Abstract
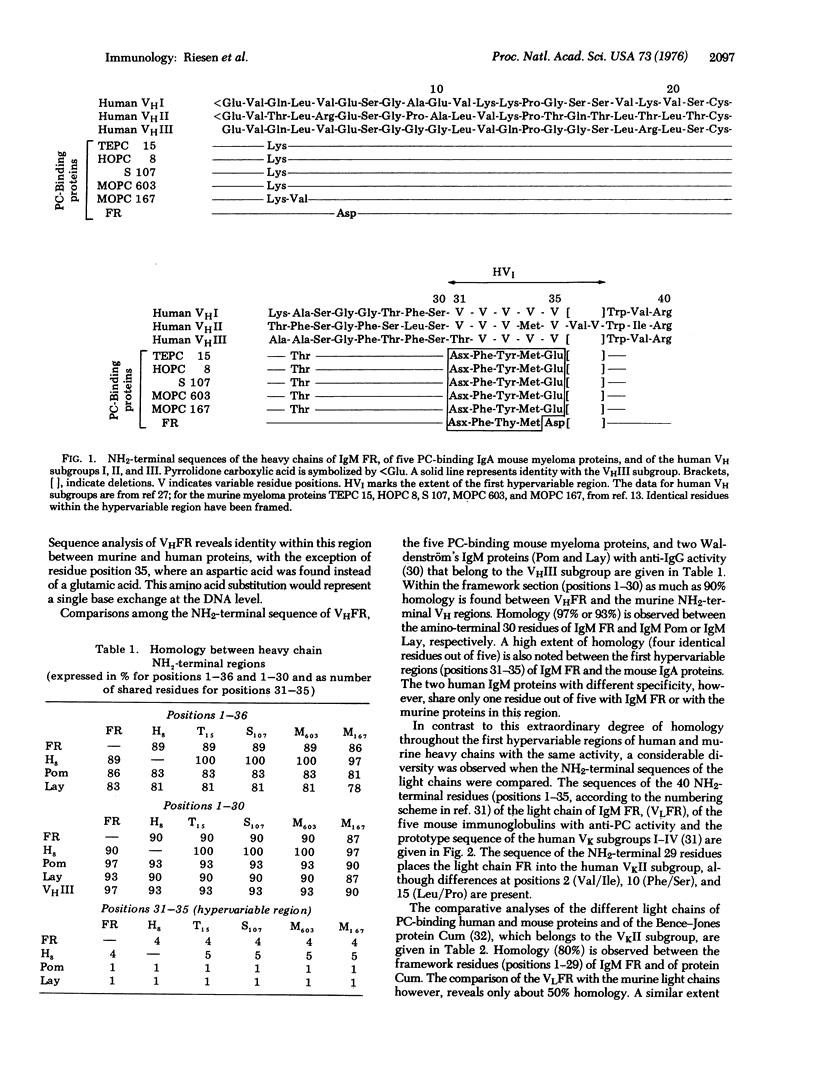
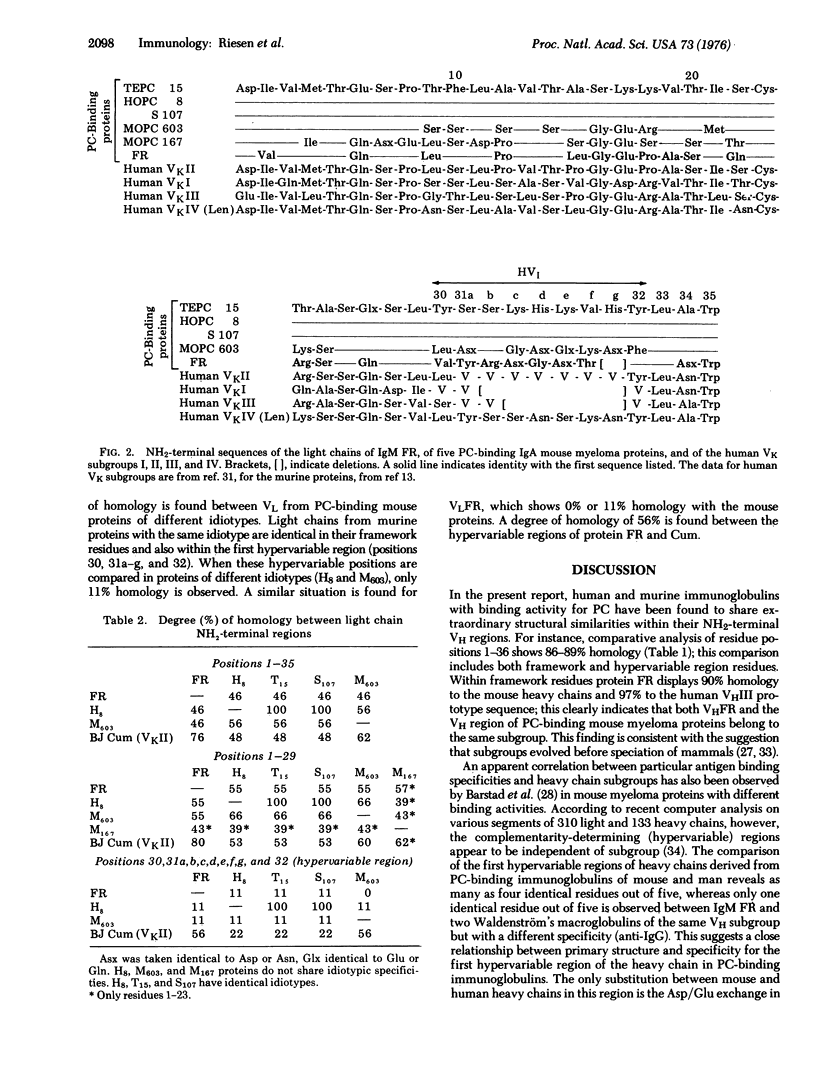
The NH2-terminal 36 residues of the heavy chain and the NH2-terminal 40 residues of the light chain from a human Waldenström's IgM with binding activity for phosphorylcholine (phosphocholine) are compared with the published sequences of five mouse IgA myeloma proteins with the same activity. An extensive structural similarity; i.e., 3 amino acid interchanges within framework residues, and one in the hypervariable region, is noted between the heavy chains of both species. The light chains, however, show a considerable diversity and, in contrast to the heavy chain, no correlation between the primary structure of the first hypervariable region and the binding specificity is apparent. The finding of a very similar heavy chain variable region in two different species that are separated by about 75 million years in evolution favors the concept of stable transmission of variable region genes throughout evolution.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D. Is terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase a somatic mutagen in lymphocytes? Nature. 1974 Mar 29;248(447):409–411. doi: 10.1038/248409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barstad P., Farnsworth V., Weigert M., Cohn M., Hood L. Mouse immunoglobulin heavy chains are coded by multiple germ line variable region genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4096–4100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barstad P., Rudikoff S., Potter M., Cohn M., Konigsberg W., Hood L. Immunoglobulin structure: amino terminal sequences of mouse myeloma proteins that bind phosphorylcholine. Science. 1974 Mar 8;183(4128):962–966. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4128.962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boigne J. M., Boigne N., Rosa J. Description d'une ultramicrométhode d'analyse séquentielle des peptides. J Chromatogr. 1970 Mar 4;47(2):238–246. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(70)80033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgois Alain, Fougereau Michel. Partial amino acid sequence of the variable region of a mouse gammaG2a immunoglobulin heavy chain. Evidence for the existence of a third sub-group of variability for the heavy chain pool. FEBS Lett. 1970 Jun 27;8(5):265–268. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80283-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun D. G., Huser J., Jaton J. Identical sequence of light chains from rabbit anti-streptococcal antibodies. Nature. 1975 Nov 27;258(5533):363–365. doi: 10.1038/258363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunitzer G., Schrank B., Ruhfus A. Zum vollständigen und autoatischen Abbau von Peptiden nach der Quadrolmethode. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1970 Dec;351(12):1589–1590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner S., Milstein C. Origin of antibody variation. Nature. 1966 Jul 16;211(5046):242–243. doi: 10.1038/211242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Kehoe J. M. Hypervariable regions, idiotypy, and the antibody-combining site. Adv Immunol. 1975;20:1–40. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Kehoe J. M. Structure of antibodies with shared idiotypy: the complete sequence of the heavy chain variable regions of two immunoglobulin M anti-gamma globulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4032–4036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Kehoe J. M. Variable region sequences of five human immunoglobulin heavy chains of the VH3 subgroup: definitive identification of four heavy chain hypervariable regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):845–848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Kunkel H. G. Amino acid sequence similarities in two human anti gamma globulin antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):87–92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Tung A. S., Nisonoff A. Structural studies on induced antibodies with defined idiotypic specificities. II. The light chains of anti-p-azophenylarsonate antibodies from A/J mice bearing a cross-reactive idiotype. J Immunol. 1975 Aug;115(2):414–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D., Weigert M. Immunochemical analysis of the cross-reacting idiotypes of mouse myeloma proteins with anti-dextran activity and normal anti-dextran antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):235–239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn M. The take-home lesson--1971. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Dec 31;190:529–584. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb13562.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman P., Begg G. A protein sequenator. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Mar;1(1):80–91. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gally J. A., Edelman G. M. The genetic control of immunoglobulin synthesis. Annu Rev Genet. 1972;6:1–46. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.06.120172.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilschmann N. Die vollständige Aminosäuresequenz des Bence-Jones-Proteins Cum. (kappa-Typ) Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1967 Dec;348(12):1718–1722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L. E. Two genes, one polypeptide chain--fact or fiction? Fed Proc. 1972 Jan-Feb;31(1):177–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., Talmage D. W. Mechanism of antibody diversity: germ line basis for variability. Science. 1970 Apr 17;168(3929):325–334. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3929.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerne N. K. The somatic generation of immune recognition. Eur J Immunol. 1971 Jan;1(1):1–9. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830010102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler H., Shimizu A., Paul C., Moore V., Putnam F. W. Three variable-gene pools common to IgM, IgG and IgA immunoglobulins. Nature. 1970 Sep 26;227(5265):1318–1320. doi: 10.1038/2271318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG J. Genes and antibodies. Science. 1959 Jun 19;129(3364):1649–1653. doi: 10.1126/science.129.3364.1649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKean D., Potter M., Hood L. Mouse immunoglobulin chains. Partial amino acid sequence of a kappa chain. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb;12(4):749–759. doi: 10.1021/bi00728a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKean D., Potter M., Hood L. Mouse immunoglobulin chains. Pattern of sequence variation among kappa chains with limited sequence differences. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb;12(4):760–771. doi: 10.1021/bi00728a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudin J., Michel M. Idiotypy of rabbit antibodies. II. Comparison of idiotypy of various kinds of antibodies formed in the same rabbits against Salmonella typhi. J Exp Med. 1969 Sep 1;130(3):619–642. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.3.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisano J. J., Bronzert T. J. Analysis of amino acid phenylthiohydantoins by gas chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 25;244(20):5597–5607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riesen W., Rudikoff S., Oriol R., Potter M. An IgM Waldenström with specificity against phosphorylcholine. Biochemistry. 1975 Mar 11;14(5):1052–1057. doi: 10.1021/bi00676a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudikoff S., Mushinski E. B., Potter M., Glaudemans C. P., Jolley M. E. Six BALB-c IgA myeloma proteins that bind beta-(1-6)-D-galactan. Partial amino acid sequences and idiotypes. J Exp Med. 1973 Nov 1;138(5):1095–1105. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.5.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M., Hilschmann N. Len.)Len. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1975 May;356(5):507–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal D. M., Padlan E. A., Cohen G. H., Rudikoff S., Potter M., Davies D. R. The three-dimensional structure of a phosphorylcholine-binding mouse immunoglobulin Fab and the nature of the antigen binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4298–4302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. C., Pink J. R., Fudenberg H. H., Ohms J. A variable region subclass of heavy chains common to immunoglobulins G, A, and M and characterized by an unblocked amino-terminal residue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):657–663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigert M. G., Cesari I. M., Yonkovich S. J., Cohn M. Variability in the lambda light chain sequences of mouse antibody. Nature. 1970 Dec 12;228(5276):1045–1047. doi: 10.1038/2281045a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T., Kabat E. A. An analysis of the sequences of the variable regions of Bence Jones proteins and myeloma light chains and their implications for antibody complementarity. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):211–250. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T., Kabat E. A., Bilofsky H. Similarities among hypervariable segments of immunoglobulin chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5107–5110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


