Abstract
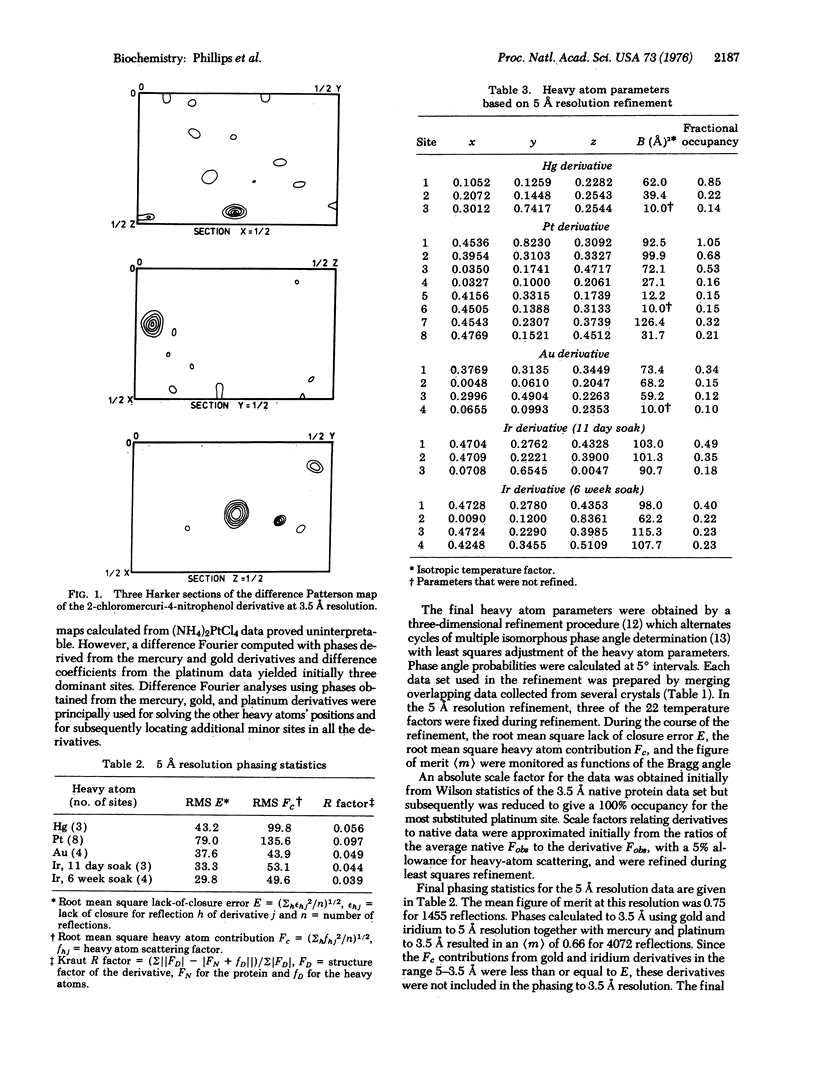
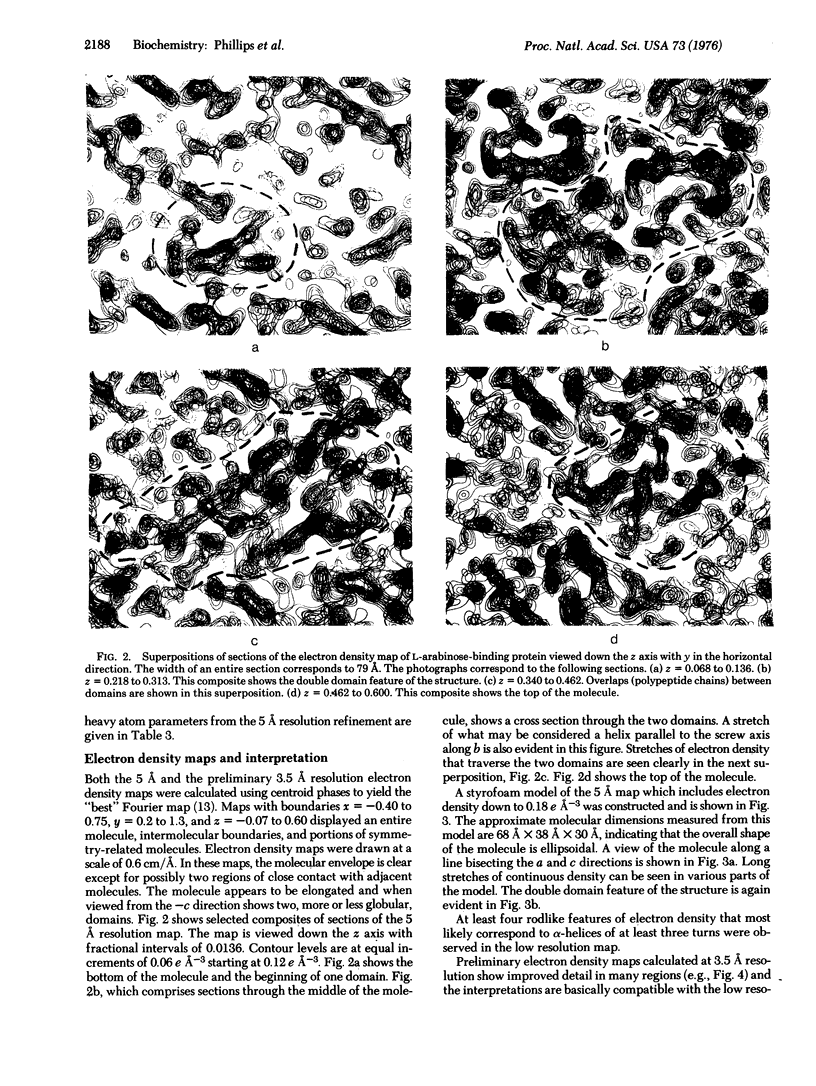
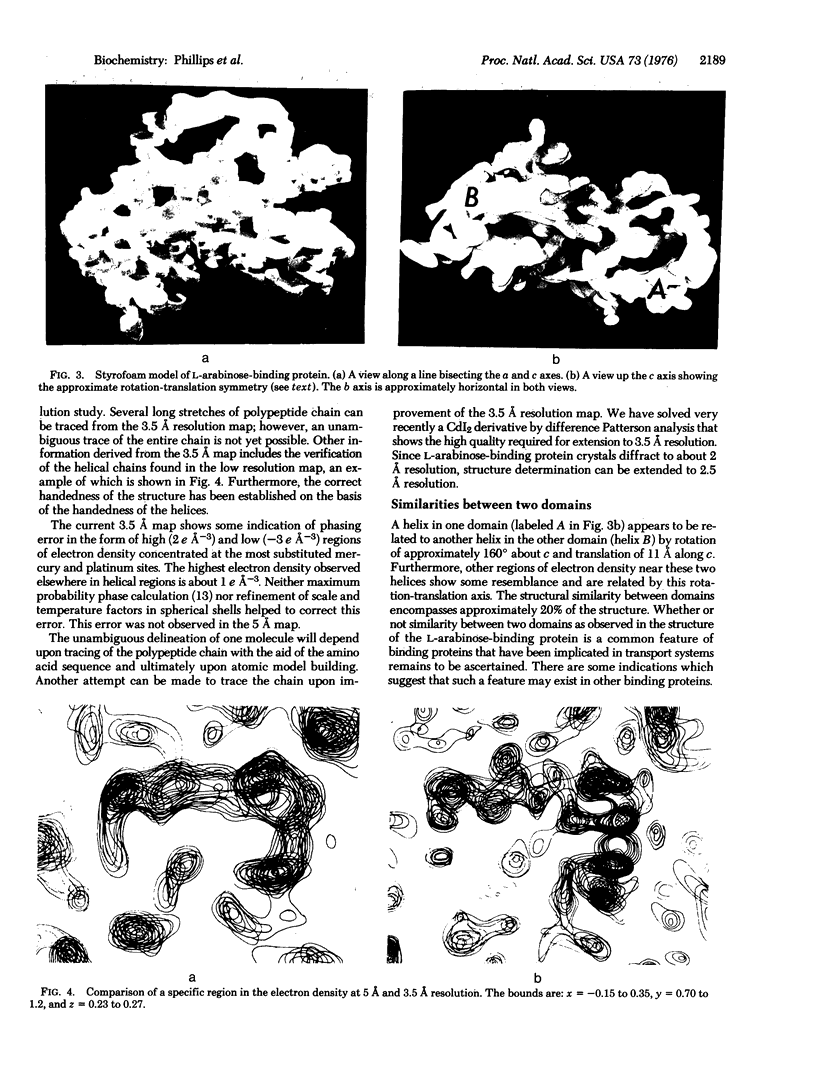
The three-dimensional crystal structure of the L-arabinose-binding protein from E. coli, an essential component in the active transport of L-arabinose, has been solved at 5 A resolution using the method of multiple isomorphous replacement. Five heavy atom derivatives were used. A preliminary 3.5 A electron density map has also been calculated. The results indicate that the molecule is ellipsoidal with approximate dimensions 68 A X 38 A X 30 A. Two similar domains within the molecule (which is a single polypeptide chain) are related by an approximate noncrystallographic rotation-translation axis. This relationship involves approximately 20% of the structure.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J. Chemotaxis in bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:341–356. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boos W. Bacterial transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):123–146. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.001011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg R. W., Englesberg E. L-arabinose binding protein from Escherichia coli B-r. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):423–432. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.423-432.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffat K., Fullmer C. H., Wasserman R. H. Preliminary crystallographic data for a calcium binding protein from bovine intestine. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 5;97(4):661–664. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80066-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxender D. L. Membrane transport proteins. Biomembranes. 1974;5:25–79. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-7389-6_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons R. G., Hogg R. W. A comparison of the L-arabinose- and D-galactose-binding proteins of Escherichia coli B-r. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3608–3614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons R. G., Hogg R. W. Crystallization and characterization of the L-arabinose-binding protein of Escherichia coli B-r. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3602–3607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quiocho F. A., Phillips G. N., Jr, Parsons R. G., Hogg R. W. Letter: Crystallographic data of an L-arabinose-binding protein from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 25;86(2):491–493. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyckoff H. W., Doscher M., Tsernoglou D., Inagami T., Johnson L. N., Hardman K. D., Allewell N. M., Kelly D. M., Richards F. M. Design of a diffractometer and flow cell system for X-ray analysis of crystalline proteins with applications to the crystal chemistry of ribonuclease-S. J Mol Biol. 1967 Aug 14;27(3):563–578. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]