Abstract
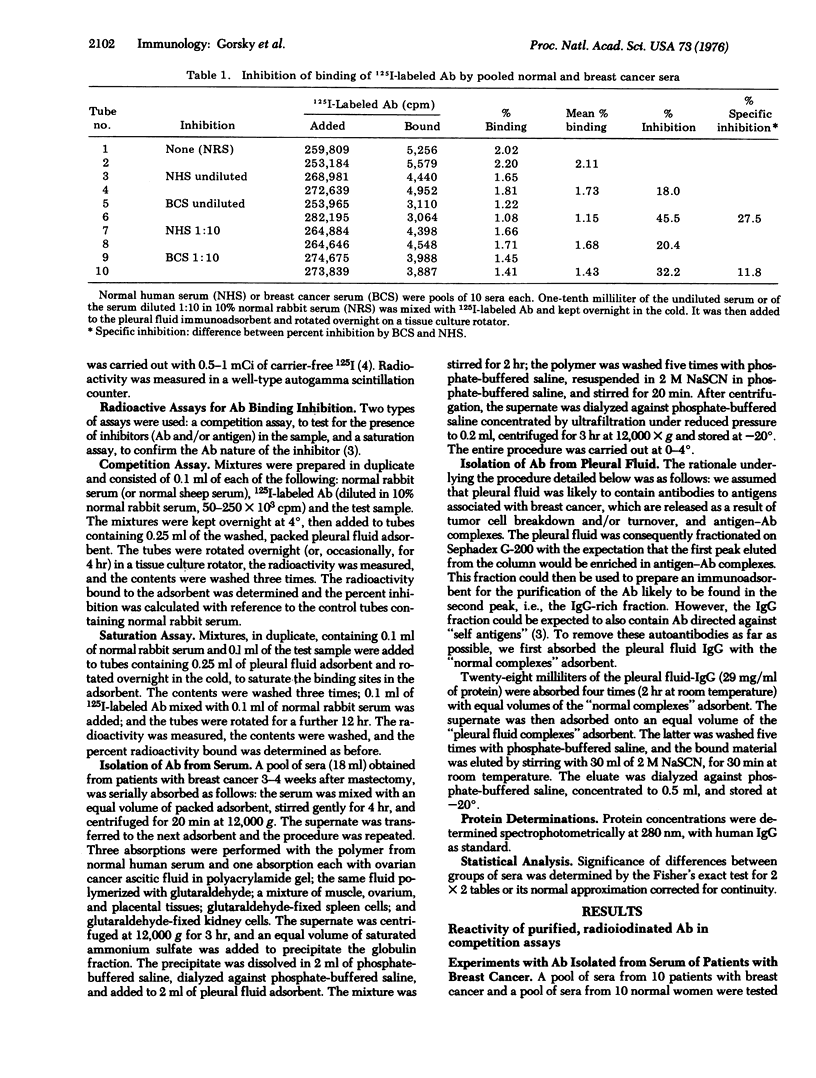
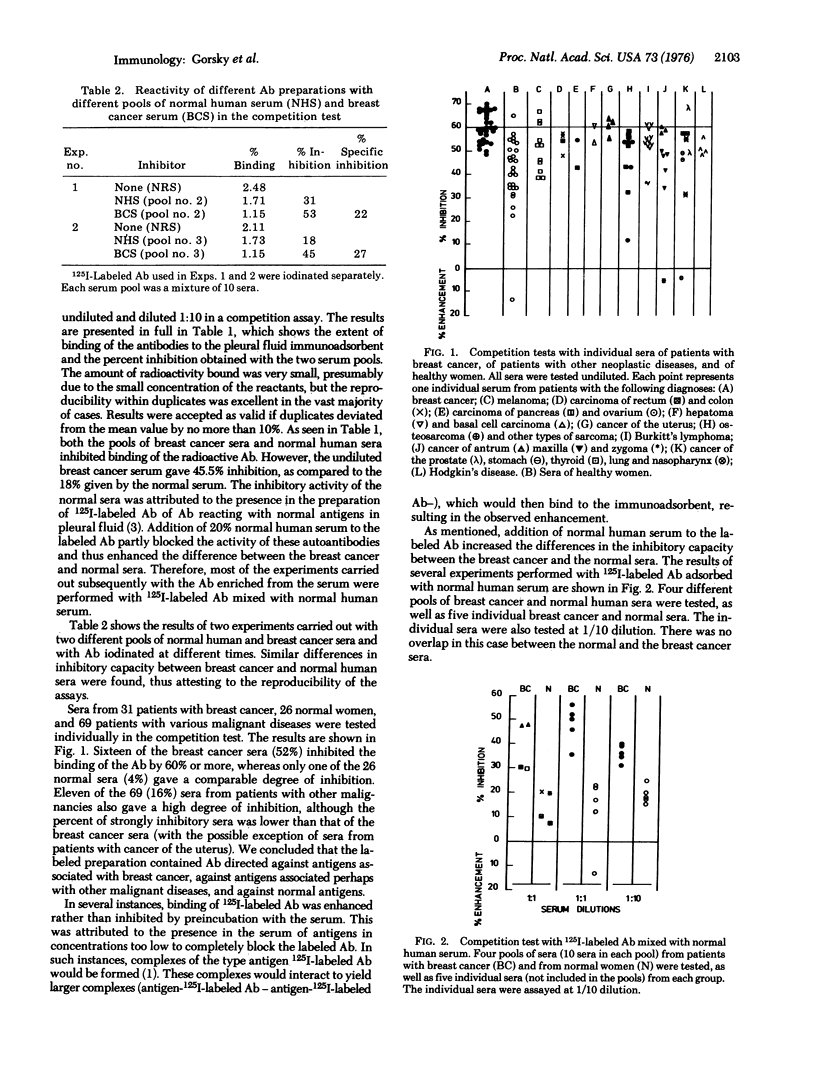
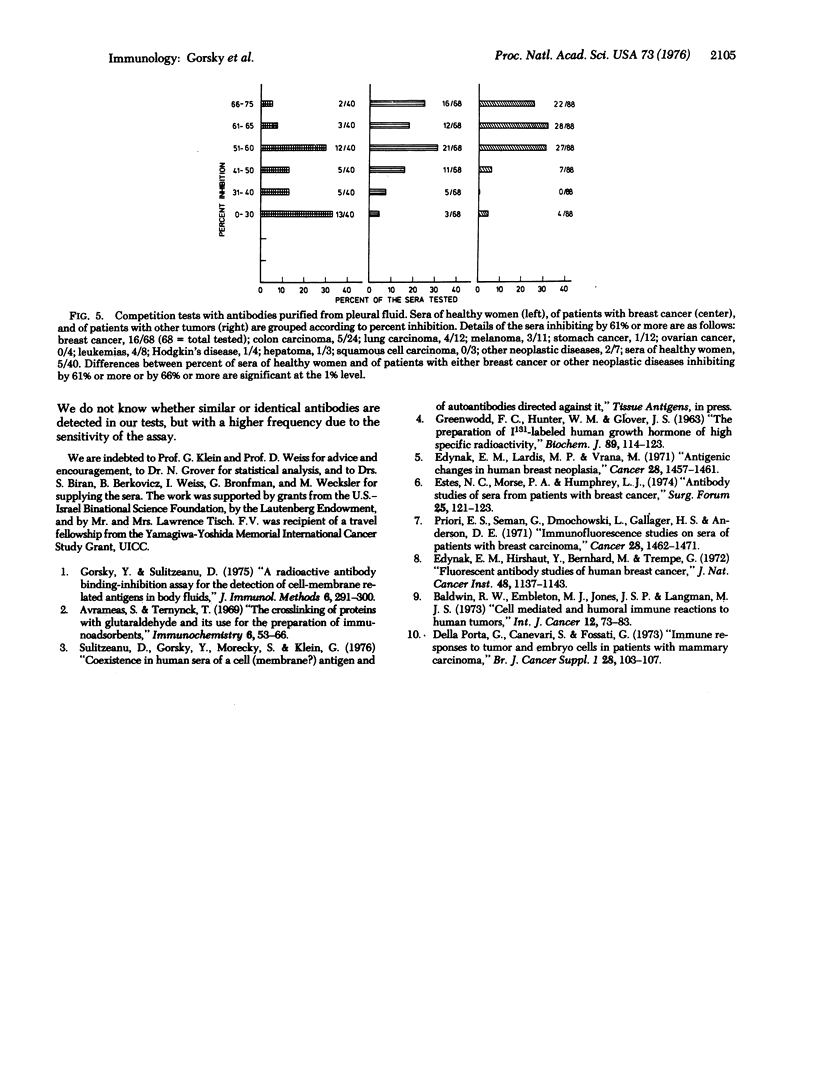
Antibodies were specifically purified, with the use of pleural fluid antigens entrapped in a polyacrylamide gel as immunoadsorbent, from a pool of sera from patients with breast cancer and from the pleural effusion of an individual patient. The purified antibodies were radioiodinated and tested for capacity to bind to the pleural fluid adsorbent. Binding of the radiolabeled antibodies was inhibited by many of the sera from women with breast cancer to a much greater extent than by sera of healthy women. With purified antibodies originating from the serum, 52% of the breast cancer sera and 16% of sera from patients with other malignancies were more inhibitory than were 95% of the sera of healthy women. In the tests with antibodies eluted from pleural fluid, 24% of the breast cancer sera and 25% of the sera from patients with other neoplastic diseases were more inhibitory than were 95% of the normal sera. We concluded that sera of patients with breast cancer may contain antibodies against antigens associated with breast cancer as well as additional antibodies against antigens that are also found in patients with other neoplastic diseases or in normal individuals. Individual breast cancer sera may inhibit binding of the labeled antibodies against breast cancer owing to their content of antibodies, antigen(s), or both.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avrameas S., Ternynck T. The cross-linking of proteins with glutaraldehyde and its use for the preparation of immunoadsorbents. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):53–66. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin R. W., Embleton M. J., Jones J. S., Langman M. J. Cell-mediated and humoral immune reactions to human tumours. Int J Cancer. 1973 Jul 15;12(1):73–83. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910120108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della Porta G., Canevari S., Fossati G. Immune responses to tumour and embryo cells in patients with mammary carcinoma. Br J Cancer Suppl. 1973 Aug;1:103–107. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edynak E. M., Hirshaut Y., Bernhard M., Trempe G. Fluorescent antibody studies of human breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Apr;48(4):1137–1143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edynak E. M., Lardis M. P., Vrana M. Antigenic changes in human breast neoplasia. Cancer. 1971 Dec;28(6):1457–1461. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197112)28:6<1457::aid-cncr2820280619>3.0.co;2-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes N. C., Morse P. A., Jr, Humphrey L. J. Antibody studies of sera from patients with breast cancer. Surg Forum. 1974;25(0):121–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorsky Y., Sulitzeanu D. A radioactive antibody binding-inhibition assay, for the detection of cell-membrane related antigens in body fluids. J Immunol Methods. 1975 Jan;6(3):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(75)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priori E. S., Seman G., Dmochowski L., Gallager H. S., Anderson D. E. Immunofluorescence studies on sera of patients with breast carcinoma. Cancer. 1971 Dec;28(6):1462–1471. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197112)28:6<1462::aid-cncr2820280620>3.0.co;2-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


