Abstract
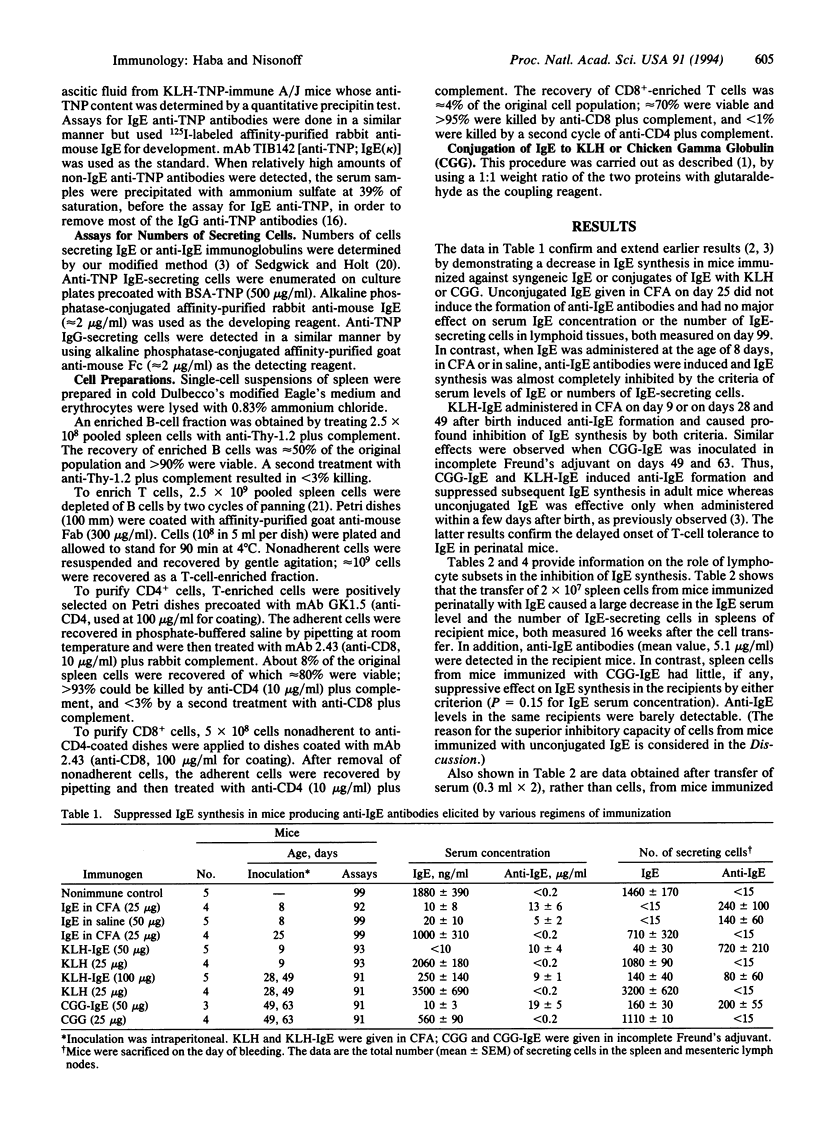
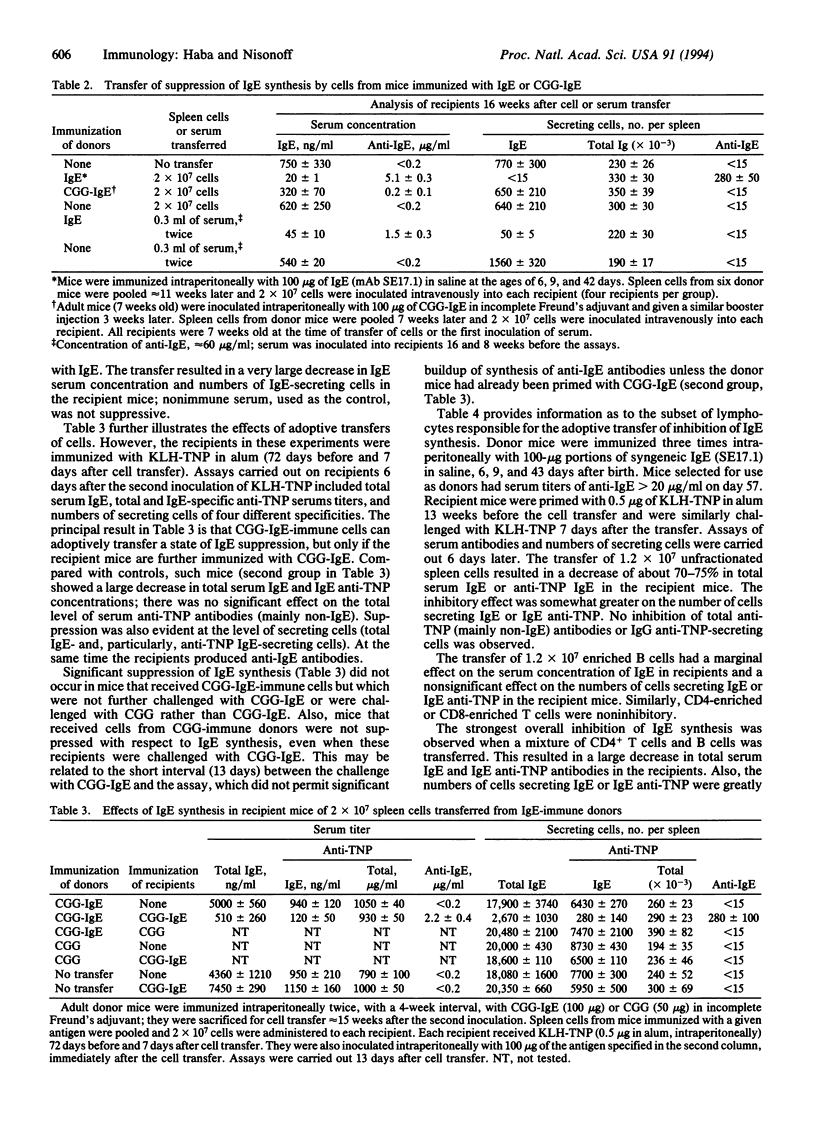
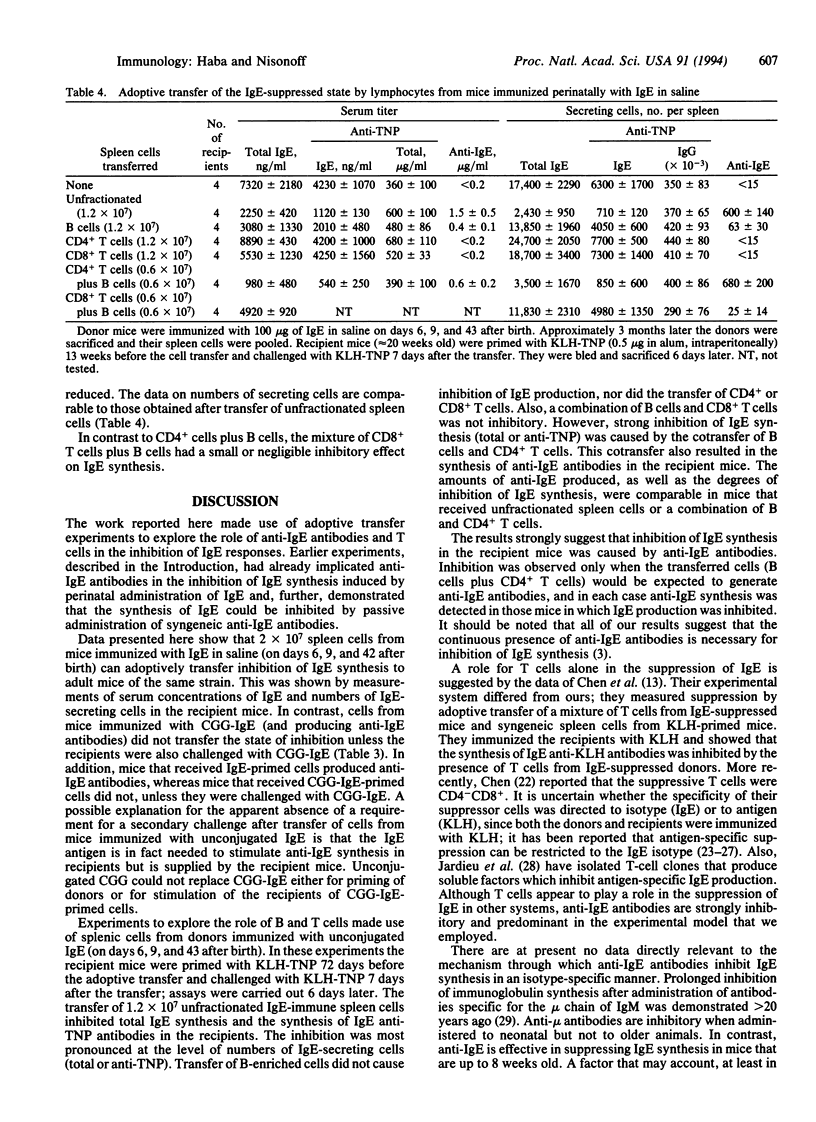
We have shown that the long-term inhibition of IgE synthesis associated with perinatal inoculation of syngeneic IgE is accompanied by the synthesis of autoantibodies to IgE. Synthesis of IgE can also be inhibited by passive transfer of syngeneic anti-IgE antibodies. In the present investigation we made use of adoptive transfer experiments to assess the relative roles of antibodies and T cells in the inhibitory process. It was found that spleen cells from IgE-suppressed mice (synthesizing anti-IgE antibodies) could adoptively transfer the state of inhibition to syngeneic adult mice. The inhibition occurred only under conditions in which the recipient mice synthesized anti-IgE antibodies. Separated B cells, CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, or a mixture of B and CD8+ T cells were ineffective. However, strong inhibition of IgE synthesis (as indicated by serum levels and numbers of IgE-secreting cells in the spleen) was observed after transfer of a mixture of B cells and CD4+ (helper) T cells. The results indicate that in this experimental model anti-IgE antibodies are the suppressive agent and that T cells do not play a role other than that of providing help to B cells for anti-IgE synthesis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benhamou L. E., Cazenave P. A., Sarthou P. Anti-immunoglobulins induce death by apoptosis in WEHI-231 B lymphoma cells. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jun;20(6):1405–1407. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozelka B. E., McCants M. L., Salvaggio J. E., Lehrer S. B. Effects of anti-epsilon on total and specific IgE levels in adult mice. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1985;78(1):51–56. doi: 10.1159/000233862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozelka B. E., McCants M. L., Salvaggio J. E., Lehrer S. B. IgE isotype suppression in anti-epsilon-treated mice. Immunology. 1982 Jul;46(3):527–532. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. S., Katz D. H. IgE class-restricted tolerance induced by neonatal administration of soluble or cell-bound IgE. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):772–788. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. S., Liu F. T., Katz D. H. IgE class-restricted tolerance induced by neonatal administration of soluble or cell-bound IgE. Cellular mechanisms. J Exp Med. 1984 Oct 1;160(4):953–970. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.4.953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. S. Mechanisms of IgE tolerance: dual regulatory T cell lesions in perinatal IgE tolerance. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Oct;21(10):2461–2467. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessein A. J., Parker W. L., James S. L., David J. R. IgE antibody and resistance to infection. I. Selective suppression of the IgE antibody response in rats diminishes the resistance and the eosinophil response to Trichinella spiralis infection. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):423–436. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson J., Radic M. Z., Camper S. A., Hardy R. R., Carmack C., Weigert M. Expression of anti-DNA immunoglobulin transgenes in non-autoimmune mice. Nature. 1991 Jan 24;349(6307):331–334. doi: 10.1038/349331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodnow C. C., Crosbie J., Adelstein S., Lavoie T. B., Smith-Gill S. J., Brink R. A., Pritchard-Briscoe H., Wotherspoon J. S., Loblay R. H., Raphael K. Altered immunoglobulin expression and functional silencing of self-reactive B lymphocytes in transgenic mice. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):676–682. doi: 10.1038/334676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haba S., Nisonoff A. IgE-secreting cells in the thymus: correlation with induction of tolerance to IgE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):5185–5187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.5185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haba S., Nisonoff A. Immunological responsiveness of neonatal A/J mice to isotypic determinants of syngeneic IgE. J Exp Med. 1988 Aug 1;168(2):713–724. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.2.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haba S., Nisonoff A. Induction of high titers of anti-IgE by immunization of inbred mice with syngeneic IgE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):5009–5013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.5009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haba S., Nisonoff A. Induction of tolerance to syngeneic IgE in neonatal mice. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 1;146(3):807–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haba S., Nisonoff A. Inhibition of IgE synthesis by anti-IgE: role in long-term inhibition of IgE synthesis by neonatally administered soluble IgE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3363–3367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haba S., Nisonoff A. Mechanisms of induction of tolerance to syngeneic IgE. Int Immunol. 1992 Jan;4(1):101–105. doi: 10.1093/intimm/4.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haba S., Nisonoff A. Production of syngeneic autoreactive monoclonal antibodies specific for isotypic determinants of IgE. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Dec 24;105(2):193–199. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90266-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haba S., Nisonoff A. Proteolytic digestion of mouse IgE. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Apr 8;138(1):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90059-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haba S., Nisonoff A. Quantitation of IgE antibodies by radioimmunoassay in the presence of high concentrations of non-IgE antibodies of the same specificity. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Dec 17;85(1):39–52. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90272-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley S. B., Crosbie J., Brink R., Kantor A. B., Basten A., Goodnow C. C. Elimination from peripheral lymphoid tissues of self-reactive B lymphocytes recognizing membrane-bound antigens. Nature. 1991 Oct 24;353(6346):765–769. doi: 10.1038/353765a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasbold J., Klaus G. G. Anti-immunoglobulin antibodies induce apoptosis in immature B cell lymphomas. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Aug;20(8):1685–1690. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayglass K. T., Gieni R. S., Stefura W. P. Long-lived reciprocal regulation of antigen-specific IgE and IgG2a responses in mice treated with glutaraldehyde-polymerized ovalbumin. Immunology. 1991 Aug;73(4):407–414. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. G., Leivers S. Tolerance induction via antigen inhalation: isotype specificity, stability, and involvement of suppressor T cells. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1982;67(2):155–160. doi: 10.1159/000233007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardieu P., Uede T., Ishizaka K. Presence of an antigen-specific T cell subset that forms IgE-suppressive factor and IgG-suppressive factor on antigenic stimulation. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):922–929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T., Hirai Y., Suemura M., Yamamura Y. Regulation of antibody response in different immunoglobulin classes. I. Selective suppression of anti-DNP IgE antibody response by preadministration of DNP-coupled mycobacterium. J Immunol. 1976 Aug;117(2):396–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawton A. R., 3rd, Cooper M. D. Modification of B lymphocyte differentiation by anti-immunoglobulins. Contemp Top Immunobiol. 1974;3:193–225. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3045-5_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mage M. G., McHugh L. L., Rothstein T. L. Mouse lymphocytes with and without surface immunoglobulin: preparative scale separation in polystyrene tissue culture dishes coated with specifically purified anti-immunoglobulin. J Immunol Methods. 1977;15(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. S., Bell E. B. Induction of an auto-anti-IgE response in rats I. Effects on serum IgE concentrations. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Mar;15(3):272–277. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. S., Bell E. B. Induction of an auto-anti-IgE response in rats. III. Inhibition of a specific IgE response. Immunology. 1989 Mar;66(3):428–433. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Tsubata T., Okamoto M., Shimizu A., Kumagai S., Imura H., Honjo T. Antigen-induced apoptotic death of Ly-1 B cells responsible for autoimmune disease in transgenic mice. Nature. 1992 May 7;357(6373):77–80. doi: 10.1038/357077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemazee D. A., Bürki K. Clonal deletion of B lymphocytes in a transgenic mouse bearing anti-MHC class I antibody genes. Nature. 1989 Feb 9;337(6207):562–566. doi: 10.1038/337562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J. Immunologic tolerance: collaboration between antigen and lymphokines. Science. 1989 Jul 14;245(4914):147–153. doi: 10.1126/science.2526369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto M., Murakami M., Shimizu A., Ozaki S., Tsubata T., Kumagai S., Honjo T. A transgenic model of autoimmune hemolytic anemia. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):71–79. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph A. K., Burrows P. D., Wabl M. R. Thirteen hybridomas secreting hapten-specific immunoglobulin E from mice with Iga or Igb heavy chain haplotype. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Jun;11(6):527–529. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. M., Dembić Z., Morahan G., Miller J. F., Bürki K., Nemazee D. Peripheral deletion of self-reactive B cells. Nature. 1991 Nov 28;354(6351):308–311. doi: 10.1038/354308a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento M., Glasebrook A. L., Fitch F. W. IgG or IgM monoclonal antibodies reactive with different determinants on the molecular complex bearing Lyt 2 antigen block T cell-mediated cytolysis in the absence of complement. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2665–2672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick J. D., Holt P. G. Induction of IgE-secreting cells and IgE isotype-specific suppressor T cells in the respiratory lymph nodes of rats in response to antigen inhalation. Cell Immunol. 1985 Aug;94(1):182–194. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90095-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick J. D., Holt P. G. Kinetics and distribution of antigen-specific IgE-secreting cells during the primary antibody response in the rat. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):2178–2183. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.2178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavnezer J., Sirlin S., Abbott J. Induction of immunoglobulin isotype switching in cultured I.29 B lymphoma cells. Characterization of the accompanying rearrangements of heavy chain genes. J Exp Med. 1985 Mar 1;161(3):577–601. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.3.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suemura M., Kishimoto T., Hirai Y., Yamamura Y. Regulation of antibody response in different immunoglobulin classes. III. In vitro demonstration of "IgE class-specific" suppressor functions of DNP-mycobacterium-primed T cells and the soluble factor released from these cells. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):149–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsubata T., Wu J., Honjo T. B-cell apoptosis induced by antigen receptor crosslinking is blocked by a T-cell signal through CD40. Nature. 1993 Aug 12;364(6438):645–648. doi: 10.1038/364645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb C. F., Gathings W. E., Cooper M. D. Effect of anti-gamma 3 antibodies on immunoglobulin isotype expression in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated cultures of mouse spleen cells. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Jul;13(7):556–559. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde D. B., Marrack P., Kappler J., Dialynas D. P., Fitch F. W. Evidence implicating L3T4 in class II MHC antigen reactivity; monoclonal antibody GK1.5 (anti-L3T4a) blocks class II MHC antigen-specific proliferation, release of lymphokines, and binding by cloned murine helper T lymphocyte lines. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2178–2183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


