Abstract
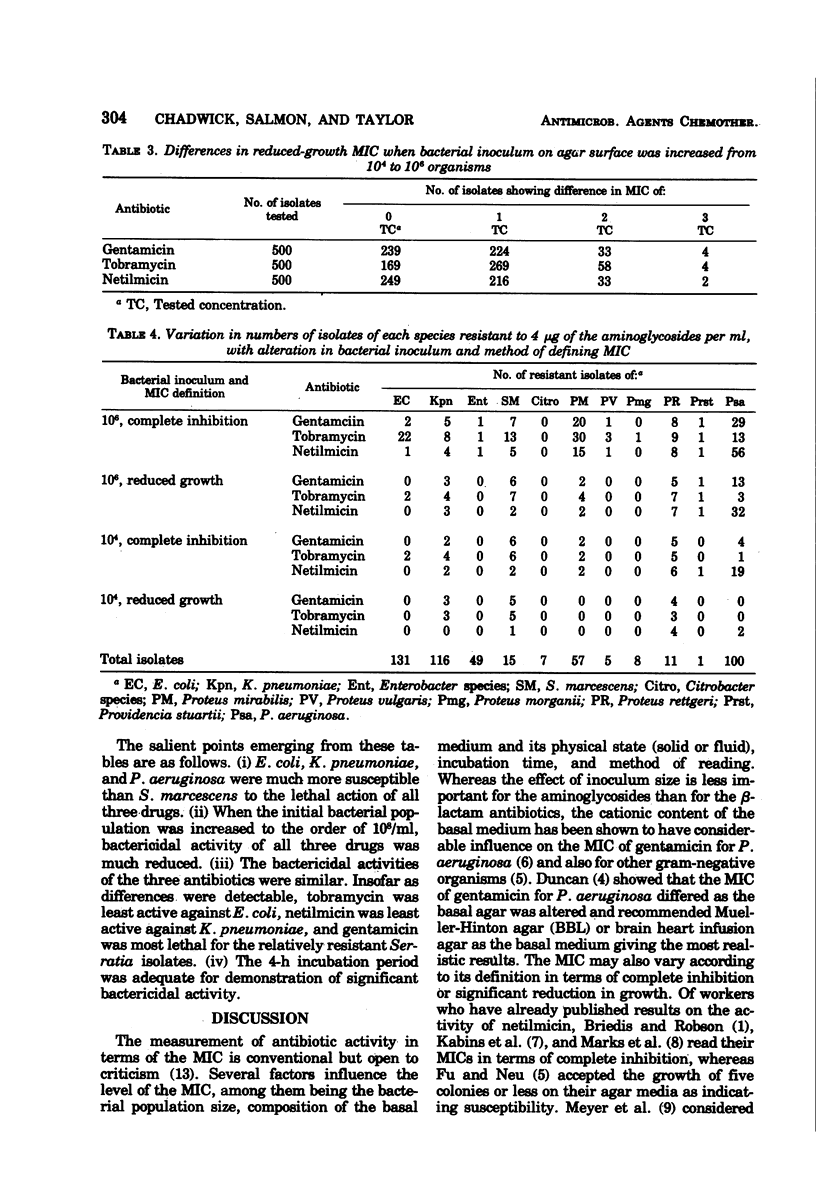
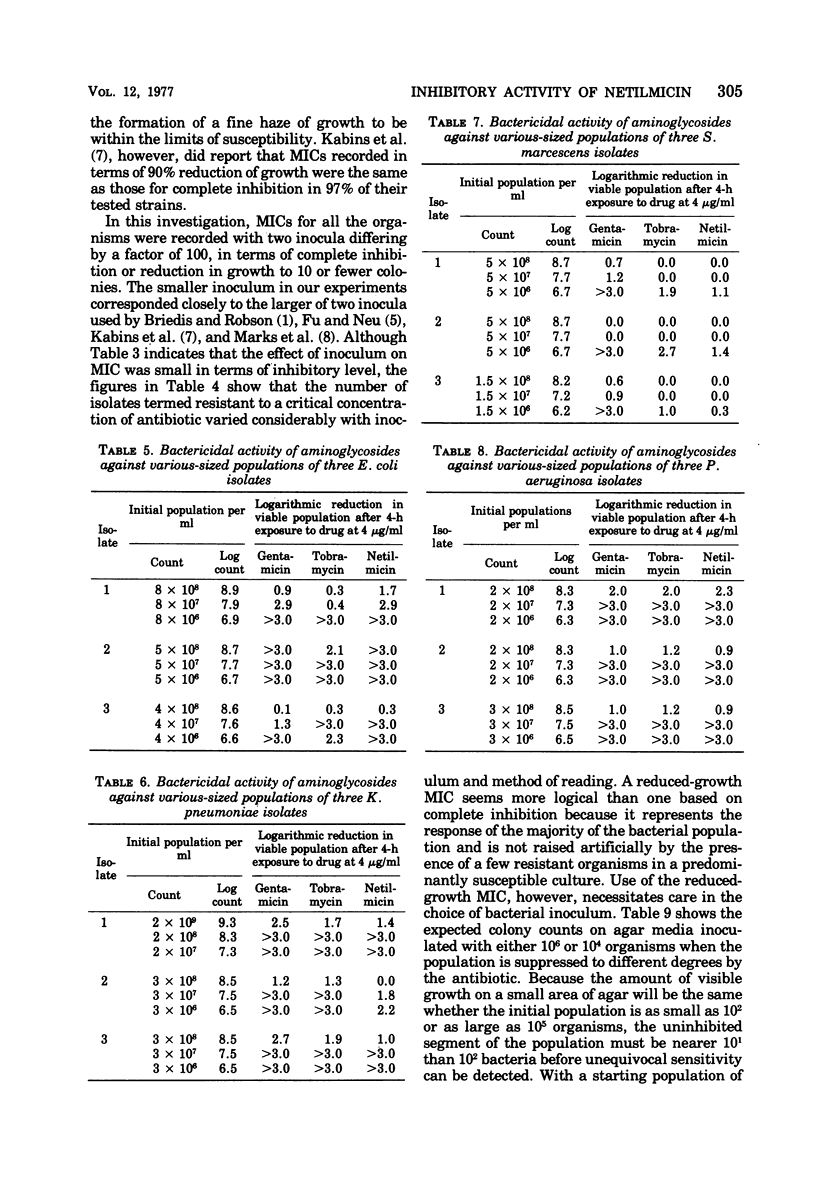
The inhibitory activity of netilmicin against 500 isolates of gram-negative bacteria was compared with those of gentamicin and tobramycin. Netilmicin was considerably less active than tobramycin and slightly less inhibitory than gentamicin for Pseudomonas aeruginosa but was at least as active against Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae as were the other two antibiotics. A few Klebsiella and Serratia isolates resistant to gentamicin and tobramycin were inhibited by netilmicin. All three antibiotics were strongly bactericidal for E. coli, K. pneumoniae and P. aeruginosa but had less lethal activity against the otherwise susceptible Serratia isolates tested. Some necessary precautions in reading minimal inhibitory concentrations on agar media are stressed, and some possible advantages of a 4-h bactericidal test, using a constant antibiotic concentration, are defined.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chadwick P., Delisle G. J., Byer M. Biochemical identification of hospital enterobacteria by replica agar plating. Can J Microbiol. 1974 Dec;20(12):1653–1664. doi: 10.1139/m74-257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan I. B. Susceptibility of 1,500 isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to gentamicin, carbenicillin, colistin, and polymyxin B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jan;5(1):9–15. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu K. P., Neu H. C. In vitro study of netilmicin compared with other aminoglycosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Sep;10(3):526–534. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.3.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrod L. P., Waterworth P. M. Effect of medium composition on the apparent sensitivity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to gentamicin. J Clin Pathol. 1969 Sep;22(5):534–538. doi: 10.1136/jcp.22.5.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabins S. A., Nathan C., Cohen S. In vitro comparison of netilmicin, a semisynthetic derivative of sisomicin, and four other aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jul;10(1):139–145. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. I., Hammerberg S., Greenstone G., Silver B. Activity of newer aminoglycosides and carbenicillin, alone and in combination, against gentamicin-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Sep;10(3):399–401. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.3.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. D., Draus L. L., Pasieczinik K. A. In vitro susceptibility of gentamicin-resistant Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa to netilmicin and selected aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):677–681. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips I., King A., Warren C., Watts B. The activity of penicillin and eight cephalosporins on Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1976 Mar;2(1):31–39. doi: 10.1093/jac/2.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


