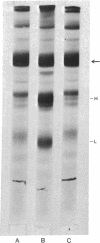
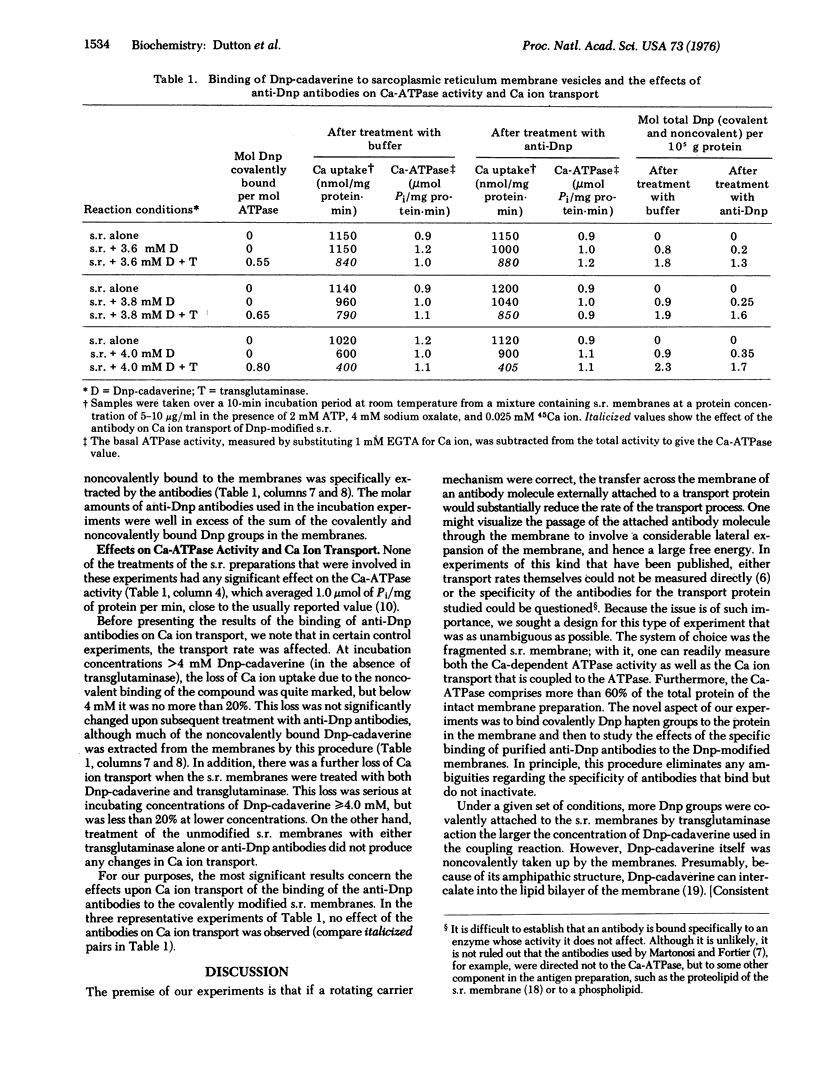
Abstract
An experiment has been carried out to test the rotating carrier mechanism of the translocation event in membrane transport. To the Ca-ATPase in intact sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes, 2,4-[3H]dinitrophenyl-cadaverine has been covalently attached by the action of the enzyme, transglutaminase. The binding of anti-2,4-dinitrophenyl antibodies to the 2,4-dinitrophenyl-modified membranes was found to have no effect on either the Ca-ATPase activity or the Ca ion transport rate of the membranes. These results rule out the rotating carrier mechanism in this system. A different scheme for the translocation process, the aggregate rearrangement mechanism, is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Connellan J. M., Chung S. I., Whetzel N. K., Bradley L. M., Folk J. E. Structural properties of guinea pig liver transglutaminase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 25;246(4):1093–1098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton A., Singer S. J. Crosslinking and labeling of membrane proteins by transglutaminase-catalyzed reactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2568–2571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARAH F. S., KERN M., EISEN H. N. The preparation and some properties of purified antibody specific for the 2,4-dinitrophenyl group. J Exp Med. 1960 Dec 1;112:1195–1210. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.6.1195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill E., Tsernoglou D., Webb L., Banaszak L. J. Polypeptide conformation of cytoplasmic malate dehydrogenase from an electron density map at 3.0 angstrom resolution. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 30;72(3):577–589. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M. K., Guidotti G. A membrane protein from human erythrocytes involved in anion exchange. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):675–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardetzky O. Simple allosteric model for membrane pumps. Nature. 1966 Aug 27;211(5052):969–970. doi: 10.1038/211969a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles A. F., Racker E. Properties of a reconstituted calcium pump. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3538–3544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J. Structural studies of sodium and potassium ion-activated adenosine triphosphatase. The relationship between molecular structure and the mechanism of active transport. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 25;250(18):7443–7449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J. The reactions of sodium and potassium ion-activated adenosine triphosphatase with specific antibodies. Implications for the mechanism of active transport. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3652–3660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenard J., Singer S. J. Protein conformation in cell membrane preparations as studied by optical rotatory dispersion and circular dichroism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Dec;56(6):1828–1835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.6.1828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis C., Shooter E. M. The proteins of rabbit skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Dec;153(2):641–655. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90383-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTONOSI A., FERETOS R. SARCOPLASMIC RETICULUM. I. THE UPTAKE OF CA++ BY SARCOPLASMIC RETICULUM FRAGMENTS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:648–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martonosi A., Donley J. R., Pucell A. G., Halpin R. A. Sarcoplasmic reticulum. XI. The mode of involvement of phospholipids in the hydrolysis of ATP by sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Jun;144(2):529–540. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90358-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martonosi A., Fortier F. The effect of anti-ATPase antibodies upon the Ca++ transport of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Sep 9;60(1):382–389. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90216-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martonosi A. Sarcoplasmic reticulum. IV. Solubilization of microsomal adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jan 10;243(1):71–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., Fleischer S. Characterization of sarcoplasmic reticulum from skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 13;241(2):356–378. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pucell A., Martonosi A. Sarcoplasmic reticulum. XIV. Acetylphosphate and carbamylphosphate as energy sources for Ca++ transport. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3389–3397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racker E., Eytan E. A coupling factor from sarcoplasmic reticulum required for the translocation of Ca2+ ions in a reconstituted Ca2+ATPase pump. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 25;250(18):7533–7534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seydoux F., Malhotra O. P., Bernhard S. A. Half-site reactivity. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1974 Mar;2(2):227–257. doi: 10.3109/10409237409105448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz M. P., Singer S. J. Biological membranes as bilayer couples. A molecular mechanism of drug-erythrocyte interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4457–4461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Nicolson G. L. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):720–731. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J. The molecular organization of membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):805–833. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.004105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A., Green N. M. Studies on the location and orientation of proteins in the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Dec 17;40(2):403–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03209.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonomura Y., Morales M. F. Change in state of spin labels bound to sarcoplasmic reticulum with change in enzymic state, as deduced from ascorbate-quenching studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3687–3691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]