Abstract
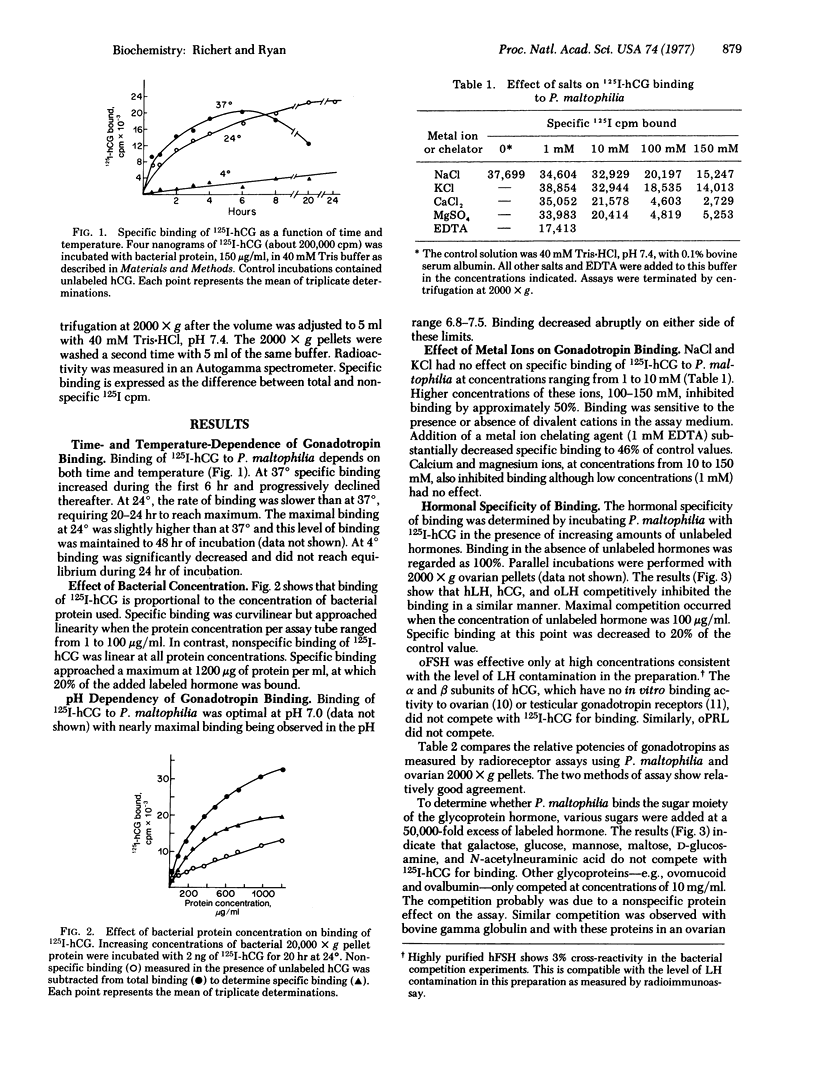
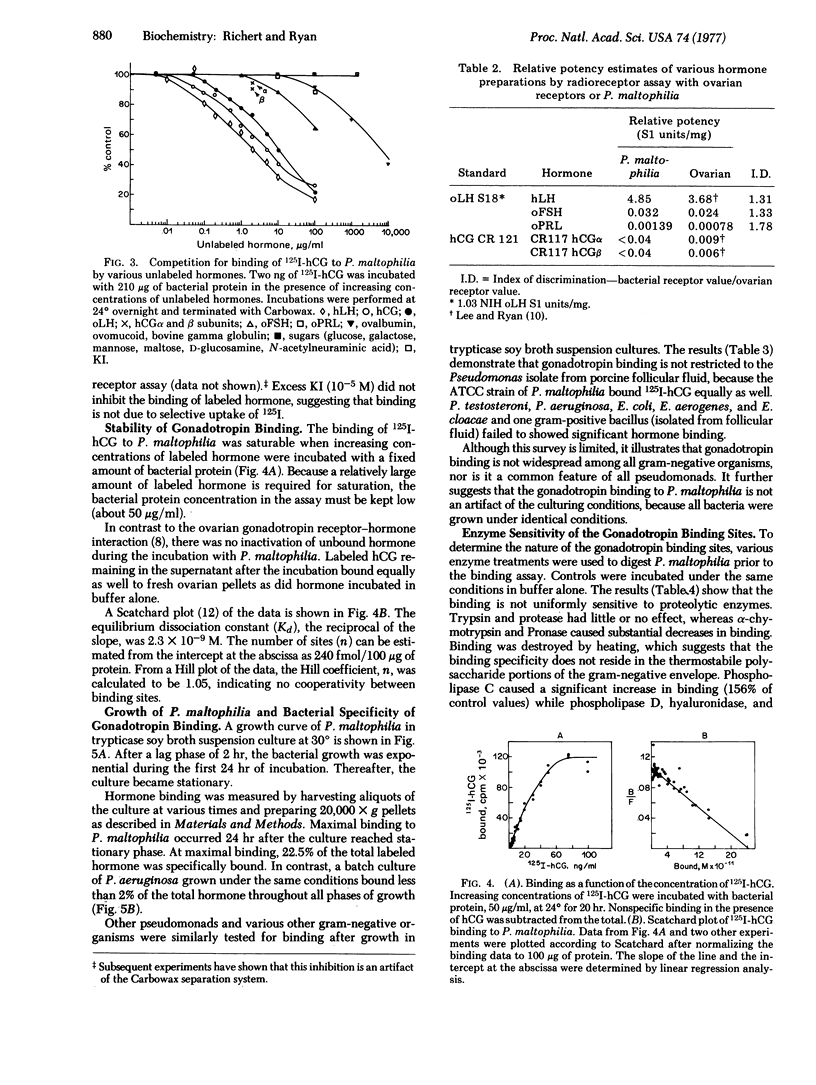
Binding of 125I-labeled human chorionic gonadotropin to Pseudomonas maltophilia is dependent on time, temperature, and pH and the binding to this procaryotic species is hormone-specific and saturable. The equilibrium dissociation constant is 2.3 X 10(-9) M. There are no cooperative interactions between binding sites (Hill coefficient, 1.05). The number of sites is estimaated as 240 fmol/100 mug of protein. NaCl and KCl, at concentrations from 1 to 10 mM, have no effect on binding. Divalent cations (Mg2+ and Ca2+) and 1 mM EDTA inhibit hormone binding. Binding is destroyed by heat or by treatment with Pronase of alpha-chymotrypsin and is increased by phospholipase C. Binding of the labeled gonadotropin is not observed with other gram-negative organisms--e.g., Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas testosteroni, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterobacter aerogenes, or Enterobacter cloacae.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Catt K. J., Dufau M. L., Tsuruhara T. Absence of intrinsic biological activity in LH and hCG subunits. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Jan;36(1):73–80. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-1-73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catt K. J., Tsuruhara T., Dufau M. L. Gonadotrophin binding sites of the rat testis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 18;279(1):194–201. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90254-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen H., Strampp A. Bacterial synthesis of substance similar to human chorionic gonadotrophin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Jul;152(3):408–410. doi: 10.3181/00379727-152-39407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Morse S. A. Alteration of growth, infectivity, and viability of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by gonadal steroids. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Feb;22(2):286–294. doi: 10.1139/m76-039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGH R., RYSCHENKOW E. Pseudomonas maltophilia, an alcaligenes-like species. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Sep;26:123–132. doi: 10.1099/00221287-26-1-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holcomb H. H., Costlow M. E., Buschow R. A., McGuire W. L. Prolactin binding in rat mammary gland during pregnancy and lactation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 25;428(1):104–112. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Yee M. L. Specific removal of proteins from the envelope of Escherichia coli by protease treatments. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):585–592. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.585-592.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y., Ryan R. J. Interaction of ovarian receptors with human luteinizing hormone and human chorionic gonadotropin. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 6;12(23):4609–4615. doi: 10.1021/bi00747a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y., Ryan R. J. Luteinizing hormone receptors: specific binding of human luteinizing hormone to homogenates of luteinized rat ovaries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3520–3523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston V. W., Livingston A. M. Some cultural, immunological, and biochemical properties of Progenitor cryptocides. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Jun;36(6):569–582. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1974.tb01602.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORA P. T., YOUNG B. G. Interaction of an endotoxin with cationic macromolecules. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Sep;26:81–95. doi: 10.1099/00221287-26-1-81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOSS J. G. EFFECT OF INORGANIC CATIONS ON BACTERICIDAL ACTIVITY OF ANIONIC SURFACTANTS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Aug;86:207–211. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.2.207-211.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voss J. G. Effects of organic cations on the gram-negative cell wall and their bactericidal activity with ethylenediaminetetra-acetate and surface active agents. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Sep;48(3):391–400. doi: 10.1099/00221287-48-3-391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Phillips K., Chen T. Steroid-receptor in Pseudomonas testosteroni released by osmotic shock. J Steroid Biochem. 1973 Nov;4(6):613–621. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(73)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


