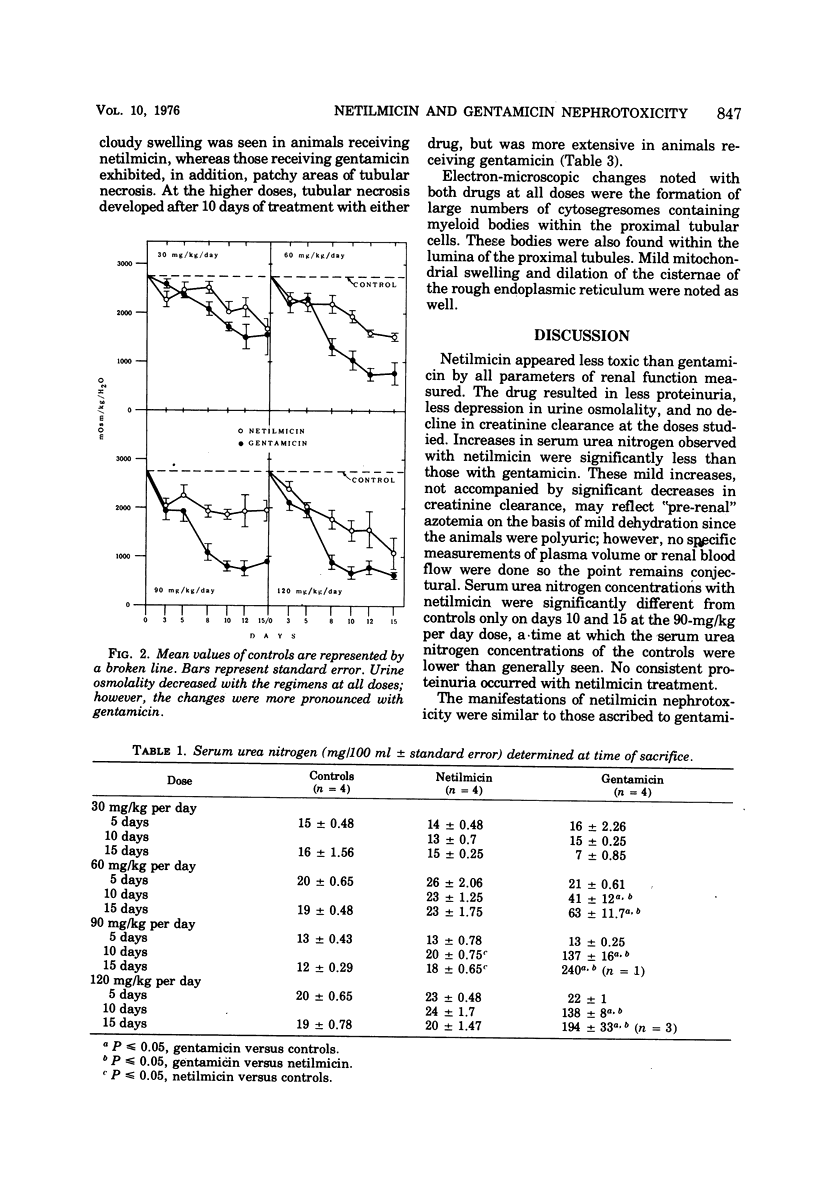
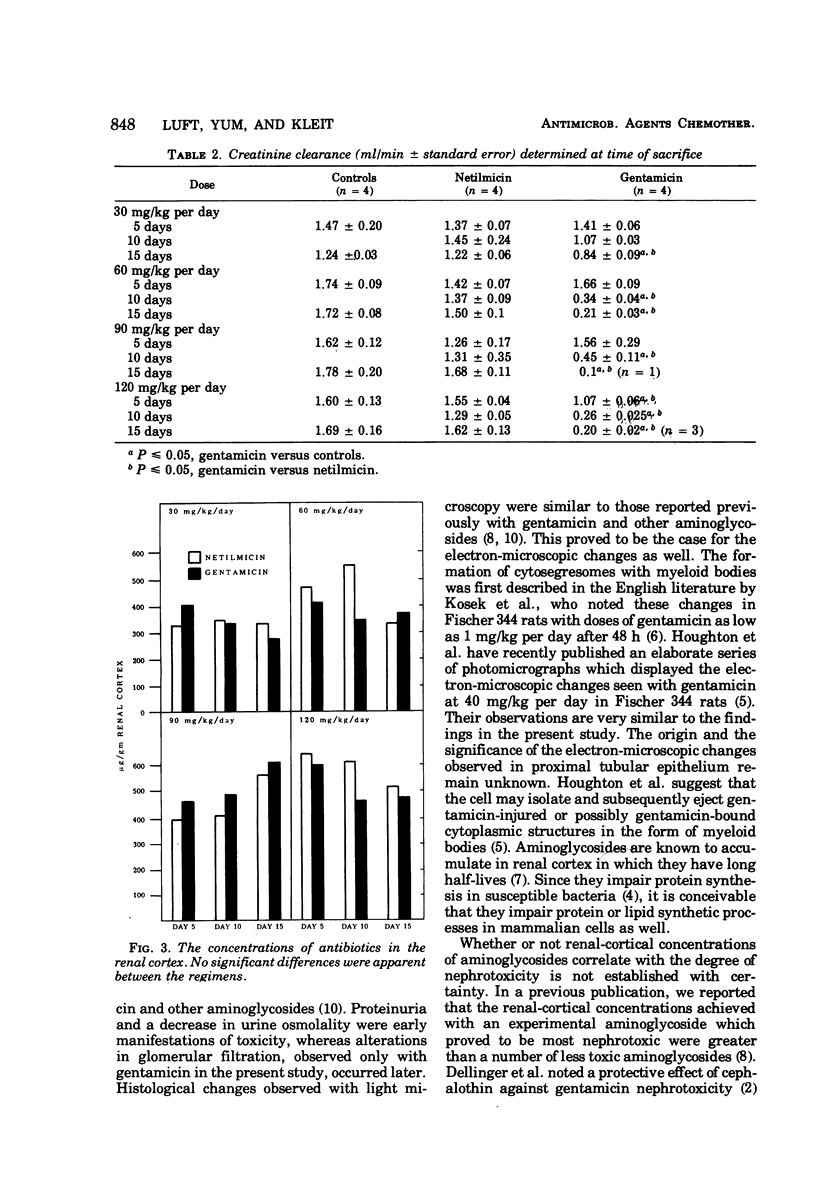
The relative nephrotoxicities of netilmicin (Sch 20569) and gentamicin were compared in rats at doses of 30, 60, 90, and 120 mg/kg per day for 15 days. Both drugs caused proteinuria and a decrease in urine osmolality; however, netilmicin produced significantly less changes at all doses than gentamicin. Whereas gentamicin resulted in a decline in creatinine clearance at all doses, netilmicin failed to cause a decline in creatinine clearance. Renal-cortical concentrations of antibiotic at sacrifice were similar in animals receiving either drug. Light-microscopic changes were less severe with netilmicin than gentamicin. Cytosegresomes with myeloid bodies were identified electron microscopically in the kidneys of animals receiving either netilmicin or gentamicin at all doses. Electron-microscopic manifestations were similar. The data indicate that in the rat, netilmicin is distinctly less nephrotoxic than gentamicin.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dellinger P., Murphy T., Barza M., Pinn V., Weinstein L. Effect of cephalothin on renal cortical concentrations of gentamicin in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Apr;9(4):587–588. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.4.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellinger P., Murphy T., Pinn V., Barza M., Weinstein L. Protective effect of cephalothin against gentamincin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jan;9(1):172–178. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.1.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn F. E., Sarre S. G. Mechanism of action of gentamicin. J Infect Dis. 1969 Apr-May;119(4):364–369. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.4-5.364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghton D. C., Hartnett M., Campbell-Boswell M., Porter G., Bennett W. A light and electron microscopic analysis of gentamicin nephrotoxicity in rats. Am J Pathol. 1976 Mar;82(3):589–612. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosek J. C., Mazze R. I., Cousins M. J. Nephrotoxicity of gentamicin. Lab Invest. 1974 Jan;30(1):48–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft F. C., Kleit S. A. Renal parenchymal accumulation of aminoglycoside antibiotics in rats. J Infect Dis. 1974 Dec;130(6):656–659. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.6.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft F. C., Patel V., Yum M. N., Patel B., Kleit S. A. Experimental aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Aug;86(2):213–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel V., Luft F. C., Yum M. N., Patel B., Zeman W., Kleit S. A. Enzymuria in gentamicin-induced kidney damage. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Mar;7(3):364–369. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.3.364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahal J. J., Jr, Simberkoff M. S., Kagan K., Moldover N. H. Bactericidal efficacy of Sch 20569 and amikacin against gentamicin-sensitive and -resistant organisms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Apr;9(4):595–599. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.4.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


