Abstract
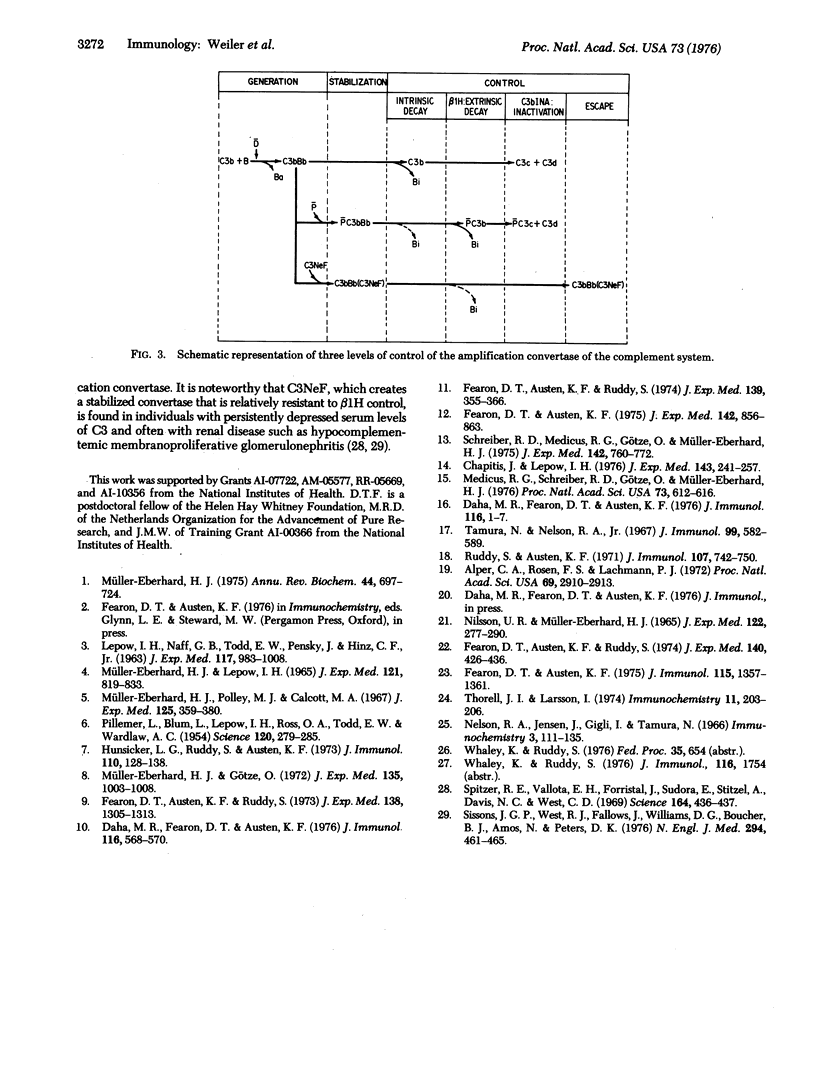
An inhibitory activity for an erythrocyte in termediate bearing the properdin (P)-stabilized amplification C3 convertase, PC3bBb, was recognized in whole normal human serum and separated from C3b inactivator by its distinct physicochemical and functional characteristics. The inhibitory activity was found to reside in a protein that was purified to homogeneity and elicited a monospecific antibody in a rabbit. This protein was identified as beta1H and found to have a serum concentration of 516 +/- 89 mug/ml (mean +/- 1 SD). beta1H produced a dose related, first-order loss of convertase function and release of 125I-Bb from the P-stabilized intermediate, indicating a mechanism of action by decay-dissociation of Bb from the complex, PC3bBb. beta1H exhibited only a limited capacity to accelerate decay of C3bBb sites stabilized with C3 nephritic factor or to release 125I-Bb from such sites. Amplification of C3 cleavage by C3bBb may well determine whether initial complement activation by the classical or alternative activating sequence is beneficial or detrimental to the host. Regulation of this amplifying function is now recognized to occur at at least three steps: intrinsic decay which reflects the inherent lability of the C3bBb convertase; extrinsic decay-dissociation of Bb which is mediated by the effect of beta1H; and inactivation of exposed C3b by C3b inactivator. The stabilization of C3bBb by activated properdin minimizes intrinsic decay and protects C3b in the bimolecular complex from C3b inactivator. beta1H restores control of the system by decay-dissociation of the bimolecular complex, therby exposing C3b to C3b inactivator whose irreversible action prevents regeneration of the convertase at that site.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper C. A., Rosen F. S., Lachmann P. J. Inactivator of the third component of complement as an inhibitor in the properdin pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2910–2913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapitis J., Lepow I. H. Multiple sedimenting species of properdin in human serum and interaction of purified properdin with the third component of complement. J Exp Med. 1976 Feb 1;143(2):241–257. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.2.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daha M. R., Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. C3 nephritic factor (C3NeF): stabilization of fluid phase and cell-bound alternative pathway convertase. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daha M. R., Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. Isolation of alternative pathway C3 convertase containing uncleaved B and formed in the presence of C3 nephritic factor (C3neF). J Immunol. 1976 Feb;116(2):568–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. Initiation of C3 cleavage in the alternative complement pathway. J Immunol. 1975 Nov;115(5):1357–1361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. Properdin: binding to C3b and stabilization of the C3b-dependent C3 convertase. J Exp Med. 1975 Oct 1;142(4):856–863. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.4.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Austen K. F., Ruddy S. Formation of a hemolytically active cellular intermediate by the interaction between properdin factors B and D and the activated third component of complement. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1305–1313. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Austen K. F., Ruddy S. Properdin factor D. II. Activation to D by properdin. J Exp Med. 1974 Aug 1;140(2):426–436. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.2.426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Austen K. F., Ruddy S. Properdin factor D: characterization of its active site and isolation of the precursor form. J Exp Med. 1974 Feb 1;139(2):355–366. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunsicker L. G., Ruddy S., Austen K. F. Alternate complement pathway: factors involved in cobra venom factor (CoVF) activation of the third component of complement (C3). J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):128–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEPOW I. H., NAFF G. B., TODD E. W., PENSKY J., HINZ C. F. Chromatographic resolution of the first component of human complement into three activities. J Exp Med. 1963 Jun 1;117:983–1008. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.6.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUELLER-EBERHARD H. J., LEPOW I. H. C'1 ESTERASE EFFECT ON ACTIVITY AND PHYSICOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF THE FOURTH COMPONENT OF COMPLEMENT. J Exp Med. 1965 May 1;121:819–833. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.5.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medicus R. G., Schreiber R. D., Götze O., Müller-Eberhard H. J. A molecular concept of the properdin pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):612–616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. Complement. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:697–724. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J., Götze O. C3 proactivator convertase and its mode of action. J Exp Med. 1972 Apr 1;135(4):1003–1008. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.4.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J., Polley M. J., Calcott M. A. Formation and functional significance of a molecular complex derived from the second and the fourth component of human complement. J Exp Med. 1967 Feb 1;125(2):359–380. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.2.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NILSSON U. R., MUELLER-EBERHARD H. J. ISOLATION OF BETA IF-GLOBULIN FROM HUMAN SERUM AND ITS CHARACTERIZATION AS THE FIFTH COMPONENT OF COMPLEMENT. J Exp Med. 1965 Aug 1;122:277–298. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. A., Jr, Jensen J., Gigli I., Tamura N. Methods for the separation, purification and measurement of nine components of hemolytic complement in guinea-pig serum. Immunochemistry. 1966 Mar;3(2):111–135. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(66)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PILLEMER L., BLUM L., LEPOW I. H., ROSS O. A., TODD E. W., WARDLAW A. C. The properdin system and immunity. I. Demonstration and isolation of a new serum protein, properdin, and its role in immune phenomena. Science. 1954 Aug 20;120(3112):279–285. doi: 10.1126/science.120.3112.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Austen K. F. C3b inactivator of man. II. Fragments produced by C3b inactivator cleavage of cell-bound or fluid phase C3b. J Immunol. 1971 Sep;107(3):742–750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber R. D., Medicus R. G., Gïtze O., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Properdin- and nephritic factor-dependent C3 convertases: requirement of native C3 for enzyme formation and the function of bound C3b as properdin receptor. J Exp Med. 1975 Sep 1;142(3):760–772. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.3.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sissons J. G., West R. J., Fallows J., Williams D. G., Boucher B. J., Amos N., Peters D. K. The complement abnormalities of lipodystrophy. N Engl J Med. 1976 Feb 26;294(9):461–465. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197602262940902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzer R. E., Vallota E. H., Forristal J., Sudora E., Stitzel A., Davis N. C., West C. D. Serum C'3 lytic system in patients with glomerulonephritis. Science. 1969 Apr 25;164(3878):436–437. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3878.436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura N., Nelson R. A., Jr Three naturally-occurring inhibitors of components of complement in guinea pig and rabbit serum. J Immunol. 1967 Sep;99(3):582–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorell J. I., Larsson I. Lactoperoxidase coupled to polyacrylamide for radio-iodination of proteins to high specific activity. Immunochemistry. 1974 Apr;11(4):203–206. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(74)90329-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


