Abstract
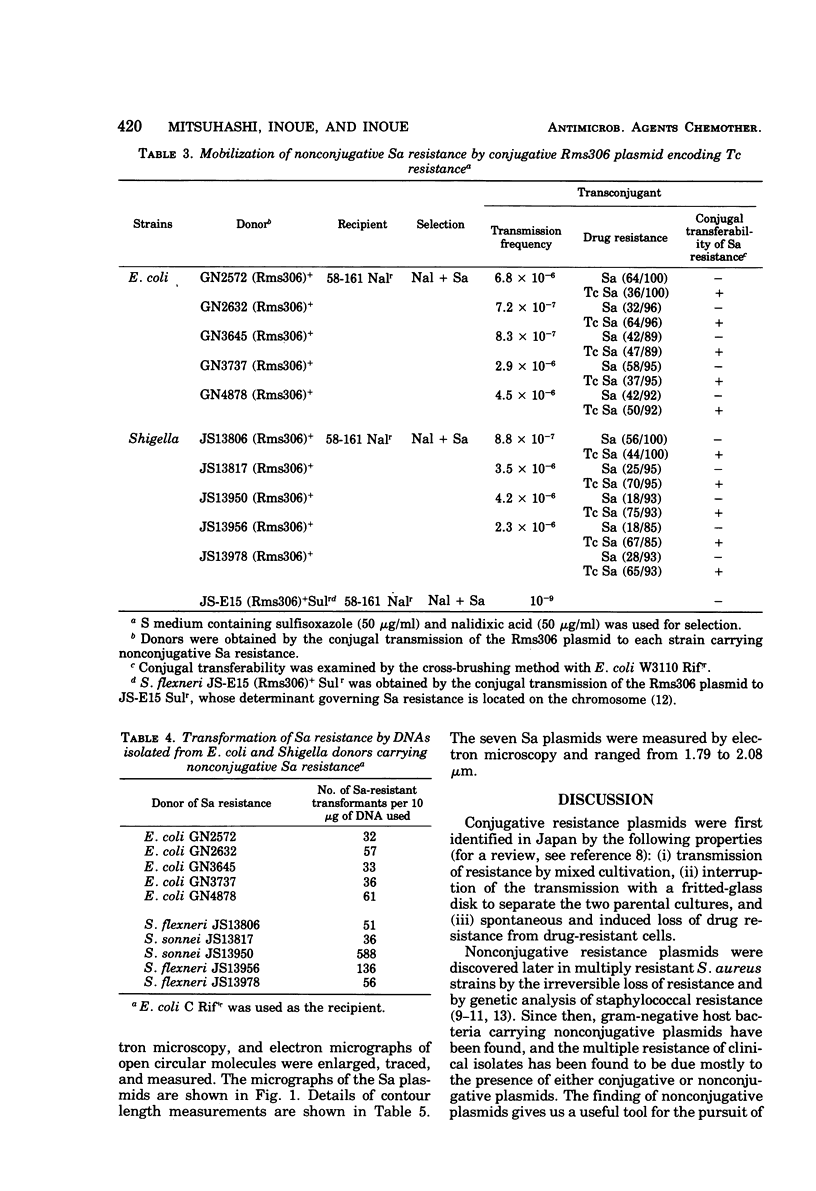
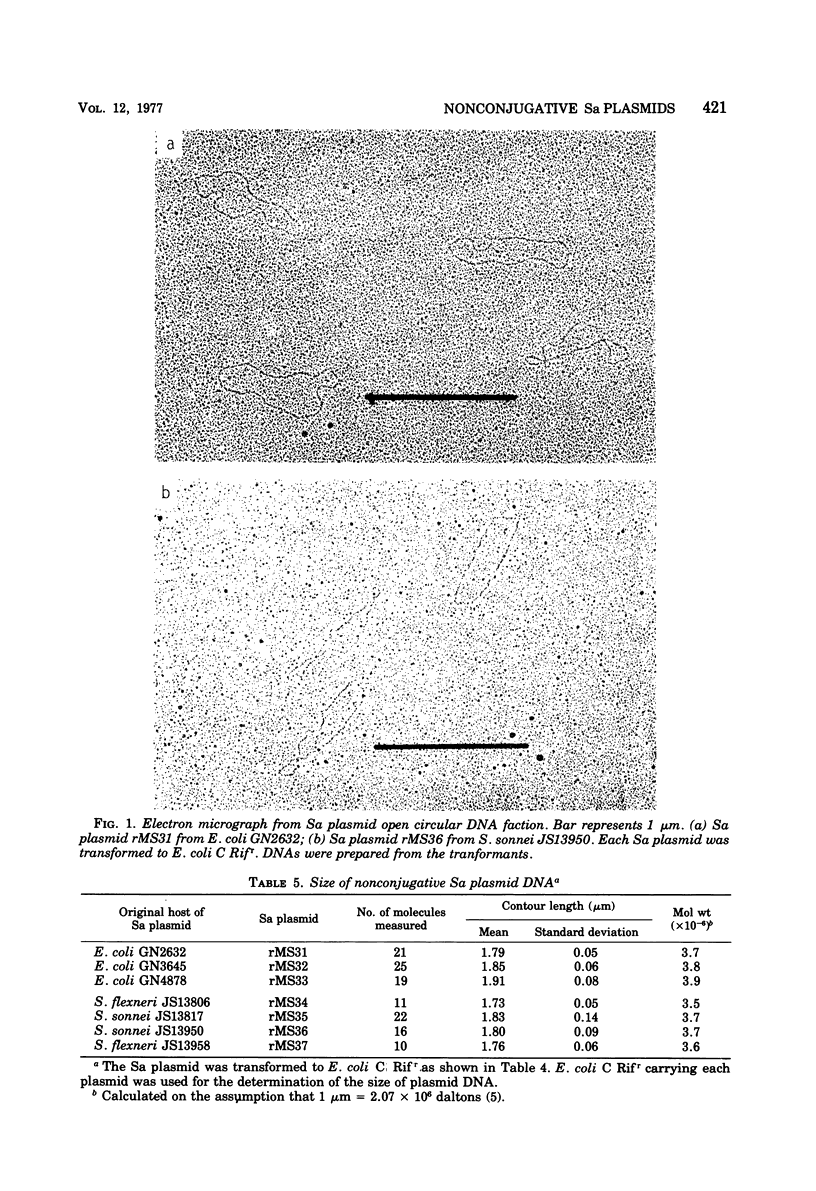
Nonconjugative plasmids encoding sulfanilamide (Sa) resistance were demonstrated at a high frequency in Shigella and Escherichia coli strains resistant to sulfanilamide. These Sa plasmids were all compatible with the standard plasmids used in compatibility testing. The sizes of seven Sa plasmids were measured by electron microscopy and ranged from 1.79 to 2.08 μm, corresponding to 3.5 to 3.9 megadaltons.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clowes R. C. Molecular structure of bacterial plasmids. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Sep;36(3):361–405. doi: 10.1128/br.36.3.361-405.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey R. B., Pittard J. Genetic and biophysical study of R plasmids conferring sulfonamide resistance in Shigella strains isolated in 1952 and 1956. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1186–1195. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1186-1195.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang D. Molecular weights of coliphages and coliphage DNA. 3. Contour length and molecular weight of DNA from bacteriophages T4, T5 and T7, and from bovine papilloma virus. J Mol Biol. 1970 Dec 28;54(3):557–565. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90126-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITSUHASHI S., MORIMURA M., KONO K., OSHIMA H. ELIMINATION OF DRUG RESISTANCE OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BY TREATMENT WITH ACRIFLAVINE. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jul;86:162–164. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.1.162-164.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuhashi S. Epidemiological and genetical study of drug resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Jpn J Microbiol. 1967 Mar;11(1):49–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1967.tb00320.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuhashi S., Inoue M., Kawabe H., Oshima H., Okubo T. Genetic and biochemical studies of drug resistance in staphylococci. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1973;1:144–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVICK R. P. ANALYSIS BY TRANSDUCTION OF MUTATIONS AFFECTING PENICILLINASE FORMATION IN STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Oct;33:121–136. doi: 10.1099/00221287-33-1-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Nagai Y., Hashimoto H., Mitsuhashi S. Distribution of R factors among Shigella strains isolated in Japan. Jpn J Microbiol. 1969 Jun;13(2):187–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1969.tb00452.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]