Abstract
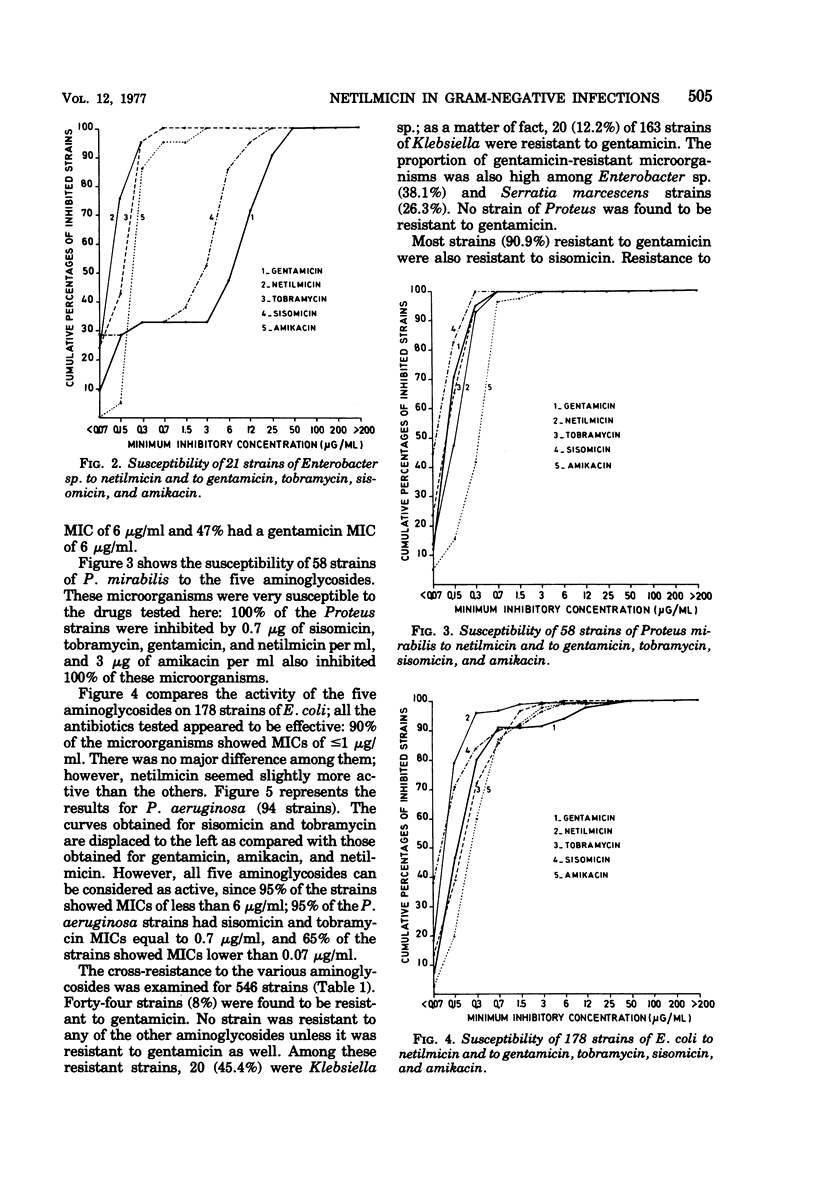
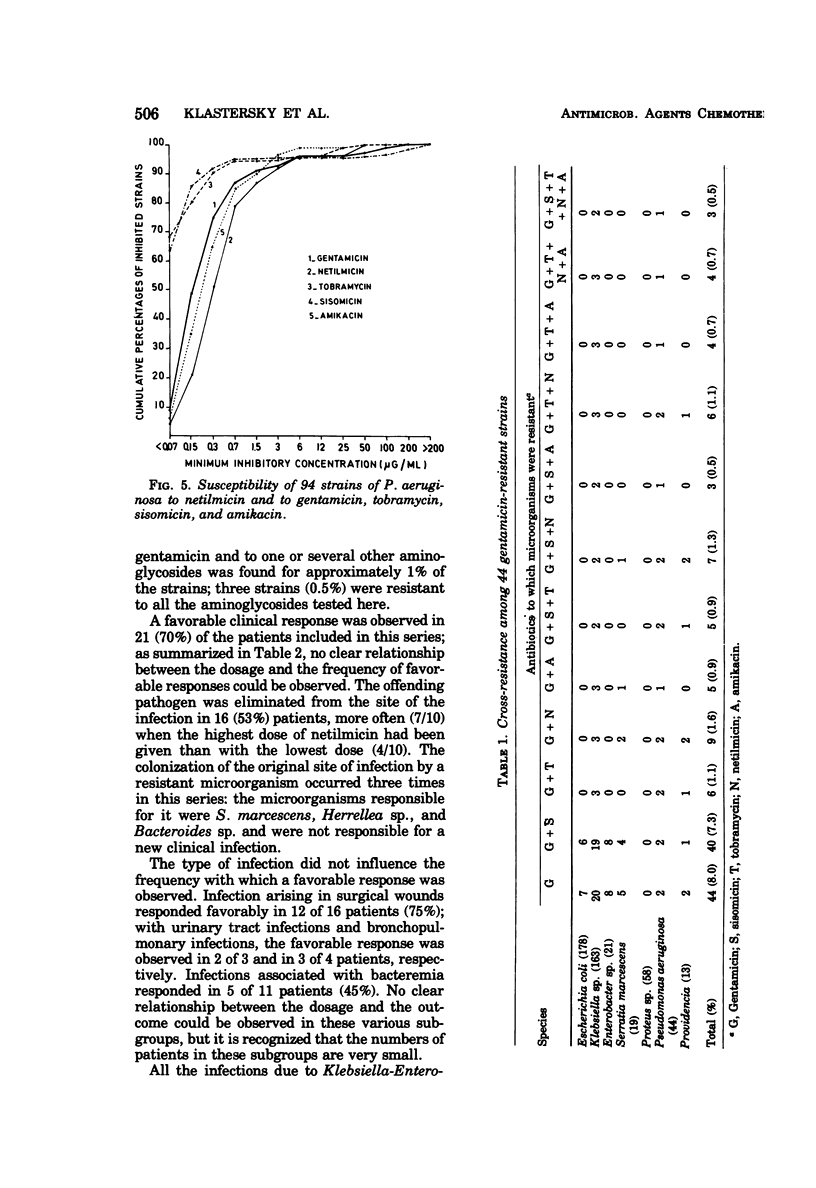
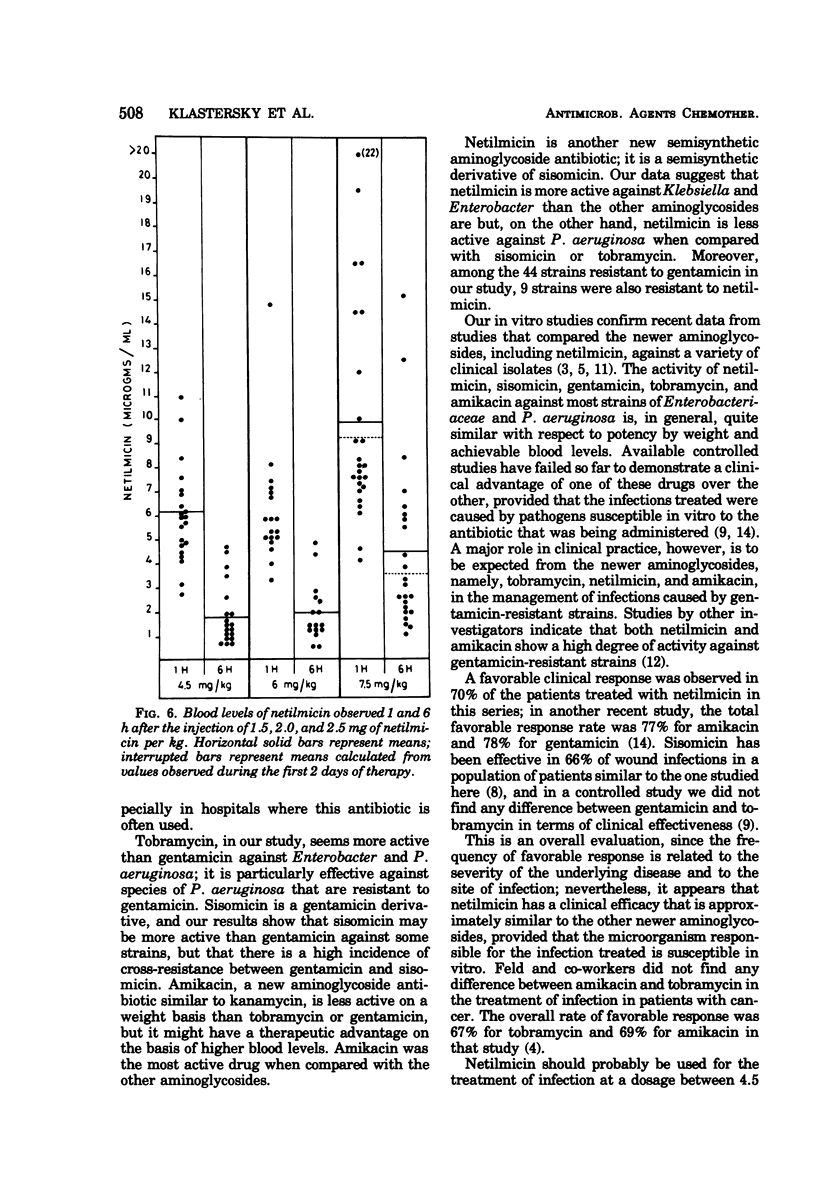
A preliminary study was conducted with netilmicin, a new aminoglycoside antibiotic. Its effectiveness was evaluated in vitro against 546 strains of Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from clinical material. Its effectiveness against gentamicin-susceptible strains was roughly similar to that of gentamicin and other newer aminoglycoside antibiotics. Cross-resistance to netilmicin was found in 9 of 44 gentamicin-resistant strains. A favorable clinical response was observed in 70% of the patients treated with a dose of netilmicin ranging from 4.5 to 7.5 mg/kg. However, the appearance of granular casts was seen in 7 of 10 patients receiving the higher dosage of netilmicin (7.5 mg/kg) and a rise in blood urea nitrogen or serum creatinine levels was observed in 5 of these patients.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bryant R. E., Hammond D. Interaction of purulent material with antibiotics used to treat Pseudomonas infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Dec;6(6):702–707. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.6.702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. W., Stout T. R. Disc plate method of microbiological antibiotic assay. II. Novel procedure offering improved accuracy. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Oct;22(4):666–670. doi: 10.1128/am.22.4.666-670.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhawan V., Marso E., Martin W. J., Young L. S. In vitro studies with netilmicin compared with amikacin, gentamicin, and tobramycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jan;11(1):64–73. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feld R., Valdivieso M., Bodey G. P., Rodriguez V. Comparison of amikacin and tobramycin in the treatment of infection in patients with cancer. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jan;135(1):61–66. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor R. J., Norden C. W. In vitro activity of netilmicin, gentamicin, and amikacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jan;11(1):126–131. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klastersky J., Cappel R., Daneau D. Clinical significance of in vitro synergism between antibiotics in gram-negative infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Dec;2(6):470–475. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.6.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klastersky J., Daneau D., Swings G., Weerts D. Antibacterial activity in serum and urine as a therapeutic guide in bacterial infections. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):187–193. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klastersky J., Hensgens C., Henri A., Daneau D. Comparative clinical study of tobramycin and gentamicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Feb;5(2):133–138. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.2.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klastersky J., Nyamubeya B., Vandenborre L. Antimicrobial effectiveness ofkanamycin, aminosidin, BB-K8, sisomicin, gentamicin and tobramycin combined with carbenicillin or cephalothin against gram-negative rods. J Med Microbiol. 1974 Nov;7(4):465–472. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-4-465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. D., Draus L. L., Pasieczinik K. A. In vitro susceptibility of gentamicin-resistant Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa to netilmicin and selected aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):677–681. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers B. R., Hirschman S. Z. Antimicrobial activity in vitro of netilmicin and comparison with sisomicin, gentamicin, and tobramycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jan;11(1):118–121. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogwizd S. M., Lerner S. A. In vitro activity of gentamicin, amikacin and netilmicin alone and in combination with carbenicillin against Serratia marcescens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Dec;10(6):878–884. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.6.878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. R., Baughman K. L., Edwards C. Q., Rogers J. F., Lietman P. S. Controlled comparison of amikacin and gentamicin. N Engl J Med. 1977 Feb 17;296(7):349–353. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197702172960701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


