Abstract
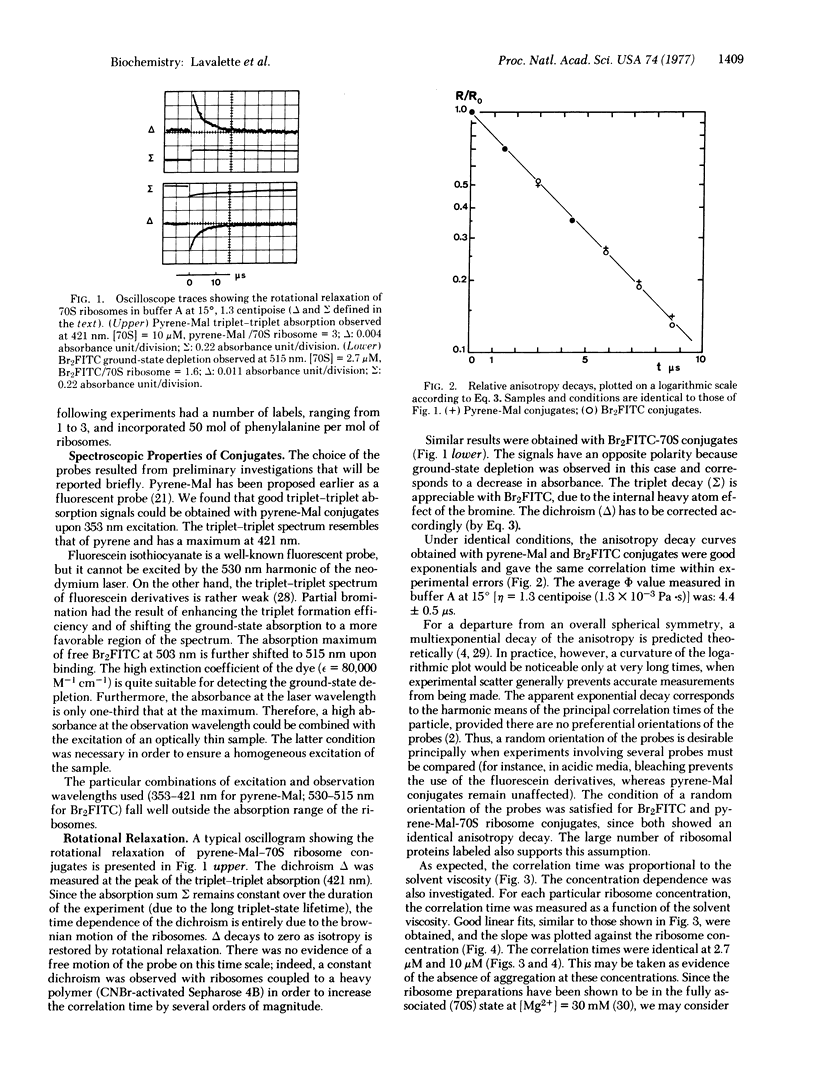
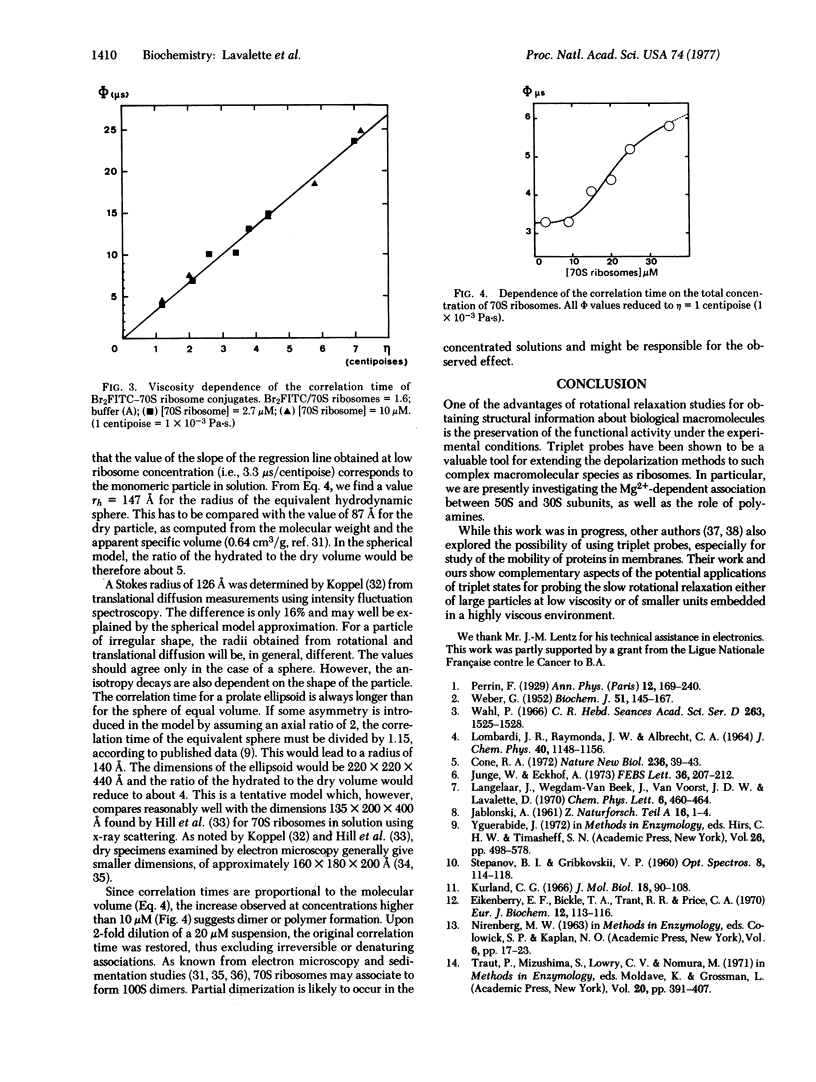
Rotational relaxation on the microsecond time scale has been followed by a depolarization technique using the properties of the long-lived triplet state of covalently bound labels. Two triplet probes, which efficiently bind to ribosomal proteins, are described. The rotational correlation time of 70S ribosomes of Escherichia coli has been measured. The average hydrodynamic radius of the functionally active 70S particle in solution has been estimated to 147 A. A concentration dependence of the correlation time has been observed, which may result from an association of the 70S ribosomes to form 100S dimers.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COHEN S. S., LICHTENSTEIN J. Polyamines and ribosome structure. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jul;235:2112–2116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry R. J., Schneider G. A spectroscopic technique for measuring slow rotational diffusion of macromolecules. 2: Determination of rotational correlation times of proteins in solution. Biochemistry. 1976 Aug 24;15(17):3657–3661. doi: 10.1021/bi00662a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone R. A. Rotational diffusion of rhodopsin in the visual receptor membrane. Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 15;236(63):39–43. doi: 10.1038/newbio236039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eikenberry E. F., Bickle T. A., Traut R. R., Price C. A. Separation of large quantities of ribosomal subunits by zonal ultracentrifugation. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jan;12(1):113–116. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00827.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaudon V., Pochon F. Magnesium dependence of the association kinetics of Escherichia coli ribosomal subunits. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 7;15(18):3903–3912. doi: 10.1021/bi00663a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginzburg I., Zamir A. Characterization of different conformational forms of 30 S ribosomal subunits in isolated and associated states: possible correlations between structure and function. J Mol Biol. 1975 Apr 25;93(4):465–476. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90240-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginzburg I., Zamir A. Functional roles and interactions of sulfhydryl proteins of 30 S ribosomal subunits. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jan 25;100(3):387–398. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. E., Thompson J. D., Anderegg J. W. X-ray scattering study of ribosomes from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 Aug 28;44(1):89–102. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90406-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K., Cantor C. R. Surface topography of the 30 s Escherichia coli ribosomal subunit: reactivity towards fluorescein isothiocyanate. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 20;67(2):265–275. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90240-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junge W., Eckhof A. On the orientation of chlorophyll-a1 in the functional membrane of photosynthesis. FEBS Lett. 1973 Oct 15;36(2):207–212. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80370-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltschmidt E., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. VII. Two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for fingerprinting of ribosomal proteins. Anal Biochem. 1970 Aug;36(2):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90376-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koppel D. E. Study of Escherichia coli ribosomes by intensity fluctuation spectroscopy of scattered laser light. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 18;13(13):2712–2719. doi: 10.1021/bi00710a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurland C. G. The requirements for specific sRNA binding by ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jun;18(1):90–108. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80079-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. B. Reaction of N-ethyl maleimide with the ribosomes of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1971 Aug 28;60(1):169–184. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90456-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RINDERKNECHT H. Ultra-rapid fluorescent labelling of proteins. Nature. 1962 Jan 13;193:167–168. doi: 10.1038/193167b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razi Naqvi K., Gonzalez-Rodriguez J., Cherry R. J., Chapman D. Spectroscopic technique for studying protein rotation in membranes. Nat New Biol. 1973 Oct 24;245(147):249–251. doi: 10.1038/newbio245249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter N., Elson D., Spitnik-Elson P. Structural alterations in the 30 S ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli observed with the fluorescent probe N-(3-pyrene) maleimide. FEBS Lett. 1975 Sep 15;57(2):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80704-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBER G. Polarization of the fluorescence of macromolecules. I. Theory and experimental method. Biochem J. 1952 May;51(2):145–155. doi: 10.1042/bj0510145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weltman J. K., Szaro R. P., Frackelton A. R., Jr, Dowben R. M., Bunting J. R., Cathou B. E. N-(3-pyrene)maleimide: a long lifetime fluorescent sulfhydryl reagent. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 10;248(9):3173–3177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. W., Yarbrough L. R. N-(1-pyrene)maleimide: a fluorescent cross-linking reagent. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 29;15(13):2863–2868. doi: 10.1021/bi00658a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


