Abstract
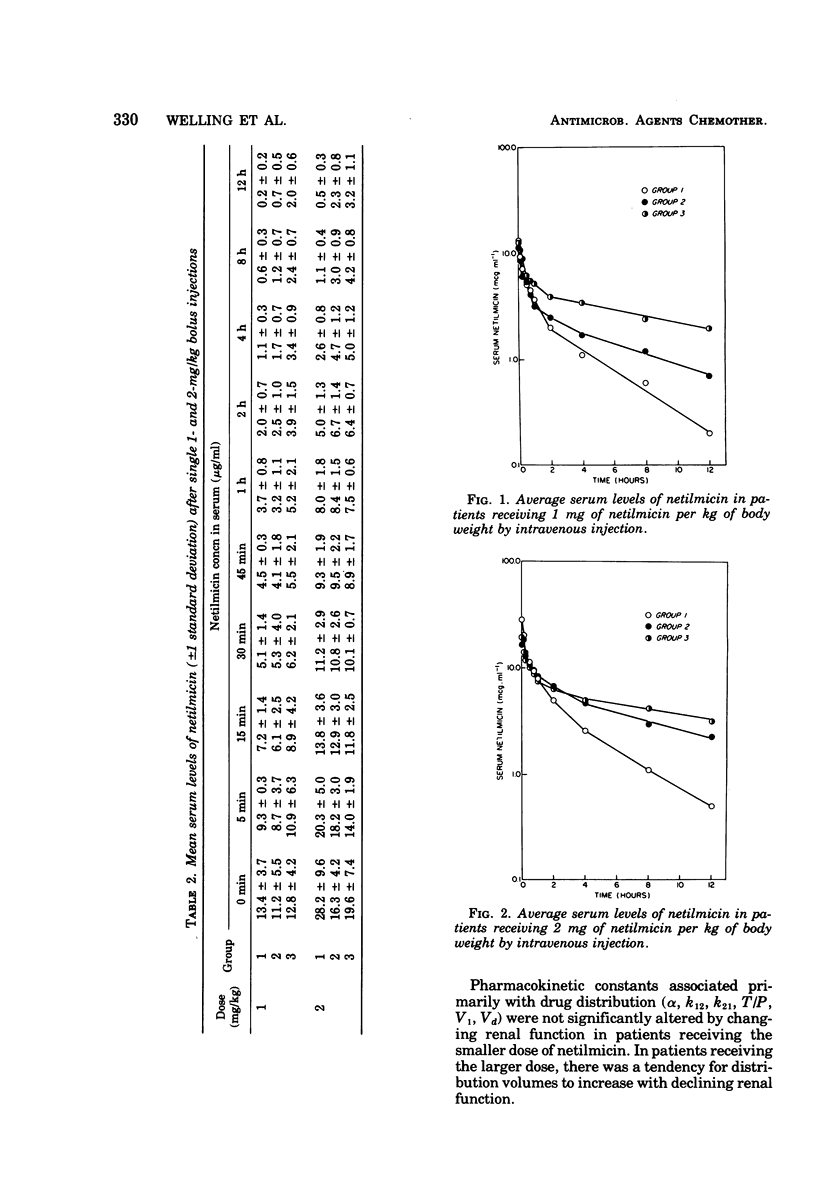
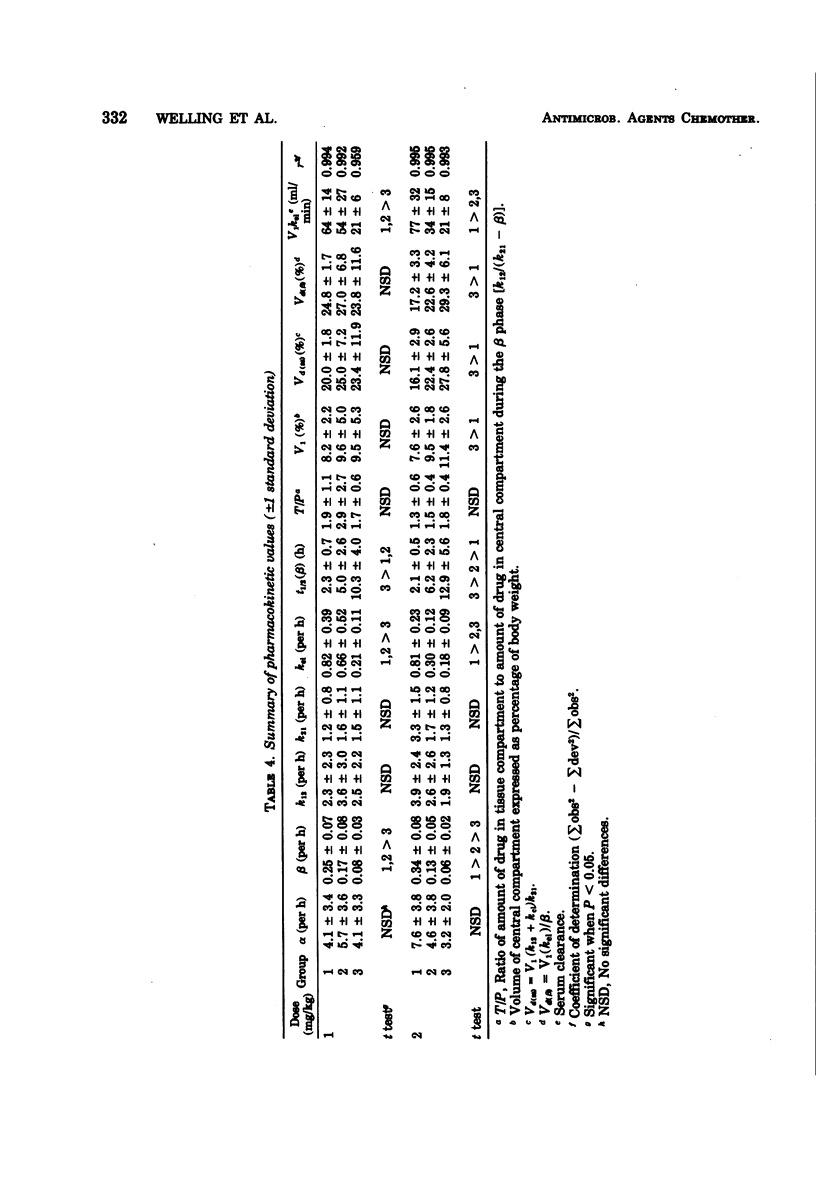
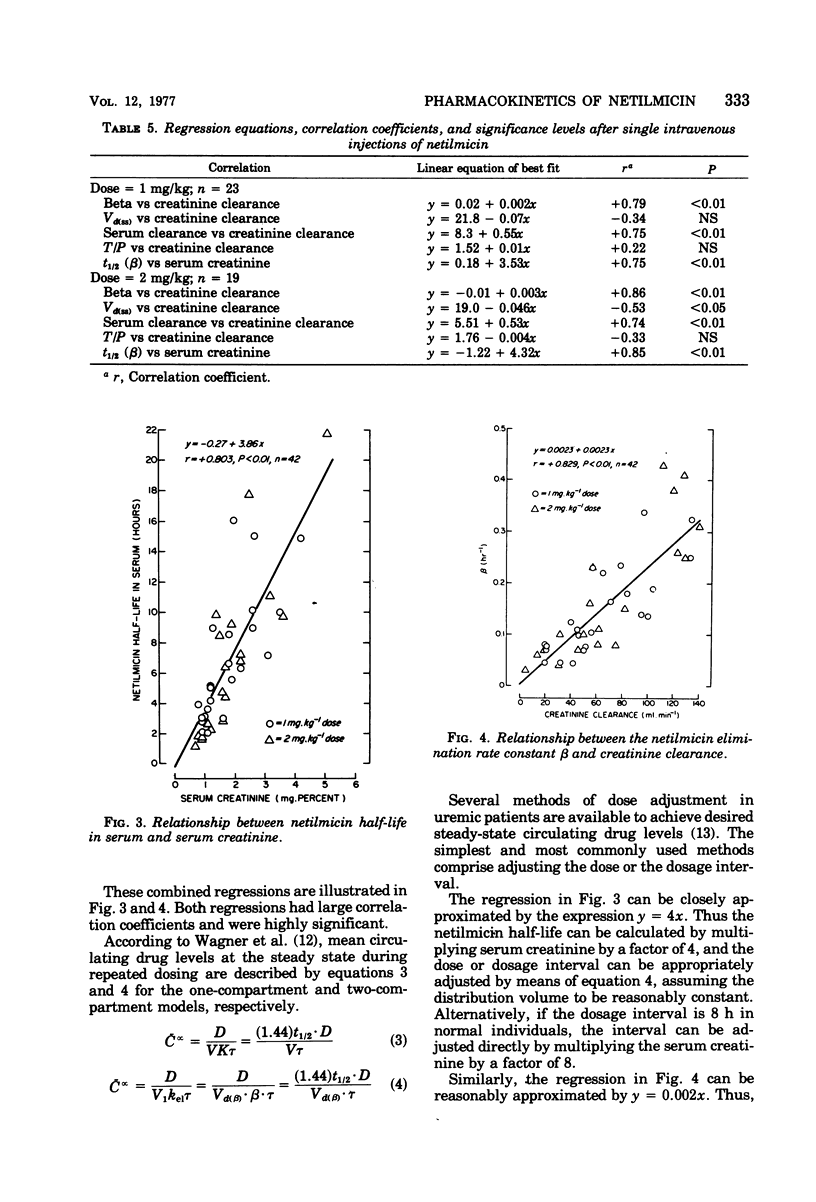
The pharmacokinetics of the new aminoglycoside antibiotic netilmicin were examined after single intravenous injections at two different dose levels to elderly male patients. The durg obeyed two-compartment model kinetics in serum, and elimination was monoexponential from 1 to 2 h after dosing. Netilmicin levels in serum were above minimum inhibitory concentration values for most susceptible organisms for up to 8 h after dosing in normal individuals and for at least 12 h in uremic patients. Urine levels of netilmicin were uniformly above minimum inhibitory concentration values throughout 24 h after dosing. Netilmicin distribution characteristics were largely independent of both dose level and renal function. Netilmicin elimination kinetics were independent of dose level but were markedly influenced by renal function. Relationships are described between netilmicin elimination and renal function indicators, which provide a basis for dosage adjustment in individuals with renal function impairment.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gyselynck A. M., Forrey A., Cutler R. Pharmacokinetics of gentamicin: distribution and plasma and renal clearance. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124 (Suppl):S70–S76. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.supplement_1.s70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jusko W. J., Gibaldi M. Effects of change in elimination on varous parameters of the two-compartment open model. J Pharm Sci. 1972 Aug;61(8):1270–1273. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600610820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kampmann J., Hansen J. M., Siersbaek-Nielsen K., Kristensen M. Serum creatinine and drug half-lives. JAMA. 1973 Jan 8;223(2):193–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft F. C., Yum M. N., Kleit S. A. Comparative nephrotoxicities of netilmicin and gentamicin in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Nov;10(5):845–849. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.5.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers B. R., Hirschman S. Z. Antimicrobial activity in vitro of netilmicin and comparison with sisomicin, gentamicin, and tobramycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jan;11(1):118–121. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. H., Arcieri G., Weinstein M. J., Waitz J. A. Biological activity of netilmicin, a broad-spectrum semisynthetic aminoglycoside antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Nov;10(5):827–836. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.5.827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosegaard A., Welling P. G., Madsen P. O. Gentamicin and gentamicin C1 in the treatment of complicated urinary tract infections: comparative study of efficacy, tolerance, and pharmacokinetics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Mar;7(3):328–332. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.3.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosegaard A., Welling P. G., Tse F. L., Madsen P. Treatment with sisomicin of complicated urinary tract infections in patients with varying degrees of renal function impairment, pharmacokinetics and dosage adjustment. Infection. 1975;3(3):143–147. doi: 10.1007/BF01641336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahal J. J., Jr, Simberkoff M. S., Kagan K., Moldover N. H. Bactericidal efficacy of Sch 20569 and amikacin against gentamicin-sensitive and -resistant organisms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Apr;9(4):595–599. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.4.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riegelman S., Loo J., Rowland M. Concept of a volume of distribution and possible errors in evaluation of this parameter. J Pharm Sci. 1968 Jan;57(1):128–133. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600570125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. G., Northam J. I., Alway C. D., Carpenter O. S. Blood levels of drug at the equilibrium state after multiple dosing. Nature. 1965 Sep 18;207(5003):1301–1302. doi: 10.1038/2071301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welling P. G., Craig W. A., Gordon A. L., Kunin C. M. Pharmacokinetics of cefazolin in normal and uremic subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1974 Apr;15(4):344–353. doi: 10.1002/cpt1974154344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welling P. G., Shaw W. R., Uman S. J., Tse F. L., Craig W. A. Pharmacokinetics of minocycline in renal failure. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Nov;8(5):532–537. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.5.532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


