Abstract
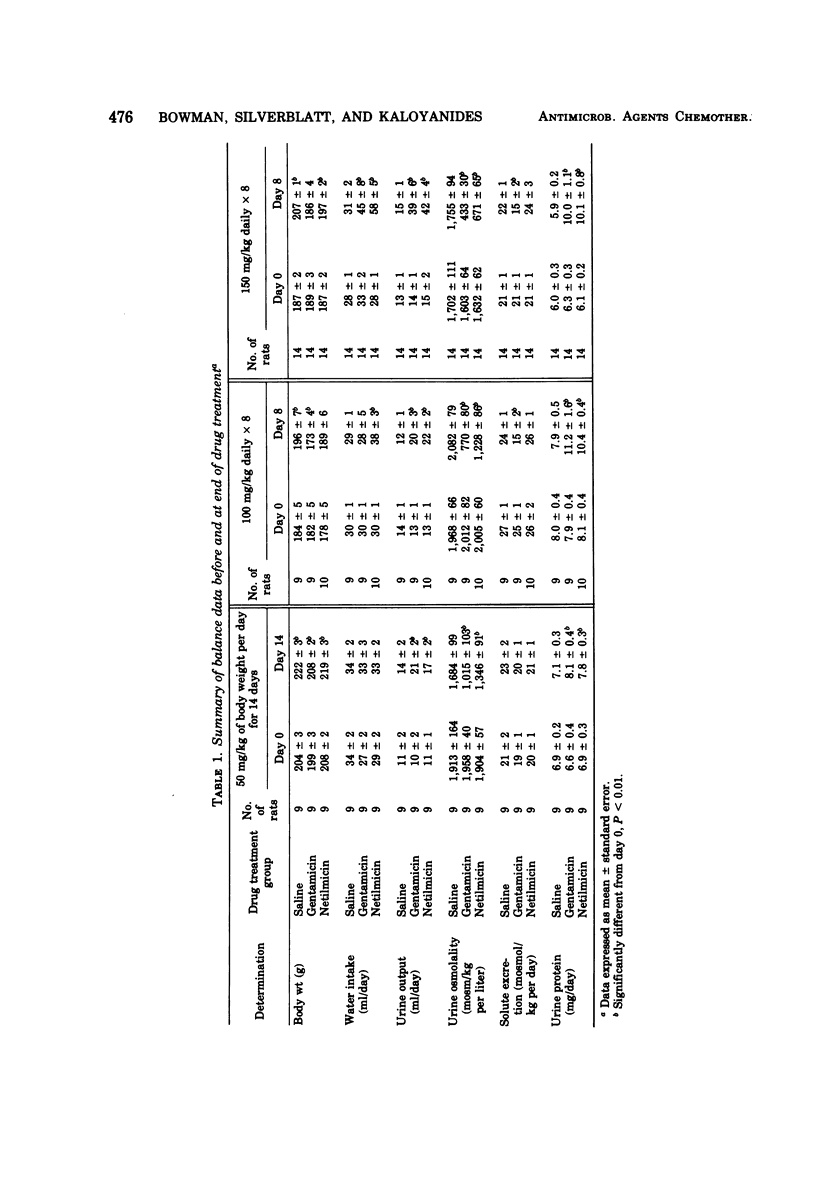
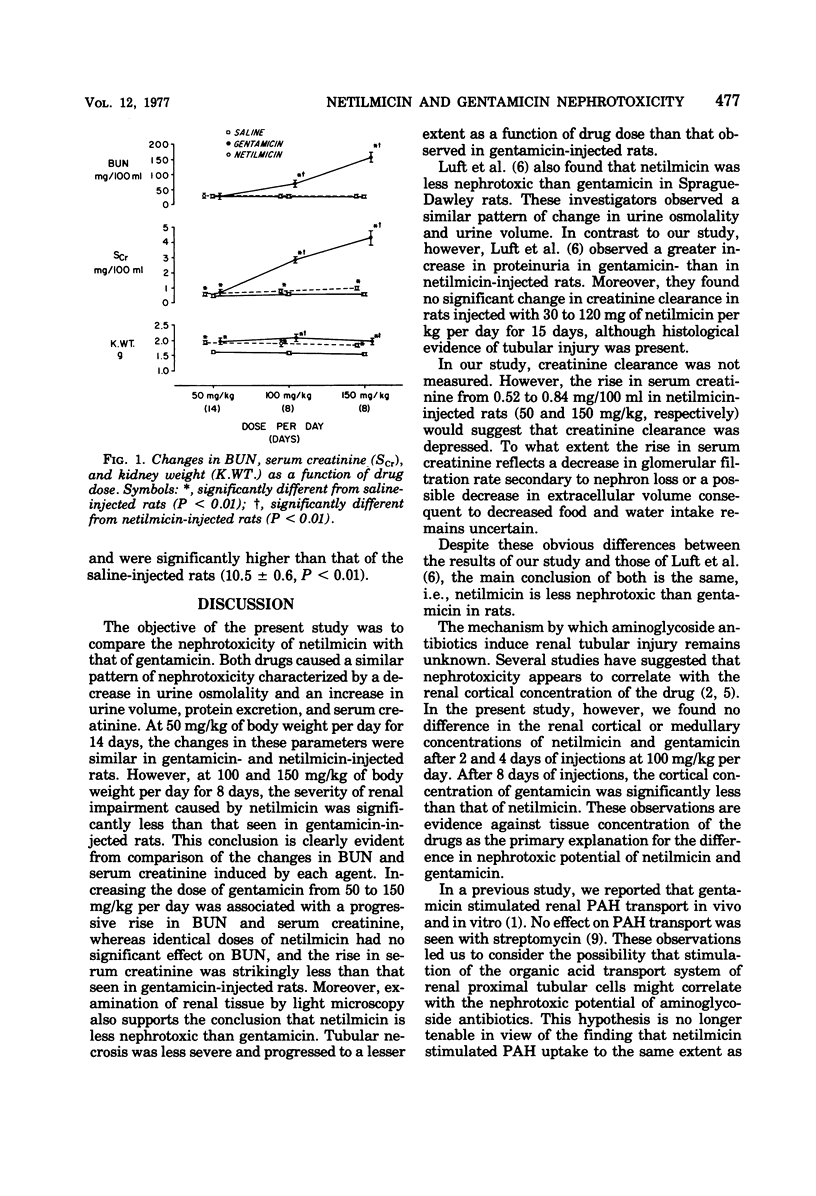
The nephrotoxicity of netilmicin relative to that of gentamicin was examined in Sprague-Dawley rats. Balance studies were performed on rats injected with netilmicin or gentamicin (50 mg/kg per day for 14 days, 100 mg/kg per day for 8 days, and 150 mg/kg per day for 8 days). Control rats were injected with saline. Both drugs caused a dose-related decrease in urine osmolality and increases in urine volume, water intake, and serum creatinine; however, the magnitude of these changes was significantly less in netilmicin- than in gentamicin-injected rats. Light microscopy of renal tissue revealed less proximal tubular cell necrosis in netilmicin- than in gentamicin-injected rats. There was no significant difference between the renal cortical concentrations of the two drugs. Both drugs stimulated uptake of p-aminohippurate in rat renal cortical slices to the same degree. The data indicate that netilmicin is less nephrotoxic than gentamicin in rats, that the difference in nephrotoxicity cannot be explained by a difference in drug concentration in the renal cortex, and that the ability of aminoglycosides to stimulate the organic acid transport system of proximal tubular cells does not correlate with their nephrotoxic potential.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen L., Lapkin R., Kaloyanides G. J. Effect of gentamicin on renal function in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Apr;193(1):264–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellinger P., Murphy T., Barza M., Pinn V., Weinstein L. Effect of cephalothin on renal cortical concentrations of gentamicin in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Apr;9(4):587–588. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.4.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith L. D., Bulger R. E., Trump B. F. The ultrastructure of the functioning kidney. Lab Invest. 1967 Feb;16(2):220–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft F. C., Patel V., Yum M. N., Patel B., Kleit S. A. Experimental aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Aug;86(2):213–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft F. C., Yum M. N., Kleit S. A. Comparative nephrotoxicities of netilmicin and gentamicin in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Nov;10(5):845–849. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.5.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. H., Arcieri G., Weinstein M. J., Waitz J. A. Biological activity of netilmicin, a broad-spectrum semisynthetic aminoglycoside antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Nov;10(5):827–836. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.5.827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahal J. J., Jr, Simberkoff M. S., Kagan K., Moldover N. H. Bactericidal efficacy of Sch 20569 and amikacin against gentamicin-sensitive and -resistant organisms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Apr;9(4):595–599. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.4.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


