Abstract
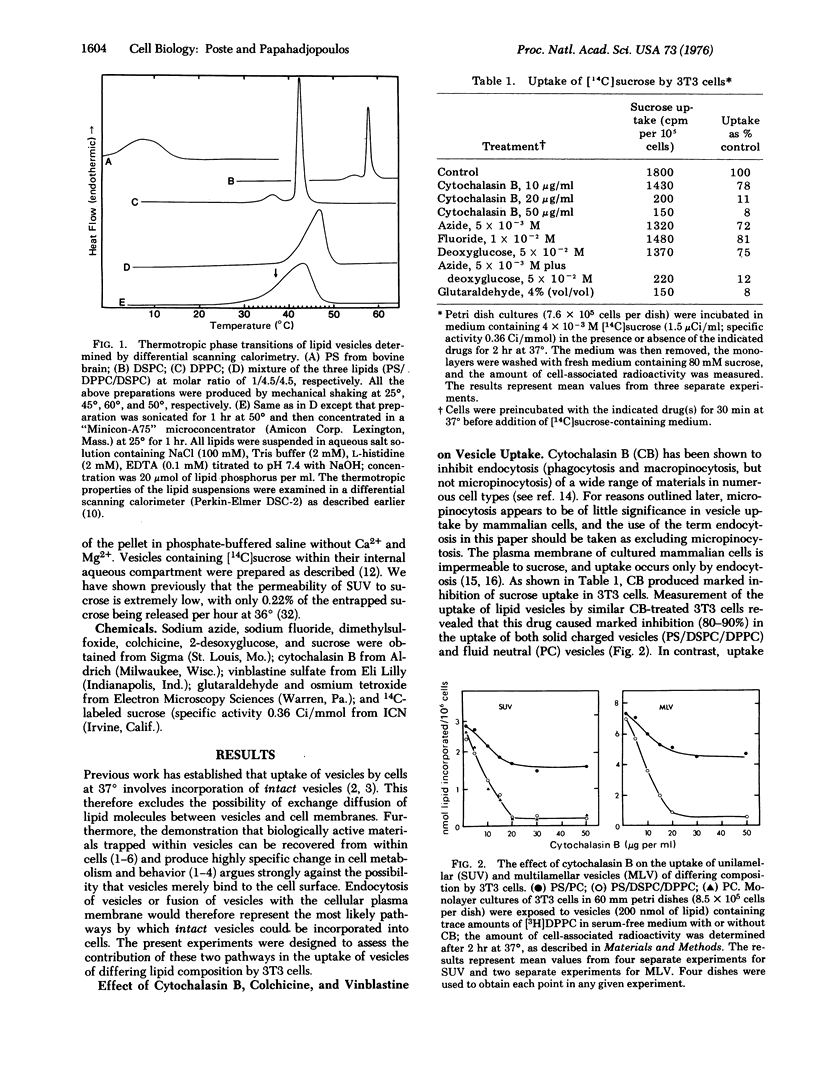
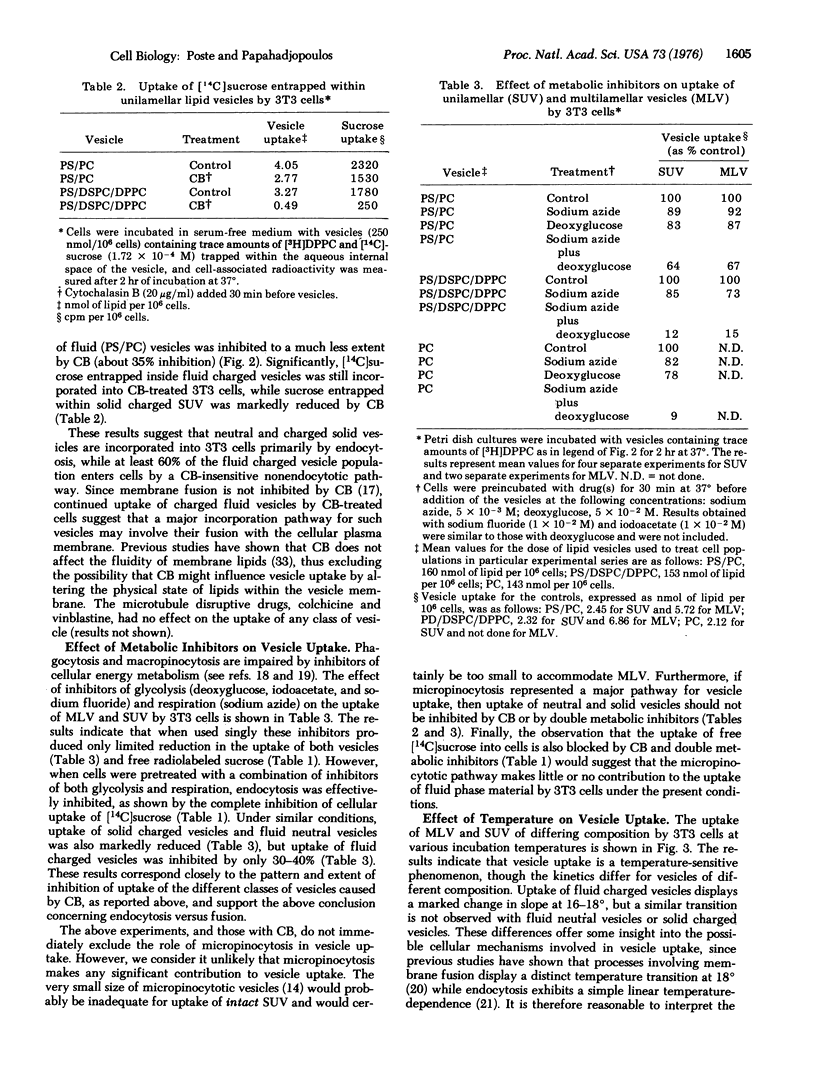
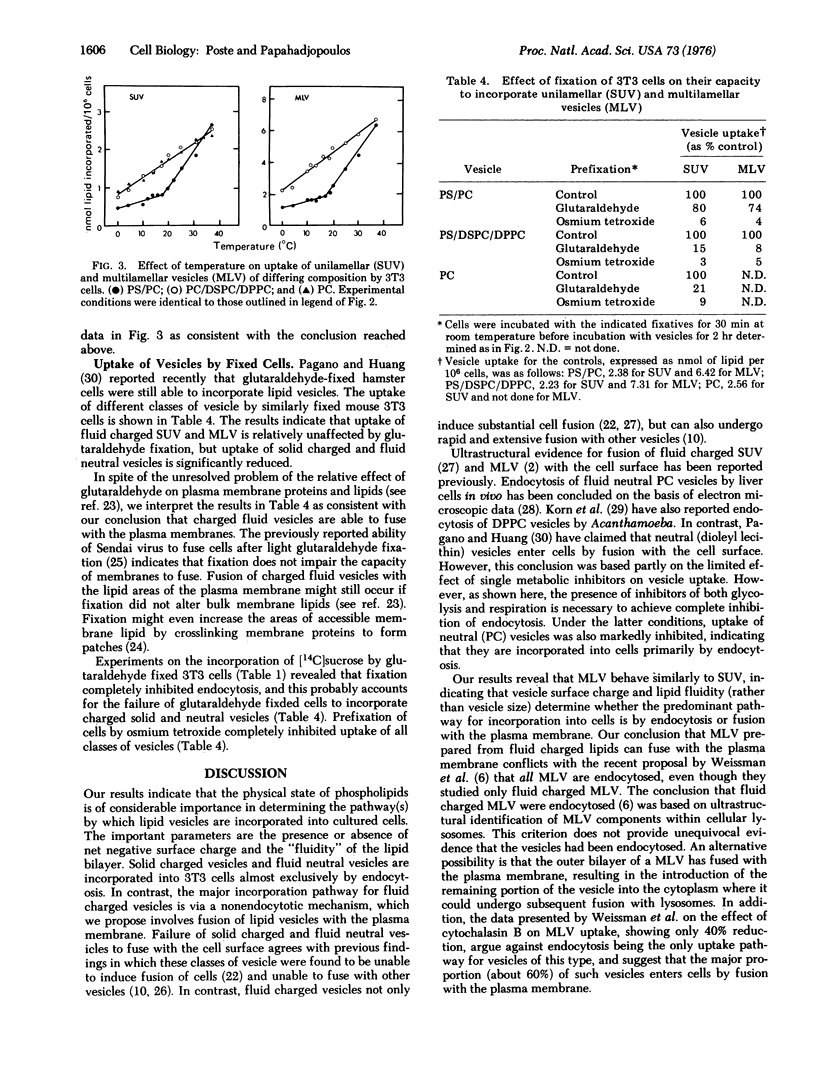
The mechanisms involved in the uptake of uni- and multi-lamellar lipid vesicles by BALB/c mouse 3T3 cells have been investigated. Vesicles are incorporated into cells both by endocytosis and by a nonendocytotic mechanism which we propose involves fusion of vesicles with the plasma membrane. The nonendocytotic pathway predominates in the uptake of negatively charged vesicles composed of phospholipids that are "fluid" (phosphatidylserine/phosphatidylcholine) at 37 degrees. Neutral fluid vesicles (phosphatidylcholine) and negatively charged vesicles prepared from "solid" phospholipids (phosphatidylserine/distearylphosphatidylcholine/dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine) are instead incorporated largely by endocytosis. Uptake of the latter classes of vesicle is reduced (80-90% inhibition) by inhibitors of cellular energy metabolism and by cytochalasin B.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bangham A. D., Standish M. M., Watkins J. C. Diffusion of univalent ions across the lamellae of swollen phospholipids. J Mol Biol. 1965 Aug;13(1):238–252. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80093-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker G., Ashwood-Smith M. J. Endocytosis in Chinese hamster fibroblasts. Inhibition by glucose. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Dec;82(2):310–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90346-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon S., Cohn Z. A. The macrophage. Int Rev Cytol. 1973;36:171–214. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60218-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost P., Brooks U. J., Griffith O. H. Fluidity of phospholipid bilayers and membranes after exposure to osmium tetroxide and gluteraldehyde. J Mol Biol. 1973 May 15;76(2):313–318. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90394-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARNOVSKY M. L. Metabolic basis of phagocytic activity. Physiol Rev. 1962 Jan;42:143–168. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1962.42.1.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor H. L., Prestegard J. H. Fusion of fatty acid containing lecithin vesicles. Biochemistry. 1975 Apr 22;14(8):1790–1795. doi: 10.1021/bi00679a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn E. D., Bowers B., Batzri S., Simmons S. R., Victoria E. J. Endycytosis and exocytosis: role of microfilaments and involvement of phospholipids in membrane fusion. J Supramol Struct. 1974;2(5-6):517–528. doi: 10.1002/jss.400020502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagunoff D., Wan H. Temperature dependence of mast cell histamine secretion. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jun;61(3):809–811. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.3.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee W. E., Goff C. W., Schoknecht J., Smith M. D., Cherian K. The interaction of cationic liposomes containing entrapped horseradish peroxidase with cells in culture. J Cell Biol. 1974 Nov;63(2 Pt 1):492–504. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.2.492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin F., MacDonald R. Liposomes can mimic virus membranes. Nature. 1974 Nov 8;252(5479):161–163. doi: 10.1038/252161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayhew E., Poste G., Cowden M., Tolson N., Maslow D. Cellular binding of 3H-cytochalasin B. J Cell Physiol. 1974 Dec;84(3):373–382. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040840306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nermut M. V., Ward B. J. Effect of fixatives on fracture plane in red blood cells. J Microsc. 1974 Sep;102(Pt 1):29–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1974.tb03963.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano R. E., Huang L. Interaction of phospholipid vesicles with cultured mammalian cells. II. Studies of mechanism. J Cell Biol. 1975 Oct;67(1):49–60. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano R. E., Huang L., Wey C. Interaction of phospholipid vesicles with cultured mammalian cells. Nature. 1974 Nov 8;252(5479):166–167. doi: 10.1038/252166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D., Jacobson K., Nir S., Isac T. Phase transitions in phospholipid vesicles. Fluorescence polarization and permeability measurements concerning the effect of temperature and cholesterol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 6;311(3):330–348. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90314-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D., Mayhew E., Poste G., Smith S., Vail W. J. Incorporation of lipid vesicles by mammalian cells provides a potential method for modifying cell behaviour. Nature. 1974 Nov 8;252(5479):163–166. doi: 10.1038/252163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D., Nir S., Oki S. Permeability properties of phospholipid membranes: effect of cholesterol and temperature. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jun 20;266(3):561–583. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(72)90001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D. Phospholipid model membranes. 3. Antagonistic effects of Ca2+ and local anesthetics on the permeability of phosphatidylserine vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 15;211(3):467–477. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90252-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D., Poste G., Mayhew E. Cellular uptake of cyclic AMP captured within phospholipid vesicles and effect on cell-growth behaviour. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Sep 23;363(3):404–418. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90079-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D., Poste G., Schaeffer B. E. Fusion of mammalian cells by unilamellar lipid vesicles: inflluence of lipid surface charge, fluidity and cholesterol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 27;323(1):23–42. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90429-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D., Poste G., Schaeffer B. E., Vail W. J. Membrane fusion and molecular segregation in phospholipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 30;352(1):10–28. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D., Vail W. J., Jacobson K., Poste G. Cochleate lipid cylinders: formation by fusion of unilamellar lipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 3;394(3):483–491. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90299-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poste G., Allison A. C. Membrane fusion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 28;300(4):421–465. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(73)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman Y. E., Wright B. J. Liposomes containing chelating agents. Cellular penetration and a possible mechanism of metal removal. J Cell Biol. 1975 Apr;65(1):112–122. doi: 10.1083/jcb.65.1.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryser H. J. Uptake of protein by mammalian cells: an underdeveloped area. The penetration of foreign proteins into mammalian cells can be measured and their functions explored. Science. 1968 Jan 26;159(3813):390–396. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3813.390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Silver J. M., Cohn Z. A. Pinocytosis in fibroblasts. Quantitative studies in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1974 Dec;63(3):949–969. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.3.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toister Z., Loyter A. The mechanism of cell fusion. II. Formation of chicken erythrocyte polykaryons. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 25;248(2):422–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R., Rosenberg M., Estensen R. Endocytosis in Chang liver cells. Quantitation by sucrose- 3 H uptake and inhibition by cytochalasin B. J Cell Biol. 1971 Sep;50(3):804–817. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.3.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Bloomgarden D., Kaplan R., Cohen C., Hoffstein S., Collins T., Gotlieb A., Nagle D. A general method for the introduction of enzymes, by means of immunoglobulin-coated liposomes, into lysosomes of deficient cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):88–92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


