Abstract
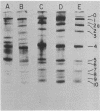
Initiation factor IF-E3 from rabbit reticulocytes was isolated from a high salf extract of ribosomes prepared according to the procedure of Schreier and Staehelin (J. Mol9 Biol, 73, 329-349, 1973). The factor was highly purified from the crude extract by ammonium sulfate fractionation, sucrose gradient centrifugation, salf gradient elution from DEAE-cellulose and phosphocellulose columns, and glycerol gradient centrifugation. IF-E3 stimulated cell-free protein synthesis dependent on an exogenous globin mRNA fraction 4- to 5-fold. The factor under nondenaturing conditions behaved as a large multipolypeptide complex, but was separated into 11 major protein components by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis with urea and sodium dodecyl sulfate. The stoichiometry and molecular weights (range: 28,000-140,000) of the IF-E3 proteins were determined. None of the components corresponded to ribosomal proteins found in high salt-washed ribosomes. 14CH3-IF-E3 was prepared by reductive alkylation without detectable loss of its initiation factor activity, and bound stoichiometrically to 40S ribosomal subunits, but not to 60S or 80S ribosomes. 14CH3-IF-E3 isolated from the 40S complex contained only nine of the 11 original protein components.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S. L., Safer B., Anderson W. F., Merrick W. C. Eukaryotic initiation complex formation. Evidence for two distinct pathways. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 10;250(23):9083–9089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falvey A. K., Staehelin T. Structure and function of mammalian ribosomes. I. Isolation and characterization of active liver ribosomal subunits. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90042-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freienstein C., Blobel G. Nonribosomal proteins associated with eukaryotic native small ribosomal subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3392–3396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy S. J., Kurland C. G., Voynow P., Mora G. The ribosomal proteins of Escherichia coli. I. Purification of the 30S ribosomal proteins. Biochemistry. 1969 Jul;8(7):2897–2905. doi: 10.1021/bi00835a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issinger O. G., Kiefer M. C., Traut R. R. Specificity of ATP-dependent and GTP-dependent protein kinases with respect to ribosomal proteins of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Nov 1;59(1):137–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. H., Kyner D., Acs G. Protein initiation in eukaryotes: formation and function of a ternary complex composed of a partially purified ribosomal factor, methionyl transfer RNA, and guanosine triphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):41–45. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. H., Kyner D., Acs G. Protein synthesis initiation in eukaryotes. Characterization of ribosomal factors from mouse fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6416–6425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mets L. J., Bogorad L. Two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis: an improved method for ribosomal proteins. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jan;57(1):200–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90065-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima S., Nomura M. Assembly mapping of 30S ribosomal proteins from E. coli. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1214–1214. doi: 10.1038/2261214a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Staehelin T. Initiation of eukaryotic protein synthesis: (Met-tRNA f -40S ribosome) initiation complex catalysed by purified initiation factors in the absence of mRNA. Nat New Biol. 1973 Mar 14;242(115):35–38. doi: 10.1038/newbio242035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Staehelin T. Initiation of mammalian protein synthesis: the importance of ribosome and initiation factor quality for the efficiency of in vitro systems. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 19;73(3):329–349. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90346-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundkvist I. C., Staehelin T. Structure and function of free 40 S ribosome subunits: Characterization of initiation factors. J Mol Biol. 1975 Dec 15;99(3):401–418. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]