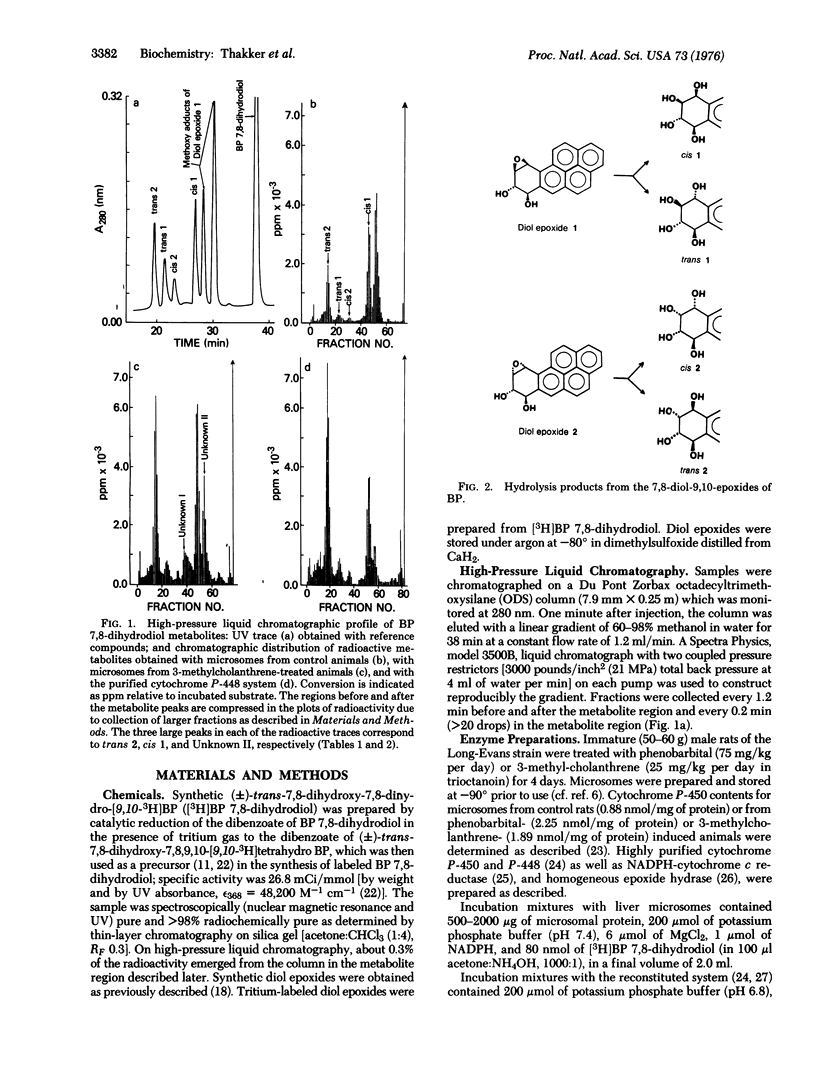
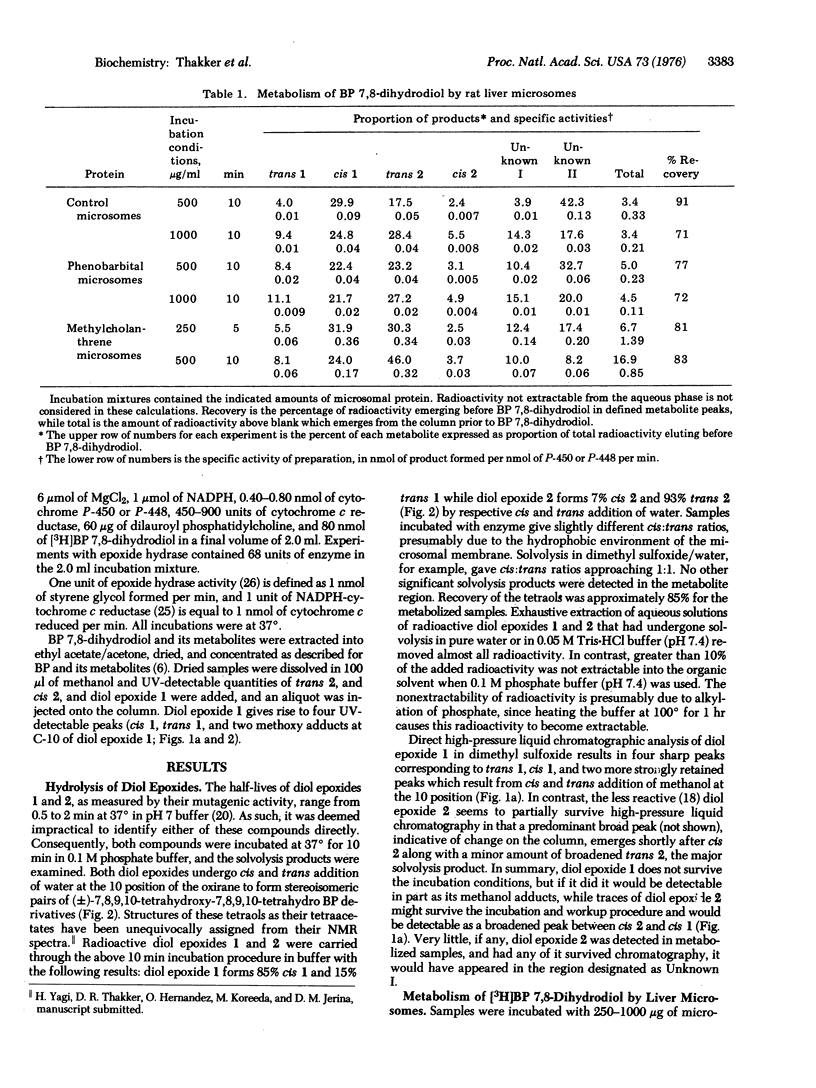
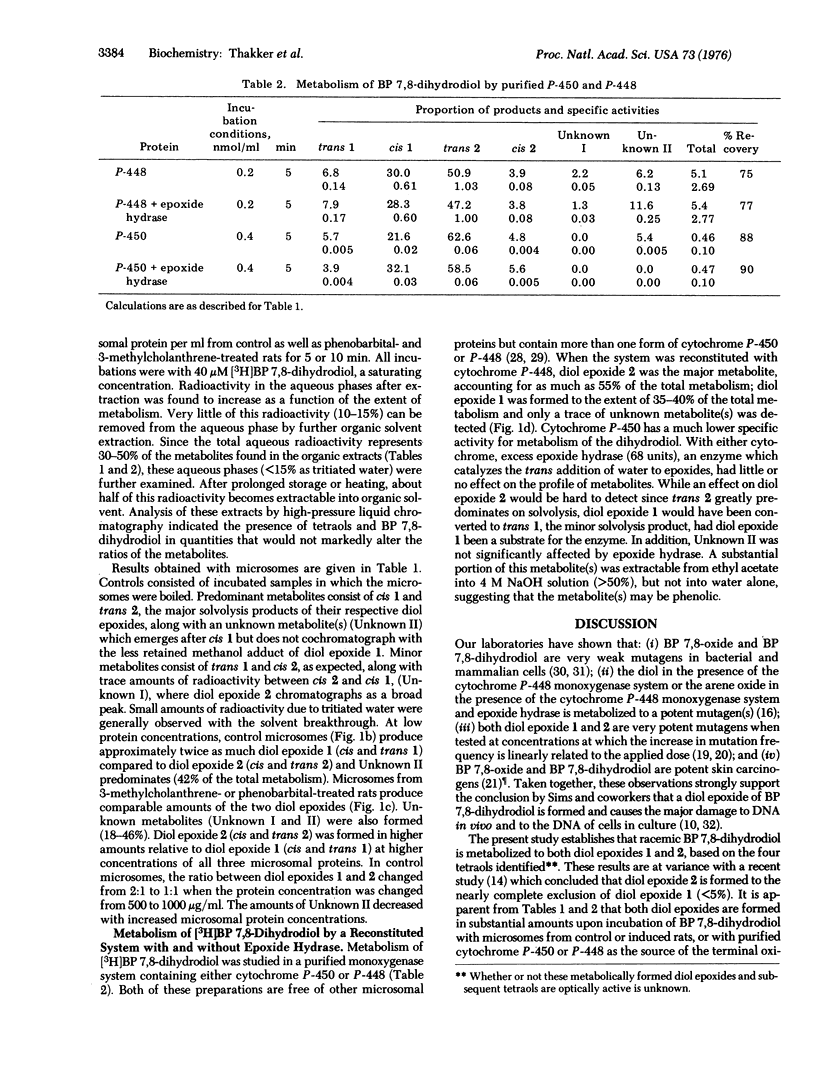
Abstract
Metabolites of (+/-)-trans 7,8-dihydroxy-7,8-dihydrobenzo[a]pyrene formed by a rat liver microsomes and by a highly purified monoxygenase system were analyzed by high-pressure liquid chromatography. Four stereoisomeric tetraols of 7,8,9,10-tetrahydrobenzo[a]pyrene, known solvolysis products of the two highly mutagenic stereoisomers of the 9,10-epoxide of the 7,8-dihydrodiol, were identified as products. The ratio of the two highly unstable diol epoxides formed (7 beta,8alpha-dihydroxy-9beta,10beta-epoxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrobenzo[a]pyrene, diol epoxide 1; 7beta,8alpha-dihydroxy-9alpha,10alpha-epoxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrobenzo[a]pyrene, diol epoxide 2) ranged from about 1.7 to 0.4. The diol epoxides are sufficiently reactive to alkylate phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) at 37 degrees. Microsomes, particularly those from control animals, formed a substantial amount of an additional metabolite that appears to be phenolic. In analogy to benzo[a]pyrene, the metabolism of the 7,8-dihydrodiol shows similar induction after pretreatment of rats with phenobarbital or 3-methylcholanthrene. Neither diol epoxide appears to be a substrate for epoxide hydrase based on the ratis of tetraols formed in the presence or absence of epoxide hydrase. In view of the known carcinogenicity of benzo[a]pyrene 7,8-oxide and 7,8-dihydrodiol and of the marked mutagenicity of the stereoisomeric diol epoxides, both of these diol epoxides qualify for consideration as "ultimate carcinogen(s)" of benzo[a]pyrene.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Booth J., Sims P. 8,9-Dihydro-8,9-dihydroxybenz(a)anthracene 10,11-oxide: a new type of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon metabolite. FEBS Lett. 1974 Oct 1;47(1):30–33. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80419-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth J., Sims P. Different pathways involved in the metabolism of the 7,8- and 9,10-dohydrodiols of benzo(a)pyrene. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Apr 15;25(8):979–980. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90326-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgen A., Darvey H., Castagnoli N., Crocker T. T., Rasmussen R. E., Wang I. Y. Metabolic conversion of benzo(a)pyrene by Syrian hamster liver microsomes and binding of metabolites to deoxyribonucleic acid. J Med Chem. 1973 May;16(5):502–506. doi: 10.1021/jm00263a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capdevila J., Jernström B., Vadi H., Orrenius S. Cytochrome P-450-linked activation of 3-hydroxybenzo(alpha)pyrene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Aug 4;65(3):894–900. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80469-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daudel P., Duquesne M., Vigny P., Grover P. L., Sims P. Fluorescence spectral evidence that benzo(a)pyrene-DNA products in mouse skin arise from diol-epoxides. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 1;57(3):250–253. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80310-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Strobel H. W. Preparation of homogeneous NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase from rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Apr 21;63(4):845–852. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90644-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T., Mahadevan V., Jerina D. M., Yogi H., Yeh H. J. Oxidation of the carcinogens benzo [a] pyrene and benzo [a] anthracene to dihydrodiols by a bacterium. Science. 1975 Jul 25;189(4199):295–297. doi: 10.1126/science.1145203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder G. M., Yagi H., Jerina D. M., Levin W., Lu A. Y., Conney A. H. Metabolism of benzo[a]pyrene. Effect of substrate concentration and 3-methylcholanthrene pretreatment on hepatic metabolism by microsomes from rats and mice. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Oct;170(2):557–566. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90151-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder G., Yagi H., Dansette P., Jerina D. M., Levin W., Lu A. Y., Conney A. H. Effects of inducers and epoxide hydrase on the metabolism of benzo(a)pyrene by liver microsomes and a reconstituted system: analysis by high pressure liquid chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4356–4360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman E., Sachs L., Yang S. K., Gelboin V. Identification of mutagenic metabolites of benzo(a)pyrene in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):607–611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerina D. M., Daly J. W. Arene oxides: a new aspect of drug metabolism. Science. 1974 Aug 16;185(4151):573–582. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4151.573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin W., Ryan D., West S., Lu A. Y. Preparation of partially purified, lipid-depleted cytochrome P-450 and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-cytochrome c reductase from rat liver microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 25;249(6):1747–1754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin W., Wood A. W., Yagi H., Dansette P. M., Jerina D. M., Conney A. H. Carcinogenicity of benzo[a]pyrene 4,5-, 7,8-, and 9,10-oxides on mouse skin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):243–247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu A. Y., Ryan D., Jerina D. M., Daly J. W., Levin W. Liver microsomal expoxide hydrase. Solubilization, purification, and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 25;250(20):8283–8288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaveille C., Bartsch H., Grover P. L., Sims P. Mutagenicity of non-K-region diols and diol-epoxides of benz(a)anthracene and benzo(a)pyrene in S. typhimurium TA 100. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Sep 16;66(2):693–700. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90565-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OMURA T., SATO R. THE CARBON MONOXIDE-BINDING PIGMENT OF LIVER MICROSOMES. II. SOLUBILIZATION, PURIFICATION, AND PROPERTIES. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2379–2385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P., Grover P. L. Epoxides in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon metabolism and carcinogenesis. Adv Cancer Res. 1974;20:165–274. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60111-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P., Grover P. L., Swaisland A., Pal K., Hewer A. Metabolic activation of benzo(a)pyrene proceeds by a diol-epoxide. Nature. 1974 Nov 22;252(5481):326–328. doi: 10.1038/252326a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaisland A. J., Hewer A., Pal K., Keysell G. R., Booth J., Grover P. L., Sims P. Polycyclic hydrocarbon epoxides: the involvement of 8,9-dihydro-8,9-dihydroxybenz (a) anthracene 10,11-oxide in reactions with the DNA of benz (a) anthracene-treated hamster embryo cells. FEBS Lett. 1974 Oct 1;47(1):34–38. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80420-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. E., Lu A. Y., Ryan D., West S. B., Kawalek J., Levin W. Multiple forms of rat liver cytochrome P-450. Immunochemical evidence with antibody against cytochrome P-448. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1385–1391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiebel F. J. Metabolism of monohydroxybenzo(a)pyrenes by rat liver microsomes and mammalian cells in culture. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Jun;168(2):609–621. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90293-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wislocki P. G., Wood A. W., Chang R. L., Levin W., Yagi H., Hernandez O., Dansette P. M., Herina D. M., Conney A. H. Mutagenicity and cytotoxicity of benzo(a)pyrene arene oxides, phenols, quinones, and dihydrodiols in bacterial and mammalian cells. Cancer Res. 1976 Sep;36(9 PT1):3350–3357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wislocki P. G., Wood A. W., Chang R. L., Levin W., Yagi H., Hernandez O., Jerina D. M., Conney A. H. High mutagenicity and toxicity of a diol epoxide derived from benzo(a)pyrene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Feb 9;68(3):1006–1012. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91246-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood A. W., Goode R. L., Chang R. L., Levin W., Conney A. H., Yagi H., Dansette P. M., Jerina D. M. Mutagenic and cytotoxic activity of benzol[a]pyrene 4,5-, 7,8-, and 9,10-oxides and the six corresponding phenols. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3176–3180. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood A. W., Levin W., Lu A. Y., Yagi H., Hernandez O., Jerina D. M., Conney A. H. Metabolism of benzo(a)pyrene and benzo (a)pyrene derivatives to mutagenic products by highly purified hepatic microsomal enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 25;251(16):4882–4890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood A. W., Wislocki P. G., Chang R. L., Levin W., Lu A. Y., Yagi J., Hernandez O., Herina D. M., Conney A. H. Mutagenicity and cytotoxicity of benzo(a)pyrene benzo-ring epoxides. Cancer Res. 1976 Sep;36(9 PT1):3358–3366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi H., Hernandez O., Jerina D. M. Letter: Synthesis of (+/-)-7 beta,8alpha-dihydroxy-9 beta,10beta-epoxy-7,8,-9,10-tetrahydrobenzo(a)pyrene, a potential metabolite of the carcinogen benzo(a)pyrene with stereochemistry related to the antileukemic triptolides. J Am Chem Soc. 1975 Nov 12;97(23):6881–6883. doi: 10.1021/ja00856a057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


