Abstract
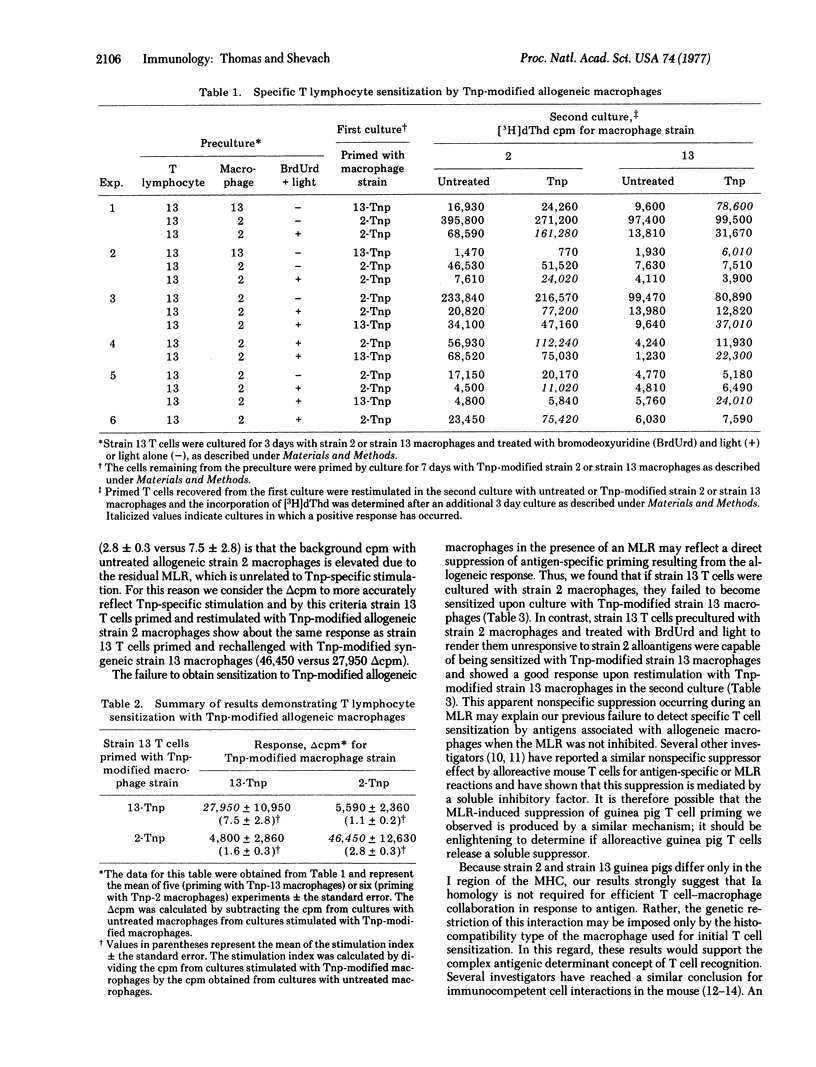
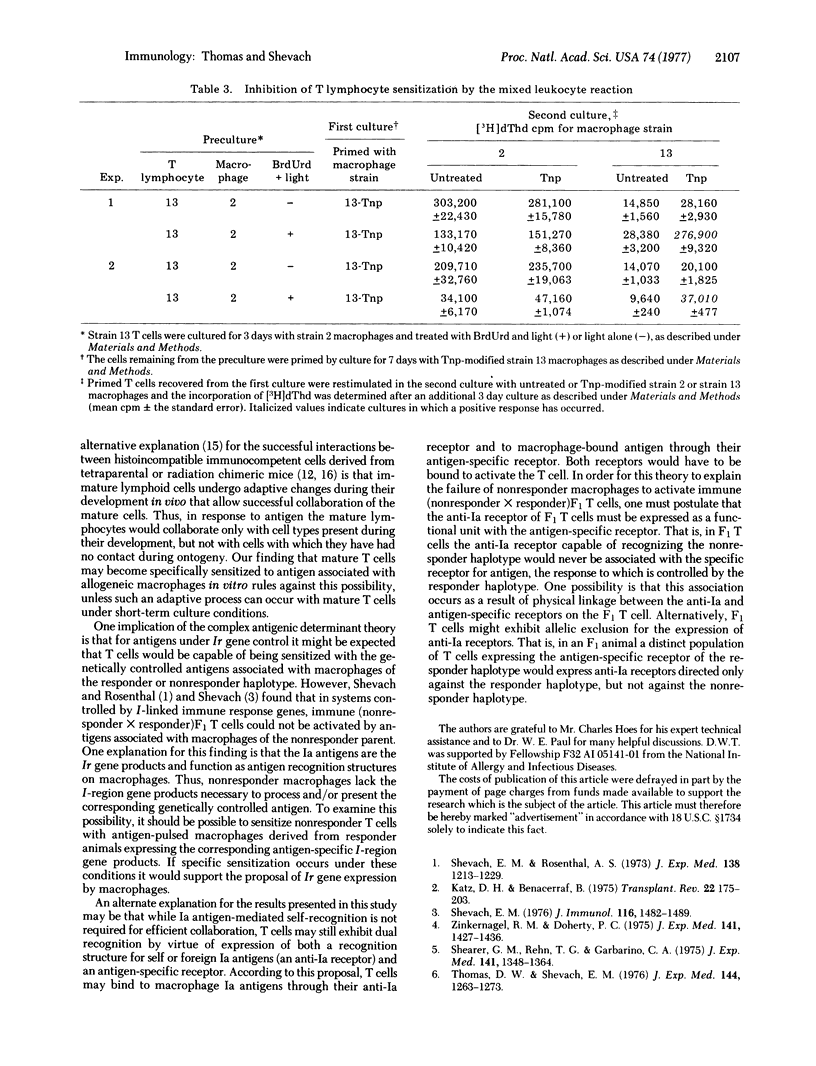
Alloreactive guinea pig thymus-derived (T) cells generated in vitro were rendered unresponsive to allogeneic macrophages by treatment with bromodeoxyuridine and light. The remaining T cells were subsequently primed and rechallenged in tissue culture with trinitrophenyl (Tnp)-modified syngeneic or allogeneic macrophages. By this procedure we found that the remaining T cells primed with Tnp-modified allogeneic macrophages could be restimulated only with Tnp-modified allogeneic, not syngeneic, macrophages. Similarily, if the remaining T cells were primed with Tnp-modified syngeneic macrophages, they could be restimulated only by Tnp-modified syngeneic, and not by allogeneic, macrophages. In contrast, no T cell sensitization with Tnp-modified syngeneic or allogeneic macrophages occurred if the alloreactive T cells were treated with light alone, suggesting that an uninhibited mixed leukocyte reaction causes nonspecific suppression of antigen-specific T cell priming. These results indicate that the genetic restriction of T cell-macrophage interactions is imposed by the type of macrophage used for initial sensitization rather than by a requirement for self-recognition through cellular interaction structures.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bechtol K. B., Freed J. H., Herzenberg L. A., McDevitt H. O. Genetic control of the antibody response to poly-L(Tyr,Glu)-poly-D,L-Ala--poly-L-Lys in C3H--CWB tetraparental mice. J Exp Med. 1974 Dec 1;140(6):1660–1675. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.6.1660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gisler R. H., Fridman W. H. Suppression of in vitro antibody synthesis by immunoglobulin-binding factor. J Exp Med. 1975 Aug 1;142(2):507–517. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.2.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greineder D. K., Shevach E. M., Rosenthal A. S. Macrophage-lymphocyte interaction. III. Site of alloantiserum inhibition of T lymphocyte proliferation induced by allogeneic or aldehyde-bearing cells. J Immunol. 1976 Oct;117(4):1261–1266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeway C. A., Paul W. E. The specificity of cellular immune responses in guinea pigs. III. The precision of antigen recognition by T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Dec 1;144(6):1641–1656. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.6.1641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. H., Benacerraf B. The function and interrelationships of T-cell receptors, Ir genes and other histocompatibility gene products. Transplant Rev. 1975;22:175–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1975.tb01559.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. H., Chiorazzi N., McDonald J., Katz L. R. Cell interactions between histoincompatible T an B lymphocytes. IX. The failure of histoincompatible cells is not due to suppression and cannot be circumvented by carrier-priming T cells with allogeneic macrophages. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 PT2):1853–1859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Vadas M. A., Whitelaw A., Gamble J. Role of major histocompatibility complex gene products in delayed-type hypersensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2486–2490. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfizenmaier K., Strazinski-Powitz A., Rodt H., Röllinghoff M., Wagner H. Virus and trinitrophenol hapten-specific T-cell-mediated cytotoxicity against H-2 incompatible target cells. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):999–1004. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce C. W., Kapp J. A., Benacerraf B. Regulation by the H-2 gene complex of macrophage-lymphoid cell interactions in secondary antibody responses in vitro. J Exp Med. 1976 Aug 1;144(2):371–381. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich S. S., Rich R. R. Regulatory mechanisms in cell-mediated immune responses. II. A genetically restricted suppressor of mixed lymphocyte reactions released by alloantigen-activated spleen cells. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1391–1402. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstreich D. L., Blake J. T., Rosenthal A. S. The peritoneal exudate lymphocyte. I. Differences in antigen responsiveness between peritoneal exudate and lymph node lymphocytes from immunized guinea pigs. J Exp Med. 1971 Nov 1;134(5):1170–1186. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.5.1170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearer G. M., Rehn T. G., Garbarino C. A. Cell-mediated lympholysis of trinitrophenyl-modified autologous lymphocytes. Effector cell specificity to modified cell surface components controlled by H-2K and H-2D serological regions of the murine major histocompatibility complex. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1348–1364. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shevach E. M., Rosenthal A. S. Function of macrophages in antigen recognition by guinea pig T lymphocytes. II. Role of the macrophage in the regulation of genetic control of the immune response. J Exp Med. 1973 Nov 1;138(5):1213–1229. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.5.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shevach E. M. The function of macrophages in antigen recognition by guinea pig T lymphocytes. III. Genetic analysis of the antigens mediating macrophage-T lymphocyte interaction. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1482–1489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. W., Shevach E. M. Nature of the antigenic complex recognized by T lymphocytes. I. Analysis with an in vitro primary response to soluble protein antigens. J Exp Med. 1976 Nov 2;144(5):1263–1273. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.5.1263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. H-2 compatability requirement for T-cell-mediated lysis of target cells infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Different cytotoxic T-cell specificities are associated with structures coded for in H-2K or H-2D;. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1427–1436. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


