Abstract
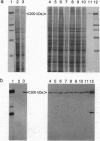
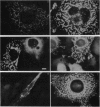
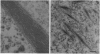
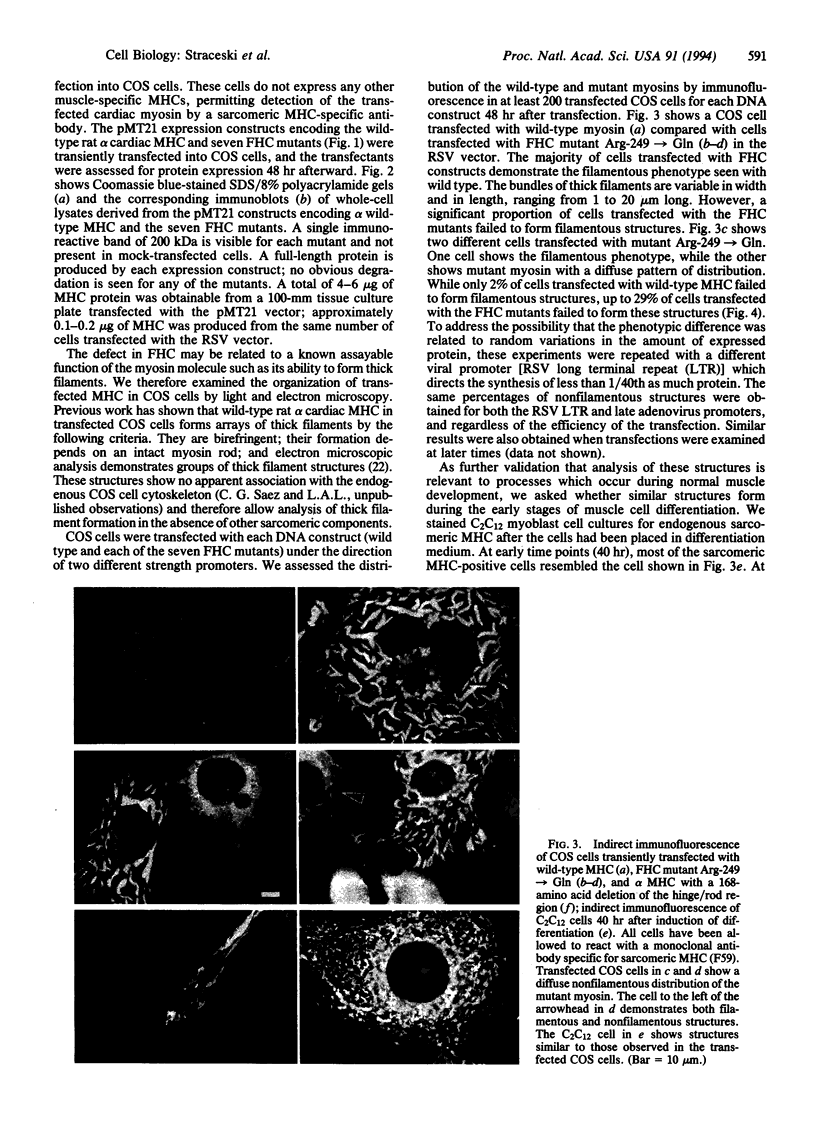
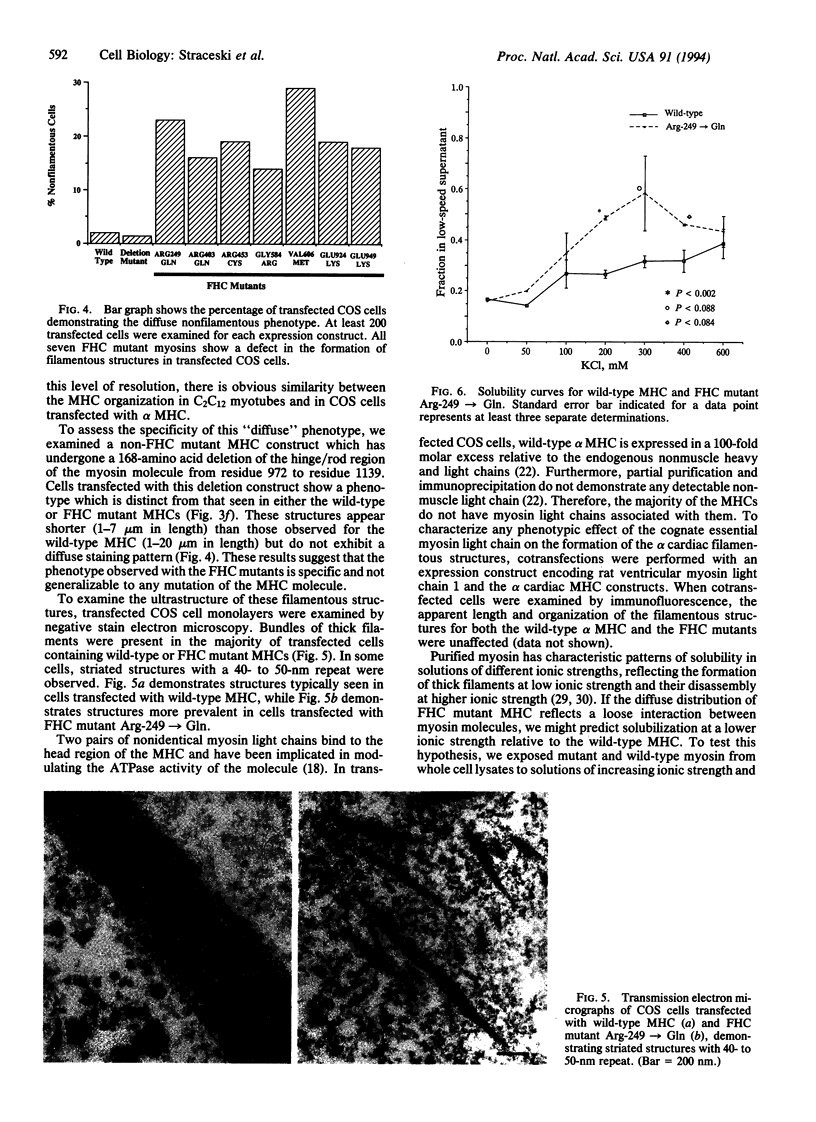
To analyze potential functional consequences of myosin heavy chain (MHC) mutations identified in patients with familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (FHC), we have assessed the stability of the mutant MHCs and their ability to form thick filaments. Constructs encoding wild-type rat alpha MHC and seven corresponding FHC missense mutants were transfected into COS cells. Immunoblot analysis suggested that FHC mutations do not grossly alter protein stability. Wild-type alpha MHC transfected into COS cells forms structures previously shown to be arrays of thick filaments, which also resemble myosin structures observed early in differentiation of muscle cells. Surprisingly, up to 29% of COS cells transfected with the FHC mutants failed to form filamentous structures. To assess whether this phenotype was specific for the FHC mutants and not generalizable to any myosin mutation, COS cells were transfected with a construct encoding an MHC with a 168-amino acid deletion of the hinge/rod region. This deletion construct formed filamentous structures with the same frequency as wild-type MHC. Biochemical analysis of one FHC mutant (Arg-249-->Gln) demonstrates that the structures formed by the mutant are solubilized at a lower ionic strength than those formed by wild-type MHC. We conclude that although the FHC mutant MHC is not labile, its assembly properties may be impaired.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beall C. J., Sepanski M. A., Fyrberg E. A. Genetic dissection of Drosophila myofibril formation: effects of actin and myosin heavy chain null alleles. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):131–140. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. S. Assembly processes in vertebrate skeletal thick filament formation. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:217–239. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.001245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dibb N. J., Brown D. M., Karn J., Moerman D. G., Bolten S. L., Waterston R. H. Sequence analysis of mutations that affect the synthesis, assembly and enzymatic activity of the unc-54 myosin heavy chain of Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jun 25;183(4):543–551. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90170-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein H. F., Waterston R. H., Brenner S. A mutant affecting the heavy chain of myosin in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol. 1974 Dec 5;90(2):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90374-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisterfer-Lowrance A. A., Kass S., Tanigawa G., Vosberg H. P., McKenna W., Seidman C. E., Seidman J. G. A molecular basis for familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: a beta cardiac myosin heavy chain gene missense mutation. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):999–1006. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90274-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knops J., Kosik K. S., Lee G., Pardee J. D., Cohen-Gould L., McConlogue L. Overexpression of tau in a nonneuronal cell induces long cellular processes. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(4):725–733. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.4.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy-Mintz P., Kielian M. Mutagenesis of the putative fusion domain of the Semliki Forest virus spike protein. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4292–4300. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4292-4300.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod A. R., Waterston R. H., Fishpool R. M., Brenner S. Identification of the structural gene for a myosin heavy-chain in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jul;114(1):133–140. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margossian S. S., Lowey S. Preparation of myosin and its subfragments from rabbit skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):55–71. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maron B. J., Lipson L. C., Roberts W. C., Savage D. D., Epstein S. E. "Malignant" hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: identification of a subgroup of families with unusually frequent premature death. Am J Cardiol. 1978 Jun;41(7):1133–1140. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(78)90870-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maron B. J., Roberts W. C., Epstein S. E. Sudden death in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: a profile of 78 patients. Circulation. 1982 Jun;65(7):1388–1394. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.65.7.1388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna W. J., Camm A. J. Sudden death in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Assessment of patients at high risk. Circulation. 1989 Nov;80(5):1489–1492. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.80.5.1489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNally E. M., Kraft R., Bravo-Zehnder M., Taylor D. A., Leinwand L. A. Full-length rat alpha and beta cardiac myosin heavy chain sequences. Comparisons suggest a molecular basis for functional differences. J Mol Biol. 1989 Dec 5;210(3):665–671. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90141-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. B., Teal S. B., Stockdale F. E. Evolutionarily conserved sequences of striated muscle myosin heavy chain isoforms. Epitope mapping by cDNA expression. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13122–13130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogami K., O'Donnell P. T., Bernstein S. I., Wright T. R., Emerson C. P., Jr Mutations of the Drosophila myosin heavy-chain gene: effects on transcription, myosin accumulation, and muscle function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1393–1397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saez L. J., Gianola K. M., McNally E. M., Feghali R., Eddy R., Shows T. B., Leinwand L. A. Human cardiac myosin heavy chain genes and their linkage in the genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5443–5459. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasson Z., Rakowski H., Wigle E. D. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Cardiol Clin. 1988 May;6(2):233–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers J. R., Soboeiro M. S., Faust K., Bengur A. R., Harvey E. V. Preparation and characterization of heavy meromyosin and subfragment 1 from vertebrate cytoplasmic myosins. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 6;27(18):6977–6982. doi: 10.1021/bi00418a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanigawa G., Jarcho J. A., Kass S., Solomon S. D., Vosberg H. P., Seidman J. G., Seidman C. E. A molecular basis for familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: an alpha/beta cardiac myosin heavy chain hybrid gene. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):991–998. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90273-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vikstrom K. L., Rovner A. S., Saez C. G., Bravo-Zehnder M., Straceski A. J., Leinwand L. A. Sarcomeric myosin heavy chain expressed in nonmuscle cells forms thick filaments in the presence of substoichiometric amounts of light chains. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1993;26(3):192–204. doi: 10.1002/cm.970260303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vybiral T., Deitiker P. R., Roberts R., Epstein H. F. Accumulation and assembly of myosin in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with the 403 Arg to Gln beta-myosin heavy chain mutation. Circ Res. 1992 Dec;71(6):1404–1409. doi: 10.1161/01.res.71.6.1404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins H., Rosenzweig A., Hwang D. S., Levi T., McKenna W., Seidman C. E., Seidman J. G. Characteristics and prognostic implications of myosin missense mutations in familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 1992 Apr 23;326(17):1108–1114. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199204233261703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]