Abstract
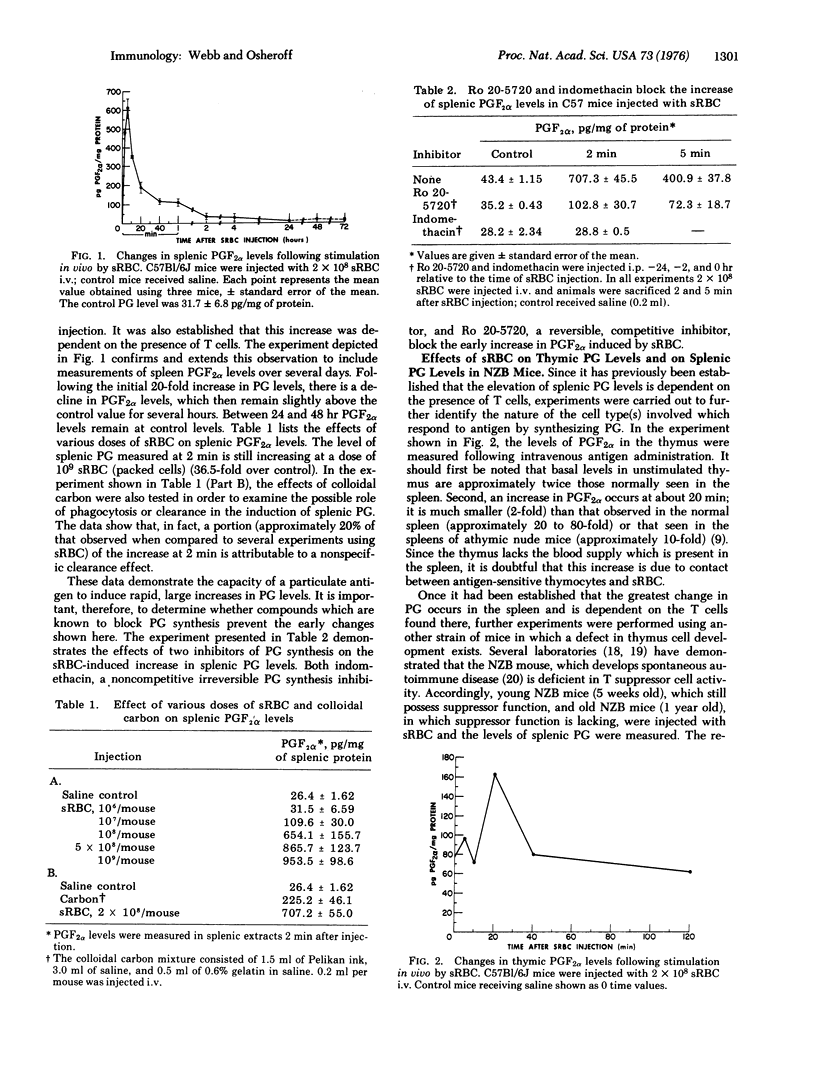
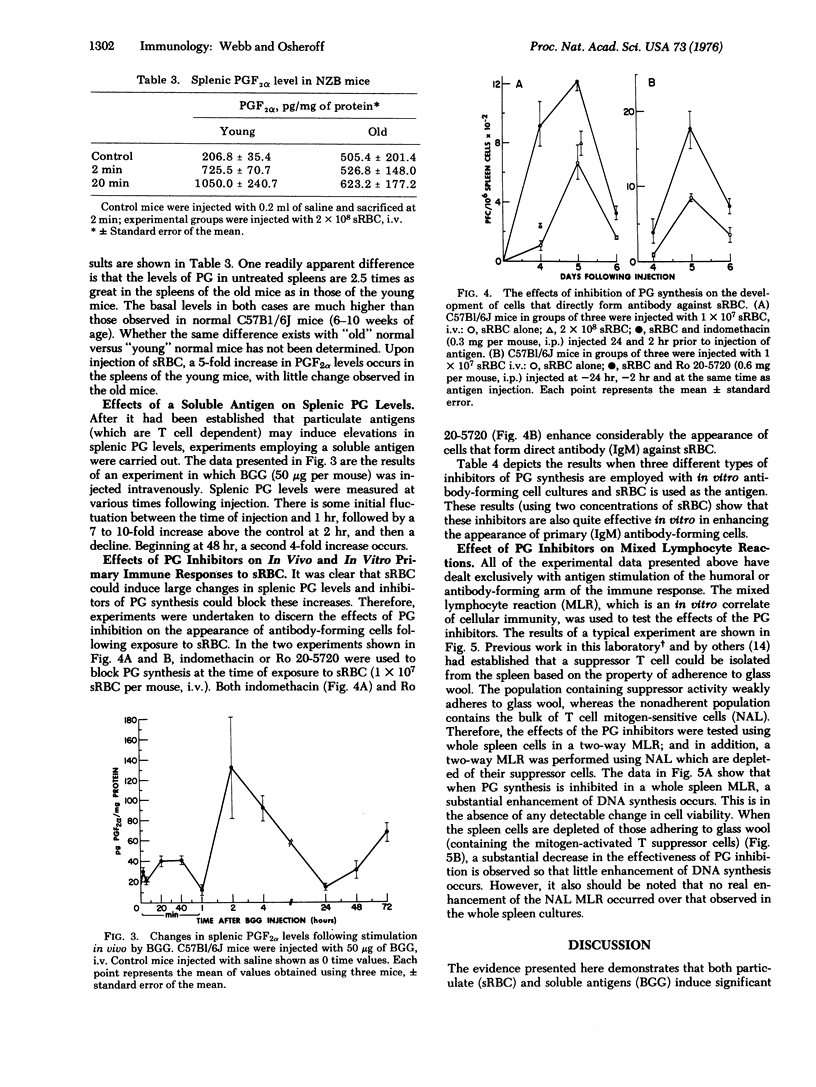
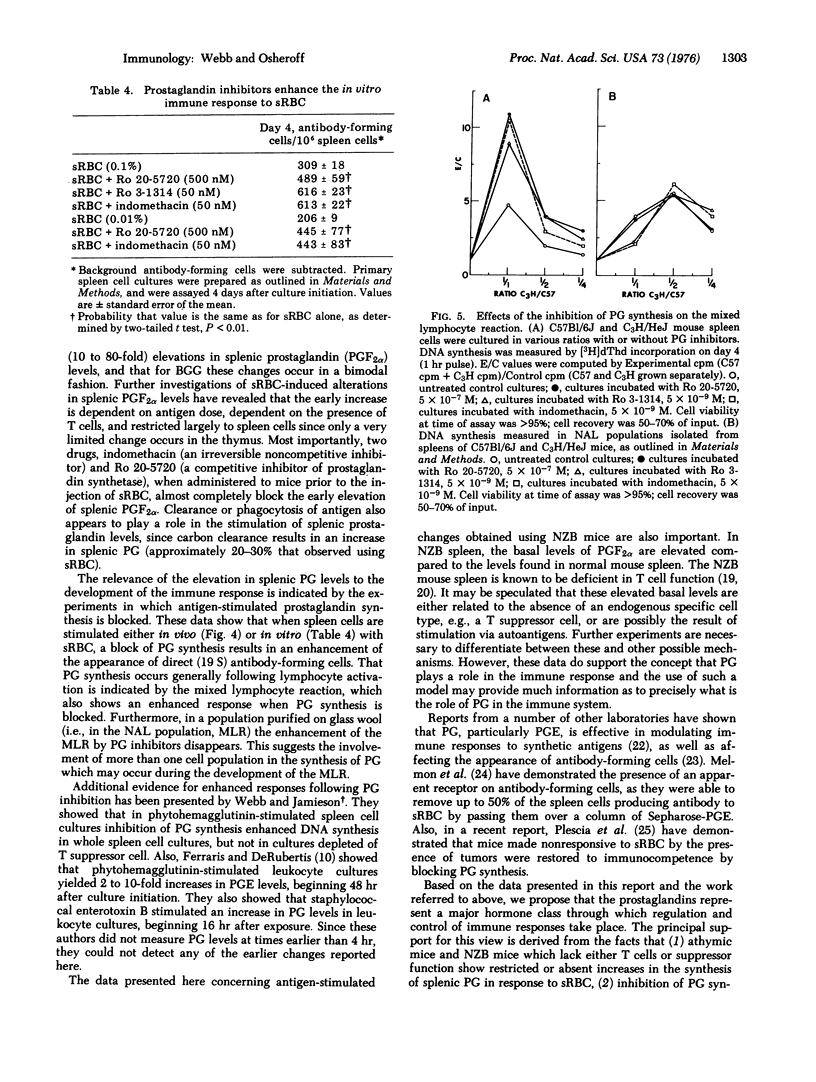
Within 2 min following the intravenous injection of sheep erythrocytes (sRBC) there occurs 20 to 80-fold increase in prostaglandin (PG) F2alpha in the spleen. This burst of synthesis is followed by a slow decline to control levels over the next 1-4 hr. No increase in splenic PGF2alpha levels is observed between 24 and 72 hr after injection. Injection of colloidal carbon results in a small increase, approximately 20% of the increase in PGF2alpha observed with sRBC. The early increase in splenic PGF2alpha levels stimulated by sRBC is also dependent upon thymus-derived (T) cells, since the increase is small or nonexistent in athymic mice and NZB mice. Also, the elevation of splenic PGF2alpha levels is blocked by the administration of indomethacin or Ro 20-5720, both of which block the synthesis of prostglandin. A small increase (2-fold) in PGF2alpha levels occurs in the thymus. A soluble antigen, bovine gamma globulin, stimulated a bimodal increase in splenic PGF2alpha levels, the early peak occurring at 2 hr and the later increase occurring at 48 hr. Using inhibitors of prostaglandin synthesis, it is possible to enhance the appearance of cells forming 19S antibody against sRBC, both in vivo and in vitro. Furthermore, inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis enhances DNA synthesis induced in a two-way mixed-lymphocyte reaction only in whole spleen cell cultures and not in cultures of spleen cells purified by passage over glass wool. Based on this evidence, it is proposed that the prostaglandins represent a major soluble mediator in the control of T cell-T cell interactions and also play an important part in T-B (bone-marrow derived) cell interactions.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler W. H., Takiguchi T., Marsh B., Smith R. T. Cellular recognition by mouse lymphocytes in vitro. I. Definition of a new technique and results of stimulation by phytohemagglutinin and specific antigens. J Exp Med. 1970 Jun 1;131(6):1049–1078. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.6.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach M. A. Differences in Cyclic AMP Changes after Stimulation by Prostaglandins and Isoproterenol in Lymphocyte Subpopulations. J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):1074–1081. doi: 10.1172/JCI108008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold D. R., Kysela S., Steinberg A. D. Decline in suppressor T cell function with age in female NZB mice. J Immunol. 1974 Jan;112(1):9–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Lichtenstein L. M., Melmon K. L., Henney C. S., Weinstein Y., Shearer G. M. Modulation of inflammation and immunity by cyclic AMP. Science. 1974 Apr 5;184(4132):19–28. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4132.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell B. V., Burstein S., Brock W. A., Speroff L. Radioimmunoassay of the F prostaglandins. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Aug;33(2):171–175. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-2-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Click R. E., Benck L., Alter B. J. Immune responses in vitro. I. Culture conditions for antibody synthesis. Cell Immunol. 1972 Feb;3(2):264–276. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dauphinee M. J., Talal N., Goldstein A. L., White A. Thymosin corrects the abnormal DNA synthetic response of NZB mouse thymocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2637–2641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Asua L. J., Clingan D., Rudland P. S. Initiation of cell proliferation in cultured mouse fibroblasts by prostaglandin F2alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2724–2728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferraris V. A., DeRubertis F. R. Release of prostaglandin by mitogen- and antigen-stimulated leukocytes in culture. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):378–386. doi: 10.1172/JCI107773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Indomethacin and aspirin abolish prostaglandin release from the spleen. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):237–239. doi: 10.1038/newbio231237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folch H., Waksman B. H. Regulation of lymphocyte responses in vitro. V. Suppressor activity of adherent and nonadherent rat lymphoid cells. Cell Immunol. 1973 Oct;9(1):12–24. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90163-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzman R. J., Bach M. L., Bach F. H., Thurman G. B., Sell K. W. Precipitation of radioactively labeled samples: a semi-automatic multiple-sample processor. Cell Immunol. 1972 Jun;4(2):182–186. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein L. M., Margolis S. Histamine release in vitro: inhibition by catecholamines and methylxanthines. Science. 1968 Aug 30;161(3844):902–903. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3844.902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall E., Youlten L. J. Proceedings: Prostaglandin E1 synthesis by phagocytosing rabbit polymorphonuclear leucocytes: its inhibition by indomethacin and its role in chemotaxis. J Physiol. 1973 Oct;234(2):98P–100P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F. T-cell regulation of immune responsiveness. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Feb 28;249:9–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29052.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishell R. I., Dutton R. W. Immunization of dissociated spleen cell cultures from normal mice. J Exp Med. 1967 Sep 1;126(3):423–442. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.3.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mozes E., Shearer G. M., Melmon K. L., Bourne H. R. In vitro correction of antigen-induced immune suppression: effects of poly(A) poly(U) and prostaglandin E. Cell Immunol. 1973 Nov;9(2):226–233. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90073-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osheroff P. L., Webb D. R., Paulsrud J. Induction of T-cell dependent splenic prostaglandin F2alpha by T-cell dependent antigen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Sep 2;66(1):425–429. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80345-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plescia O. J., Smith A. H., Grinwich K. Subversion of immune system by tumor cells and role of prostaglandins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1848–1851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strom T. B., Deisseroth A., Morganroth J., Carpenter C. B., Merrill J. P. Alteration of the cytotoxic action of sensitized lymphocytes by cholinergic agents and activators of adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2995–2999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talal N., Steinberg A. D. The pathogenesis of autoimmunity in New Zealand black mice. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1974;64(0):79–103. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65848-8_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J., Epstein R., Cohn M. Cyclic nucleotides as intracellular mediators of the expression of antigen-sensitive cells. Nature. 1973 Dec 14;246(5433):405–409. doi: 10.1038/246405a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto I., Webb D. R. Antigen-stimulated changes in cyclic nucleotide levels in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2320–2324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurier R. B., Quagliata F. Effect of prostaglandin E 1 on adjuvant arthritis. Nature. 1971 Dec 3;234(5327):304–305. doi: 10.1038/234304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


